The Turing Test evaluates a machine's ability to exhibit human-like intelligence through natural language interactions, while CAPTCHA is designed to differentiate humans from bots by presenting challenges that are easy for people but difficult for automated systems. Both play crucial roles in artificial intelligence and cybersecurity, with the Turing Test measuring cognitive capabilities and CAPTCHA enforcing access control. Advances in machine learning continue to narrow the gap, making it increasingly challenging to design CAPTCHAs that effectively block sophisticated bots.
Table of Comparison
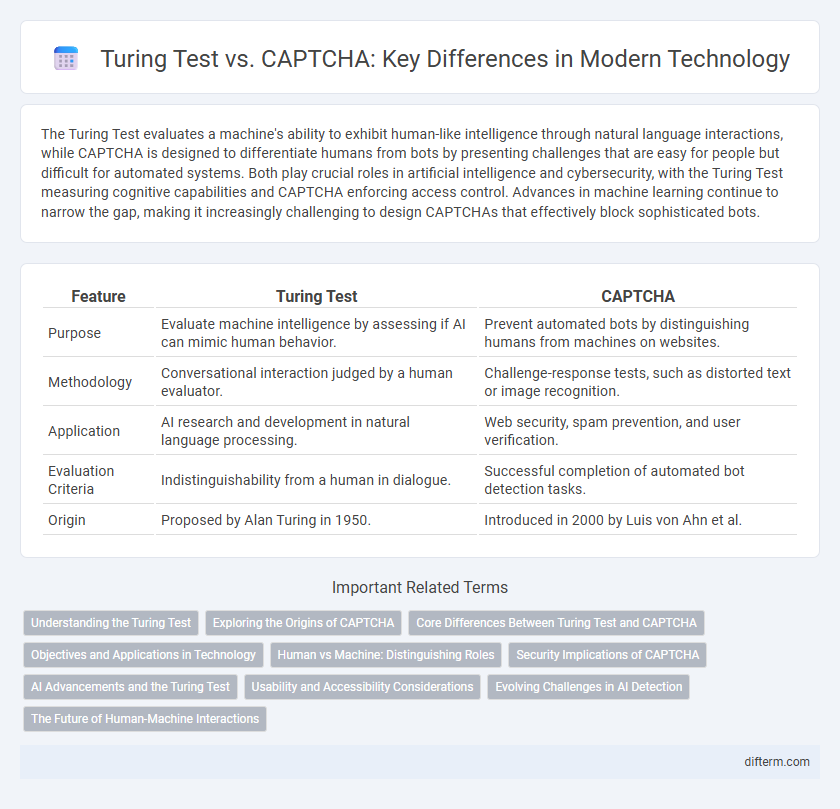
| Feature | Turing Test | CAPTCHA |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate machine intelligence by assessing if AI can mimic human behavior. | Prevent automated bots by distinguishing humans from machines on websites. |
| Methodology | Conversational interaction judged by a human evaluator. | Challenge-response tests, such as distorted text or image recognition. |
| Application | AI research and development in natural language processing. | Web security, spam prevention, and user verification. |
| Evaluation Criteria | Indistinguishability from a human in dialogue. | Successful completion of automated bot detection tasks. |
| Origin | Proposed by Alan Turing in 1950. | Introduced in 2000 by Luis von Ahn et al. |
Understanding the Turing Test
The Turing Test, proposed by Alan Turing in 1950, evaluates a machine's ability to exhibit human-like intelligence through natural language conversation. It assesses whether a computer can generate responses indistinguishable from those of a human, emphasizing cognitive capabilities rather than just task completion. Unlike CAPTCHA, which distinguishes humans from bots by challenging users with tasks difficult for automation, the Turing Test explores broader artificial intelligence and machine learning advancements.
Exploring the Origins of CAPTCHA
CAPTCHA, developed in the early 2000s by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University, originated as a tool to distinguish humans from automated bots in online environments, addressing limitations of the Turing Test in practical applications. Unlike the Turing Test, which assesses a machine's ability to exhibit human-like intelligence through conversation, CAPTCHA uses challenges such as distorted text or image recognition tasks to verify user authenticity. This innovation has become a fundamental security measure in preventing automated abuse of web services, reflecting the evolution of human-computer interaction beyond the theoretical framework of the Turing Test.
