Engine remap directly alters the car's original ECU software to optimize performance, fuel efficiency, and torque by rewriting factory data. Piggyback ECU systems work alongside the factory ECU, modifying sensor signals and parameters without changing the original software, offering easier installation and reversibility. Choosing between remap and piggyback depends on the desired level of customization, vehicle compatibility, and risk tolerance for warranty impact.
Table of Comparison
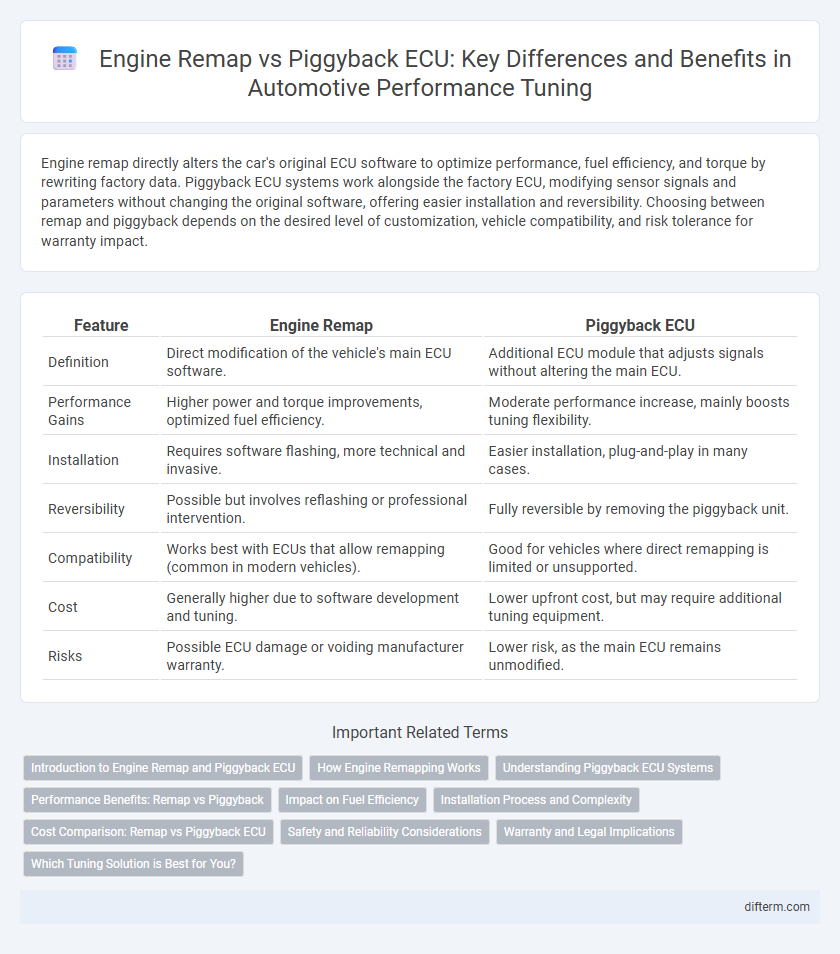
| Feature | Engine Remap | Piggyback ECU |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct modification of the vehicle's main ECU software. | Additional ECU module that adjusts signals without altering the main ECU. |
| Performance Gains | Higher power and torque improvements, optimized fuel efficiency. | Moderate performance increase, mainly boosts tuning flexibility. |
| Installation | Requires software flashing, more technical and invasive. | Easier installation, plug-and-play in many cases. |
| Reversibility | Possible but involves reflashing or professional intervention. | Fully reversible by removing the piggyback unit. |
| Compatibility | Works best with ECUs that allow remapping (common in modern vehicles). | Good for vehicles where direct remapping is limited or unsupported. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to software development and tuning. | Lower upfront cost, but may require additional tuning equipment. |
| Risks | Possible ECU damage or voiding manufacturer warranty. | Lower risk, as the main ECU remains unmodified. |
Introduction to Engine Remap and Piggyback ECU
Engine remapping involves rewriting the factory settings of an engine's ECU to optimize fuel delivery, ignition timing, and boost pressure for improved performance and efficiency. Piggyback ECU systems function as an independent module that intercepts and modifies sensor signals before they reach the stock ECU, offering adjustable tuning without altering the original engine map. Both methods enhance engine output but differ in flexibility, complexity, and impact on factory warranty.
