Wet clutches operate immersed in oil, providing smoother engagement and better heat dissipation, making them ideal for high-performance automotive applications and extended durability. Dry clutches run without lubrication, offering quicker response and lighter weight, which benefits fuel efficiency and simpler maintenance in certain vehicles. Choosing between wet and dry clutches depends on factors like vehicle type, driving conditions, and performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
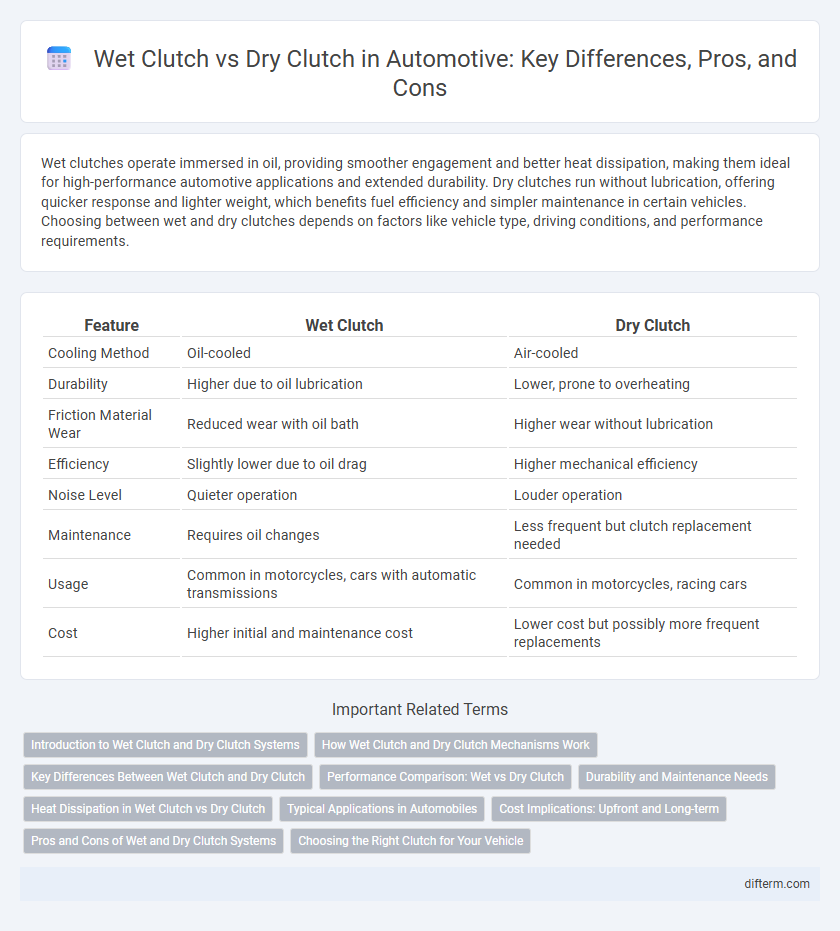
| Feature | Wet Clutch | Dry Clutch |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Method | Oil-cooled | Air-cooled |
| Durability | Higher due to oil lubrication | Lower, prone to overheating |
| Friction Material Wear | Reduced wear with oil bath | Higher wear without lubrication |
| Efficiency | Slightly lower due to oil drag | Higher mechanical efficiency |
| Noise Level | Quieter operation | Louder operation |
| Maintenance | Requires oil changes | Less frequent but clutch replacement needed |
| Usage | Common in motorcycles, cars with automatic transmissions | Common in motorcycles, racing cars |
| Cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost | Lower cost but possibly more frequent replacements |
Introduction to Wet Clutch and Dry Clutch Systems
Wet clutch systems use oil to cool and lubricate the clutch plates, enhancing durability and smoother engagement in motorcycles and automatic transmissions. Dry clutch systems operate without lubrication, offering direct power transfer and higher efficiency but with increased wear and heat generation, commonly found in manual transmissions and racing vehicles. Understanding the fundamental differences in design and operation helps in selecting the appropriate clutch type for performance, maintenance, and driving conditions.
