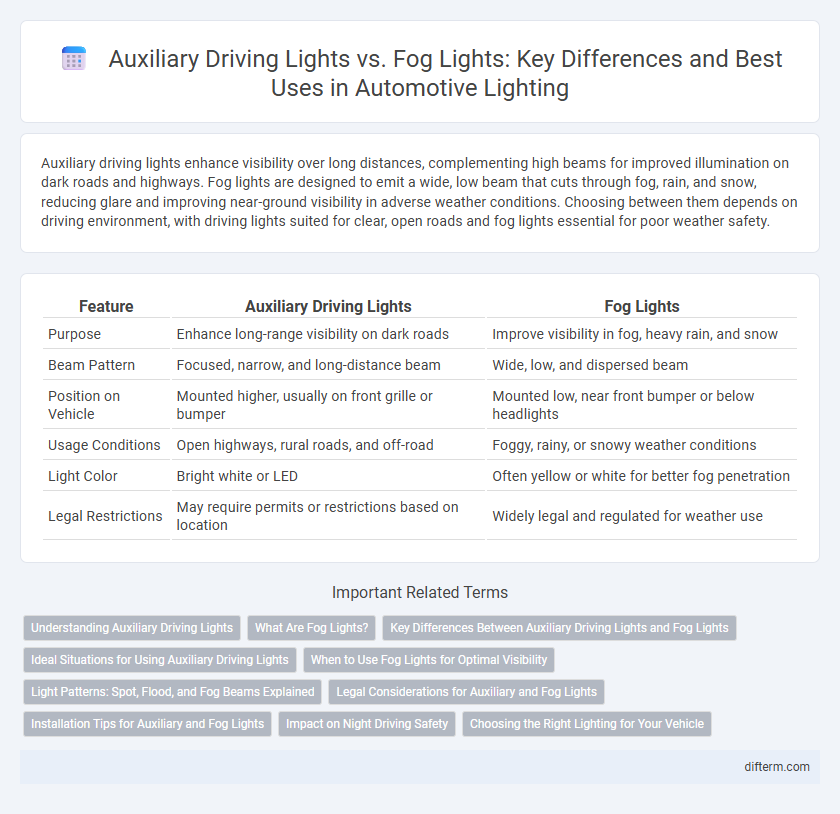
Auxiliary driving lights enhance visibility over long distances, complementing high beams for improved illumination on dark roads and highways. Fog lights are designed to emit a wide, low beam that cuts through fog, rain, and snow, reducing glare and improving near-ground visibility in adverse weather conditions. Choosing between them depends on driving environment, with driving lights suited for clear, open roads and fog lights essential for poor weather safety.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Auxiliary Driving Lights | Fog Lights |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhance long-range visibility on dark roads | Improve visibility in fog, heavy rain, and snow |
| Beam Pattern | Focused, narrow, and long-distance beam | Wide, low, and dispersed beam |
| Position on Vehicle | Mounted higher, usually on front grille or bumper | Mounted low, near front bumper or below headlights |
| Usage Conditions | Open highways, rural roads, and off-road | Foggy, rainy, or snowy weather conditions |
| Light Color | Bright white or LED | Often yellow or white for better fog penetration |
| Legal Restrictions | May require permits or restrictions based on location | Widely legal and regulated for weather use |
Understanding Auxiliary Driving Lights
Auxiliary driving lights enhance visibility on dark, open roads by providing a focused, long-range beam that extends beyond standard headlights. They are designed to improve driver reaction time and reduce eye strain during nighttime driving, especially in rural or off-road conditions. Unlike fog lights, which emit a wide, low beam to cut through fog and reduce glare near the ground, auxiliary driving lights prioritize distance illumination for enhanced road safety.
What Are Fog Lights?
Fog lights are specialized automotive lights designed to improve visibility during foggy, rainy, or snowy conditions by projecting a wide, low beam that reduces glare and illuminates the road surface directly ahead. Positioned low on the vehicle, fog lights help drivers see road edges and lane markings more clearly when standard headlights are less effective. Unlike auxiliary driving lights that enhance long-distance vision, fog lights focus on enhancing near-field visibility in poor weather environments.
