Kubernetes offers a comprehensive open-source platform for automating containerized application deployment, scaling, and management, widely supported with a vast ecosystem and strong community backing. Nomad provides a simpler and more lightweight solution for workload orchestration, emphasizing speed, flexibility, and easy integration with HashiCorp tools, making it ideal for multi-cloud and hybrid environments. Choosing between Kubernetes and Nomad depends on the complexity of the infrastructure, required scalability, and the specific use case of the pet technology environment.
Table of Comparison
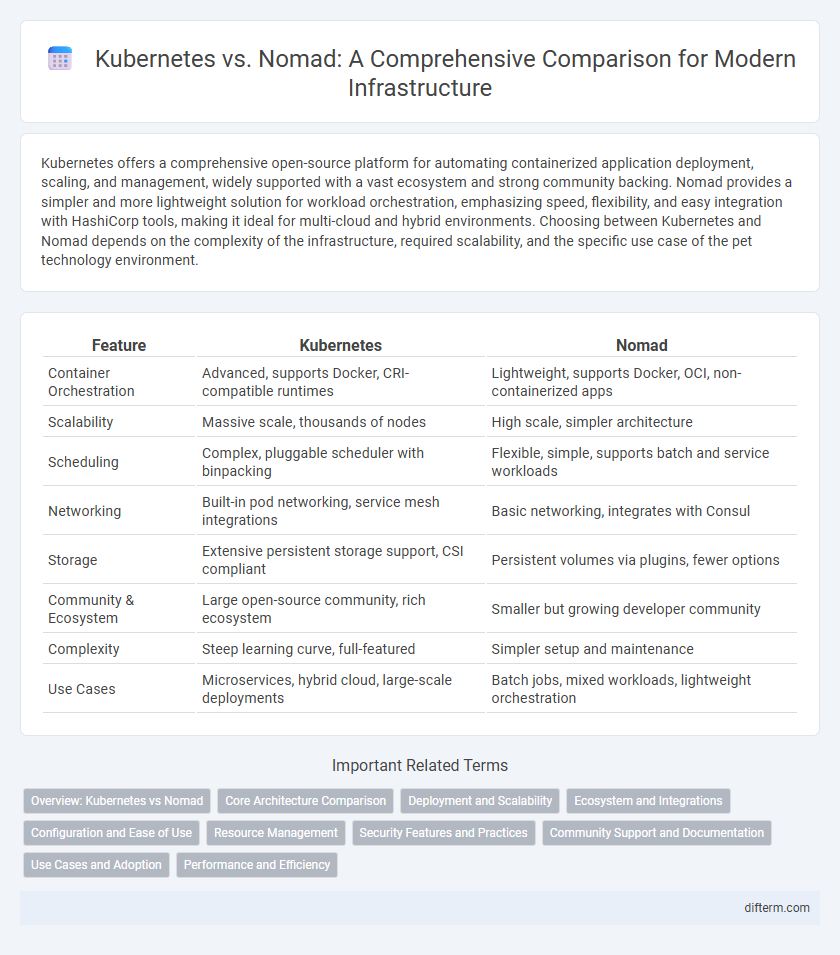
| Feature | Kubernetes | Nomad |
|---|---|---|
| Container Orchestration | Advanced, supports Docker, CRI-compatible runtimes | Lightweight, supports Docker, OCI, non-containerized apps |
| Scalability | Massive scale, thousands of nodes | High scale, simpler architecture |
| Scheduling | Complex, pluggable scheduler with binpacking | Flexible, simple, supports batch and service workloads |
| Networking | Built-in pod networking, service mesh integrations | Basic networking, integrates with Consul |
| Storage | Extensive persistent storage support, CSI compliant | Persistent volumes via plugins, fewer options |
| Community & Ecosystem | Large open-source community, rich ecosystem | Smaller but growing developer community |
| Complexity | Steep learning curve, full-featured | Simpler setup and maintenance |
| Use Cases | Microservices, hybrid cloud, large-scale deployments | Batch jobs, mixed workloads, lightweight orchestration |
Overview: Kubernetes vs Nomad
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform renowned for its extensive ecosystem and robust scalability, supporting complex deployments with automated scaling, self-healing, and load balancing. Nomad, developed by HashiCorp, offers a lightweight, flexible scheduler optimized for simplicity and multi-datacenter deployment, capable of managing containers, virtual machines, and standalone applications. While Kubernetes excels in large-scale, intricate systems with diverse workloads, Nomad provides a streamlined solution with less operational overhead, making it ideal for environments prioritizing speed and ease of use.