How Wet Clutch and Dry Clutch Mechanisms Work
Wet clutch mechanisms operate by immersing friction plates in lubricating oil, which provides cooling and reduces wear, enabling smoother engagement and better heat dissipation in high-performance automotive transmissions. Dry clutches function without oil, relying on direct friction between the clutch plate and flywheel, offering more immediate power transfer but generating higher temperatures and faster wear. The choice between wet and dry clutch systems impacts vehicle performance, maintenance intervals, and efficiency, with wet clutches favored in motorcycles and automatic transmissions, while dry clutches are common in manual gearboxes and high-performance cars.
Key Differences Between Wet Clutch and Dry Clutch
Wet clutches operate immersed in lubricating oil, enhancing heat dissipation and providing smoother engagement, making them ideal for high-performance or heavy-duty vehicles. Dry clutches function without oil, resulting in lighter weight and more direct power transfer but tend to wear faster and generate more heat under load. The choice between wet and dry clutch affects vehicle durability, performance, and maintenance frequency in automotive applications.
Performance Comparison: Wet vs Dry Clutch
Wet clutches offer superior heat dissipation and smoother engagement, making them ideal for high-performance motorcycles and automatic transmissions where consistent friction management is crucial. Dry clutches, while lighter and delivering more direct power transfer, tend to wear faster and generate more heat, limiting their use in heavy-duty or continuous high-load applications. Performance-wise, wet clutches excel in durability and reliability under sustained stress, whereas dry clutches prioritize responsiveness and minimal drag.
Durability and Maintenance Needs
Wet clutches offer enhanced durability due to continuous lubrication, reducing friction and heat buildup, which extends the lifespan of clutch components compared to dry clutches. Maintenance needs for wet clutches are generally lower since their oil bath environment helps prevent wear and contamination, though periodic oil changes are essential to maintain performance. Dry clutches, while simpler and lighter, experience higher wear rates and require more frequent adjustments or replacements due to direct friction contact without lubrication.
Heat Dissipation in Wet Clutch vs Dry Clutch
Wet clutches excel in heat dissipation due to their immersion in lubricating oil, which effectively absorbs and disperses frictional heat generated during operation. Dry clutches, lacking this oil bath, rely on air cooling and radiate heat less efficiently, often leading to higher operating temperatures and increased wear under heavy loads. Effective thermal management in wet clutches results in improved durability and consistent performance in demanding automotive applications.
Typical Applications in Automobiles
Wet clutches are commonly used in motorcycles, automatic transmissions, and heavy-duty vehicles due to their superior heat dissipation and smoother engagement under high torque conditions. Dry clutches, preferred in passenger cars and performance vehicles, offer a more direct power transfer and reduced drag, enhancing fuel efficiency and throttle response. The choice between wet and dry clutches depends on vehicle type, driving conditions, and performance requirements, influencing durability and maintenance intervals.
Cost Implications: Upfront and Long-term
Wet clutches typically incur higher upfront costs due to their complex design and the need for oil maintenance systems, but they offer longer durability and reduced wear, leading to lower long-term replacement expenses. Dry clutches have a lower initial purchase price and simpler installation but often require more frequent replacements and maintenance, increasing overall lifetime costs. In automotive applications, choosing between wet and dry clutches involves balancing initial budget constraints against future service and replacement cost projections.
Pros and Cons of Wet and Dry Clutch Systems
Wet clutch systems offer superior cooling and smoother engagement due to oil immersion, which enhances durability and reduces overheating risks in automotive applications. Dry clutch systems provide more direct power transfer and are typically lighter and more efficient but may suffer from quicker wear and increased heat buildup under heavy use. Choosing between wet and dry clutches depends on vehicle type, performance requirements, and maintenance preferences, with wet clutches favored in high-torque, heavy-duty settings and dry clutches preferred for lightweight, high-performance vehicles.
Choosing the Right Clutch for Your Vehicle
Selecting the right clutch for your vehicle involves understanding the key differences between wet and dry clutches. Wet clutches, submerged in oil, offer smoother engagement and superior heat dissipation, making them ideal for high-performance and heavy-duty applications. Dry clutches provide a more direct power transfer with less drag, often preferred in lightweight vehicles demanding quick response and fuel efficiency.
wet clutch vs dry clutch Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com