Drum brakes offer reliable performance and are often more cost-effective, making them suitable for budget-friendly automotive applications. Disc brakes provide superior stopping power and better heat dissipation, enhancing safety and performance in high-demand driving conditions. Choosing between drum brakes and disc brakes depends on vehicle type, usage, and maintenance preferences.
Table of Comparison
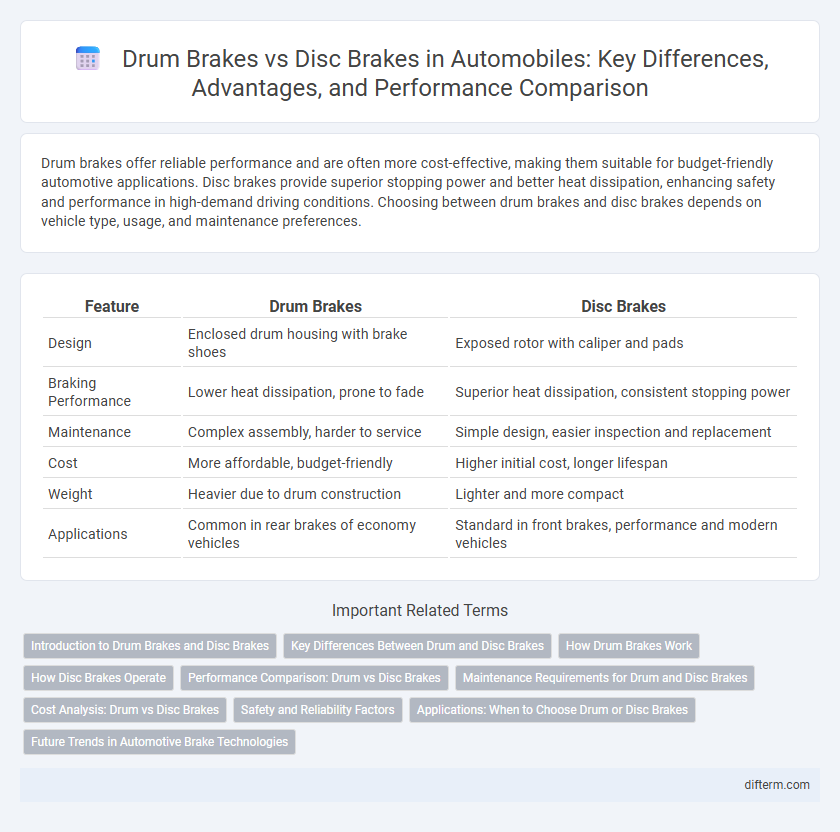
| Feature | Drum Brakes | Disc Brakes |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Enclosed drum housing with brake shoes | Exposed rotor with caliper and pads |
| Braking Performance | Lower heat dissipation, prone to fade | Superior heat dissipation, consistent stopping power |
| Maintenance | Complex assembly, harder to service | Simple design, easier inspection and replacement |
| Cost | More affordable, budget-friendly | Higher initial cost, longer lifespan |
| Weight | Heavier due to drum construction | Lighter and more compact |
| Applications | Common in rear brakes of economy vehicles | Standard in front brakes, performance and modern vehicles |
Introduction to Drum Brakes and Disc Brakes
Drum brakes consist of brake shoes that press outward against a spinning drum attached to the wheel, providing stopping power through friction within a sealed drum assembly. Disc brakes use a caliper to squeeze brake pads against a rotating disc, offering faster heat dissipation and more consistent stopping performance. While drum brakes are typically found on older or rear-wheel vehicles, disc brakes dominate front-wheel applications due to superior braking efficiency and durability.
Key Differences Between Drum and Disc Brakes
Drum brakes consist of brake shoes pressing outward against a rotating drum, offering strong holding power but slower heat dissipation compared to disc brakes, which use calipers to squeeze brake pads on a spinning disc for more efficient stopping and cooling. Disc brakes provide superior performance in wet conditions due to better water dispersion and consistent braking force, whereas drum brakes are more cost-effective and typically found in rear-wheel applications. The mechanical design of disc brakes results in less brake fade and easier maintenance, while drum brakes require fewer components but suffer from self-energizing effects that can impact brake feel.
How Drum Brakes Work
Drum brakes function by pressing brake shoes outward against a spinning drum attached to the wheel, creating friction to slow down or stop the vehicle. They use a wheel cylinder to push the shoes, which expand inside the drum, converting kinetic energy into heat. Though less effective at heat dissipation compared to disc brakes, drum brakes are still widely used in rear wheels for their cost-efficiency and self-energizing properties.
How Disc Brakes Operate
Disc brakes operate by using calipers to squeeze pairs of pads against a disc or rotor attached to the wheel, creating friction that slows the vehicle. This mechanism provides efficient heat dissipation due to the exposed design of the rotor, reducing brake fade during repetitive braking. The hydraulic system enhances responsiveness and consistent braking performance compared to drum brakes.
Performance Comparison: Drum vs Disc Brakes
Disc brakes offer superior stopping power and heat dissipation compared to drum brakes, making them more effective under high-performance and emergency braking conditions. Drum brakes tend to suffer from brake fade during prolonged use due to poor heat ventilation, whereas disc brakes maintain consistent performance by allowing better cooling. This results in disc brakes delivering more reliable and responsive braking performance for modern vehicles.
Maintenance Requirements for Drum and Disc Brakes
Drum brakes require more frequent adjustments and inspections due to their enclosed design, which can trap dust and cause uneven wear on brake shoes. Disc brakes offer easier maintenance with exposed rotors that are simpler to clean, inspect, and replace, reducing downtime and labor costs. Regular brake fluid checks and pad or shoe replacement intervals are critical for both systems to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Cost Analysis: Drum vs Disc Brakes
Drum brakes generally have lower initial manufacturing and replacement costs compared to disc brakes, making them a cost-effective choice for budget vehicles and light-duty applications. However, disc brakes offer longer service life and superior performance under high-stress conditions, which can reduce maintenance expenses over time despite their higher upfront price. Cost analysis should factor in durability, repair frequency, and performance efficiency to determine the best brake system for specific automotive needs.
Safety and Reliability Factors
Disc brakes offer superior safety and reliability compared to drum brakes due to their enhanced heat dissipation, reducing the risk of brake fade during prolonged use. The exposed design of disc brakes allows for better self-cleaning and consistent performance in wet or muddy conditions, increasing overall stopping power. Drum brakes, while cost-effective, are more prone to overheating and slower response times, making them less reliable for high-performance or heavy-duty automotive applications.
Applications: When to Choose Drum or Disc Brakes
Disc brakes are preferred for high-performance vehicles and heavy-duty applications requiring superior stopping power and heat dissipation, such as sports cars and trucks. Drum brakes remain suitable for budget-friendly, lighter vehicles and rear-wheel braking systems where cost-effectiveness and durability matter more than peak performance. Choosing between drum and disc brakes depends on factors like vehicle type, driving conditions, and maintenance preferences, with disc brakes excelling in wet conditions and drum brakes offering advantages in parking brake integration.
Future Trends in Automotive Brake Technologies
Emerging advancements in automotive brake technologies prioritize the transition from traditional drum brakes to sophisticated disc brake systems due to superior heat dissipation and enhanced stopping power. Integration of electronic braking systems (EBS) and regenerative braking in electric vehicles drives innovation, enabling improved energy efficiency and reduced wear. Future trends emphasize lightweight composite materials and smart sensors to optimize braking performance and safety in autonomous and connected vehicles.
drum brakes vs disc brakes Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com