Key Differences Between Auxiliary Driving Lights and Fog Lights
Auxiliary driving lights provide focused, long-range illumination designed to enhance visibility at higher speeds, primarily on clear roads, whereas fog lights emit a wide, low beam to minimize reflection and glare in foggy or adverse weather conditions. Driving lights are typically mounted higher on vehicles to project light further down the road, while fog lights are positioned lower to illuminate the road surface and edges effectively. The distinct beam patterns and mounting locations reflect their specialized functions for improving driver safety under different environmental conditions.
Ideal Situations for Using Auxiliary Driving Lights
Auxiliary driving lights significantly enhance visibility on dark, open roads and rural highways where standard headlights offer limited range and intensity. They are ideal for off-road adventures, providing broader illumination to detect obstacles and uneven terrain at greater distances. Unlike fog lights, which are designed for low-visibility conditions like fog or heavy rain by projecting a wide, low beam, auxiliary driving lights optimize distance and clarity during night driving on unobstructed routes.
When to Use Fog Lights for Optimal Visibility
Fog lights are designed to provide optimal visibility in low-visibility conditions such as heavy fog, rain, snow, or dust by emitting a wide, low beam that reduces glare and illuminates the road surface directly ahead. They should be used when standard headlights cause excessive reflection or glare, impairing visibility, especially within a short range of 50-100 meters. Using fog lights improperly during clear conditions can dazzle other drivers and reduce overall driving safety on the road.
Light Patterns: Spot, Flood, and Fog Beams Explained
Auxiliary driving lights feature distinct light patterns designed for specific conditions: spot beams deliver a focused, long-range light ideal for high-speed driving on open roads, while flood beams emit a wide, short-range light that enhances peripheral visibility. Fog lights produce a low, wide beam pattern specifically engineered to minimize glare and improve visibility in fog, rain, and snow by illuminating the road surface directly in front of the vehicle. Understanding these differences helps optimize vehicle lighting for enhanced safety and performance in varying driving environments.
Legal Considerations for Auxiliary and Fog Lights
Legal considerations for auxiliary driving lights and fog lights vary by jurisdiction, with specific regulations governing their installation, color, and usage to ensure road safety. Auxiliary driving lights typically must be wired to turn off when high beams are activated and are often restricted from use in certain weather conditions, while fog lights are mandated to emit amber or white light and be positioned low on the vehicle to reduce glare. Compliance with standards set by agencies such as the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the U.S. or the Economic Commission for Europe (ECE) is essential to avoid fines and ensure the lighting equipment is street legal.
Installation Tips for Auxiliary and Fog Lights
For installing auxiliary driving lights and fog lights, position auxiliary lights higher and aim them further ahead to enhance long-range visibility, while fog lights should be mounted low on the vehicle and angled downward to minimize glare and improve close-range illumination in foggy conditions. Ensure wiring harnesses are securely connected to a dedicated fused power source, and use waterproof connectors to prevent electrical issues. Proper alignment and testing of light beams are crucial for compliance with automotive safety standards and optimal driving performance.
Impact on Night Driving Safety
Auxiliary driving lights significantly enhance night driving safety by providing a broader and longer-range beam that improves visibility on dark roads and rural areas. Fog lights are designed to cut through fog, rain, and snow with a low, wide beam to reduce glare and illuminate the road surface directly in front of the vehicle. Using the correct lighting in adverse conditions reduces reaction time and increases driver awareness, ultimately minimizing the risk of accidents during nighttime driving.
Choosing the Right Lighting for Your Vehicle
Auxiliary driving lights enhance visibility over longer distances and are ideal for off-road or rural driving, providing focused, powerful beams that help spot obstacles early. Fog lights are designed to emit low, wide beams that reduce glare and improve visibility in fog, rain, or snow by illuminating the road surface directly ahead. Choosing the right lighting depends on your driving environment and weather conditions, with driving lights suited for clear, dark roads and fog lights prioritized for adverse weather to ensure safety and optimal visibility.
auxiliary driving lights vs fog lights Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com