Core Architecture Comparison
Kubernetes leverages a master-worker architecture with the control plane components like API Server, Scheduler, and Controller Manager managing the cluster state, while worker nodes run containerized applications via kubelet. Nomad employs a simpler, single binary design with a centralized server cluster that handles scheduling and resource management, supported by lightweight clients on worker nodes. Kubernetes emphasizes extensive built-in features for orchestration and self-healing, whereas Nomad prioritizes flexibility and easy integration with existing tools, providing scalable and efficient workload scheduling.
Deployment and Scalability
Kubernetes excels in deployment automation through its extensive use of declarative configurations and built-in controllers, enabling seamless scaling of containerized applications across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Nomad offers a lightweight, single binary architecture that simplifies deployment processes and scales efficiently with minimal overhead, making it suitable for heterogeneous workloads beyond containers. Both systems provide robust scalability, but Kubernetes' ecosystem supports more complex deployments, while Nomad prioritizes operational simplicity and fast scaling.
Ecosystem and Integrations
Kubernetes boasts a rich ecosystem with extensive integrations supporting cloud-native tools, monitoring systems, and storage solutions, making it ideal for complex, scalable applications. Nomad offers a simpler, lightweight ecosystem focused on seamless integration with HashiCorp tools like Consul and Vault, prioritizing flexibility and ease of deployment. The Kubernetes ecosystem's broad community support enables rapid innovation, while Nomad's integrations emphasize efficient workload orchestration across diverse infrastructures.
Configuration and Ease of Use
Kubernetes offers extensive configuration options with a steep learning curve, requiring detailed YAML files and a robust understanding of container orchestration concepts. Nomad features a simpler, more flexible configuration model with HCL syntax, making deployment quicker and easier for smaller teams or simpler workloads. Ease of use in Nomad often appeals to those seeking lightweight orchestration without the complexity Kubernetes imposes.
Resource Management
Kubernetes offers advanced resource management through automated scheduling, scaling, and self-healing features that optimize container workloads across clusters. Nomad provides lightweight, flexible resource allocation with simple integration for diverse workloads, including containers and non-containerized applications. Kubernetes excels in large-scale environments with complex orchestration needs, while Nomad emphasizes operational simplicity and efficient resource utilization.
Security Features and Practices
Kubernetes enforces robust security features including Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Network Policies for pod communication restrictions, and integrated secrets management supporting encrypted storage. Nomad prioritizes simplicity with ACLs for fine-grained access control and integrates with Vault for secret management, reducing attack surfaces through a smaller codebase. Both platforms support TLS encryption for data in transit and offer audit logging, but Kubernetes provides a more extensive security ecosystem suited for complex, multi-tenant environments.
Community Support and Documentation
Kubernetes boasts a vast and active community with extensive documentation, including official guides, tutorials, and a wealth of third-party resources that facilitate troubleshooting and learning. Nomad, while having a smaller but steadily growing community, offers clear and concise HashiCorp-maintained documentation that integrates well with other HashiCorp tools. Kubernetes' broader adoption results in more diverse community contributions, whereas Nomad emphasizes simplicity and tight documentation alignment within its ecosystem.
Use Cases and Adoption
Kubernetes dominates the enterprise market for container orchestration with extensive use cases in microservices, CI/CD pipelines, and hybrid cloud deployments, boasting a large adoption base supported by major cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure. Nomad, developed by HashiCorp, excels in lightweight, flexible workload orchestration suitable for heterogeneous clusters and supports both containerized and non-containerized applications with notable use cases in multi-region deployments and edge computing. Adoption of Nomad remains strong in organizations seeking simplicity and integration with HashiCorp's ecosystem, while Kubernetes' complex ecosystem and vast community support make it the preferred choice for large-scale, production-grade container orchestration.
Performance and Efficiency
Kubernetes manages container orchestration with a strong emphasis on scalability and robust resource allocation, often requiring more system overhead due to its complex architecture. Nomad excels in lightweight performance and efficiency by offering a simpler, single-binary design that reduces resource consumption while maintaining high throughput. Benchmarks indicate Nomad achieves faster scheduling and lower latency under heavy workloads, making it ideal for environments where performance and minimal resource use are critical.
Kubernetes vs Nomad Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com