Core Differences Between Turing Test and CAPTCHA
The Turing Test evaluates a machine's ability to exhibit human-like intelligence through natural language interaction, whereas CAPTCHA challenges users with tasks that are easy for humans but difficult for automated bots, such as image recognition or pattern identification. Unlike the Turing Test, which assesses conversational sophistication, CAPTCHA primarily serves as a security measure to prevent automated access. Core differences lie in their objectives: the Turing Test measures AI's human-likeness, while CAPTCHA verifies human presence to protect digital systems.
Objectives and Applications in Technology
The Turing Test evaluates a machine's ability to exhibit human-like intelligence through natural language processing, primarily applied in artificial intelligence research to enhance conversational agents and chatbots. CAPTCHA serves as a security mechanism designed to differentiate humans from automated bots by presenting challenges like distorted text or image recognition, crucial in protecting websites from spam and automated abuse. Both technologies address human-machine interaction but differ in objectives: Turing Test focuses on machine cognition replication, while CAPTCHA ensures user authentication and system integrity.
Human vs Machine: Distinguishing Roles
The Turing Test evaluates a machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior indistinguishable from a human, serving as a benchmark for artificial intelligence development. CAPTCHA, in contrast, functions as a security mechanism designed to differentiate human users from automated bots, protecting websites from malicious activities. Both tools emphasize the challenge of distinguishing human cognition from machine processing in evolving technological landscapes.
Security Implications of CAPTCHA
CAPTCHA enhances cybersecurity by distinguishing human users from automated bots, protecting websites from spam, fraudulent activities, and brute force attacks. Unlike the Turing Test, which measures machine intelligence, CAPTCHA specifically targets ensuring genuine user interaction to safeguard sensitive data and maintain system integrity. Its implementation helps prevent unauthorized access and reduces the risk of automated exploitation across digital platforms.
AI Advancements and the Turing Test
The Turing Test, proposed by Alan Turing in 1950, remains a foundational benchmark for evaluating a machine's ability to exhibit human-like intelligence through natural language processing. CAPTCHA tests, by contrast, are designed primarily to differentiate humans from bots by leveraging tasks that current AI finds challenging, such as image recognition or distorted text interpretation. Recent AI advancements, especially in natural language understanding and generative models, push the boundaries of the Turing Test, making it increasingly difficult to distinguish between human and machine responses in conversational contexts.
Usability and Accessibility Considerations
The Turing Test, primarily designed to evaluate machine intelligence, often lacks practical usability and poses significant challenges in accessibility due to its abstract and conversational nature. In contrast, CAPTCHA implementations focus on usability by offering visual or auditory puzzles that are quickly solvable by humans but difficult for bots, though they may exclude users with visual or cognitive impairments. Optimizing accessibility in CAPTCHA involves incorporating alternative formats like audio challenges and leveraging AI to create user-friendly validation methods that maintain security without compromising inclusivity.
Evolving Challenges in AI Detection
The Turing Test and CAPTCHA both serve as benchmarks to distinguish human intelligence from artificial intelligence, with evolving challenges driven by advancements in AI capabilities. AI models continue to improve in natural language processing, making traditional Turing Tests less effective at detecting non-human responses. Simultaneously, modern CAPTCHAs have advanced beyond distorted text images to include behavioral analysis and pattern recognition, reflecting an ongoing arms race in AI detection techniques.
The Future of Human-Machine Interactions
The future of human-machine interactions hinges on advancements beyond traditional Turing Test frameworks and CAPTCHA systems, emphasizing seamless and intuitive communication with AI. Emerging technologies leverage machine learning and natural language processing to create more adaptable and context-aware interfaces that accurately distinguish human intent from automated responses. Innovations in biometric verification and behavioral analysis are set to enhance security while providing users with frictionless authentication experiences in increasingly digitized environments.
Turing Test vs CAPTCHA Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com