How Engine Remapping Works
Engine remapping adjusts the car's ECU software by rewriting its parameters to optimize fuel injection, ignition timing, and boost pressure for improved performance and efficiency. Unlike piggyback ECU systems that add external modules to modify signals, remapping directly changes the original software, allowing precise control over engine functions. This method enhances engine responsiveness, increases horsepower, and can improve fuel economy when tailored correctly.
Understanding Piggyback ECU Systems
Piggyback ECU systems modify engine performance by intercepting and altering sensor signals before they reach the original ECU, allowing for adjustments without rewriting the ECU's firmware. Unlike engine remapping, which involves directly reprogramming the factory ECU for enhanced power and efficiency, piggyback units offer a reversible and less invasive tuning solution. These systems are particularly effective for controlling boost pressure, fuel delivery, and ignition timing in turbocharged engines, providing a flexible option for performance improvements without compromising factory settings.
Performance Benefits: Remap vs Piggyback
Engine remapping directly modifies the factory ECU software, optimizing fuel injection, ignition timing, and boost pressure for significant horsepower and torque gains. Piggyback ECUs work by intercepting and altering signals from the factory ECU, offering moderate performance improvements while retaining more of the original calibration. Remapping typically delivers superior power increases and throttle response, whereas piggyback systems provide easier installation and reversibility with less impact on engine safety parameters.
Impact on Fuel Efficiency
Engine remapping directly modifies the vehicle's original ECU parameters, optimizing fuel delivery and ignition timing to improve fuel efficiency by up to 15%. Piggyback ECU systems adjust signals externally without altering the factory ECU settings, often resulting in modest fuel gains of around 5-8%. While remapping offers more precise control for enhancing fuel economy, piggyback systems provide a reversible and less invasive solution with limited efficiency improvements.
Installation Process and Complexity
Engine remap involves directly rewriting the vehicle's ECU firmware, requiring specialized software and expertise to modify the fuel, ignition, and turbo boost parameters precisely; the installation is non-invasive but demands a thorough understanding of the engine's control logic. Piggyback ECU systems are installed alongside the stock ECU, intercepting and altering sensor signals before they reach the original unit, which simplifies installation with plug-and-play harnesses but adds complexity due to signal synchronization and potential compatibility issues. While remapping offers a cleaner electronic footprint and improved performance tuning flexibility, piggyback devices provide reversible modifications with easier installation but may introduce latency and less precise control over engine functions.
Cost Comparison: Remap vs Piggyback ECU
Engine remapping typically offers a more cost-effective solution compared to piggyback ECUs, with prices generally ranging from $300 to $700 depending on vehicle make and tuning complexity. Piggyback ECUs, while providing added customization and flexibility, often come with higher initial costs between $500 and $1,200, as well as potential ongoing expenses for tuning adjustments. The choice hinges on budget constraints and desired performance outcomes, with remaps favoring affordability and piggyback units favoring modular control.
Safety and Reliability Considerations
Engine remap offers precise control over fuel and ignition timing, enhancing engine performance while maintaining factory safety protocols when properly tuned. Piggyback ECU systems provide an extra layer of control without altering the original ECU firmware, preserving reliability but potentially limiting performance gains. Both methods require expert calibration to ensure engine safety, prevent component stress, and avoid voiding manufacturer warranties.
Warranty and Legal Implications
Engine remap involves rewriting the engine control unit (ECU) software for enhanced performance, which can void the vehicle warranty due to irreversible changes in the ECU. Piggyback ECU systems modify sensor signals without altering the main ECU, often maintaining manufacturer warranty coverage since the original ECU map remains intact. Legal implications vary by jurisdiction, but piggyback systems are typically viewed as less intrusive modifications, reducing the risk of failing emissions tests or violating vehicle regulations.
Which Tuning Solution is Best for You?
Engine remap offers a comprehensive rewrite of the factory ECU software, unlocking maximum performance gains by optimizing fuel injection, ignition timing, and boost pressure for your specific vehicle model. Piggyback ECU systems provide a more flexible, plug-and-play approach by intercepting sensor signals and adjusting parameters without altering the original ECU, ideal for users seeking reversible tuning or additional features like boost controllers. Choosing between an engine remap and a piggyback ECU depends on your goals: prioritize engine remapping for peak horsepower and efficiency, or a piggyback system for ease of installation and safer compatibility with aftermarket modifications.
engine remap vs piggyback ECU Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com