Test-Driven Development (TDD) emphasizes writing tests before code to ensure functionality meets predefined specifications, focusing primarily on the internal logic of the application. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) extends this by promoting collaboration through shared examples and scenarios, aligning development with business requirements and user behavior. Both methodologies improve software quality but BDD enhances communication between technical and non-technical stakeholders for clearer acceptance criteria.
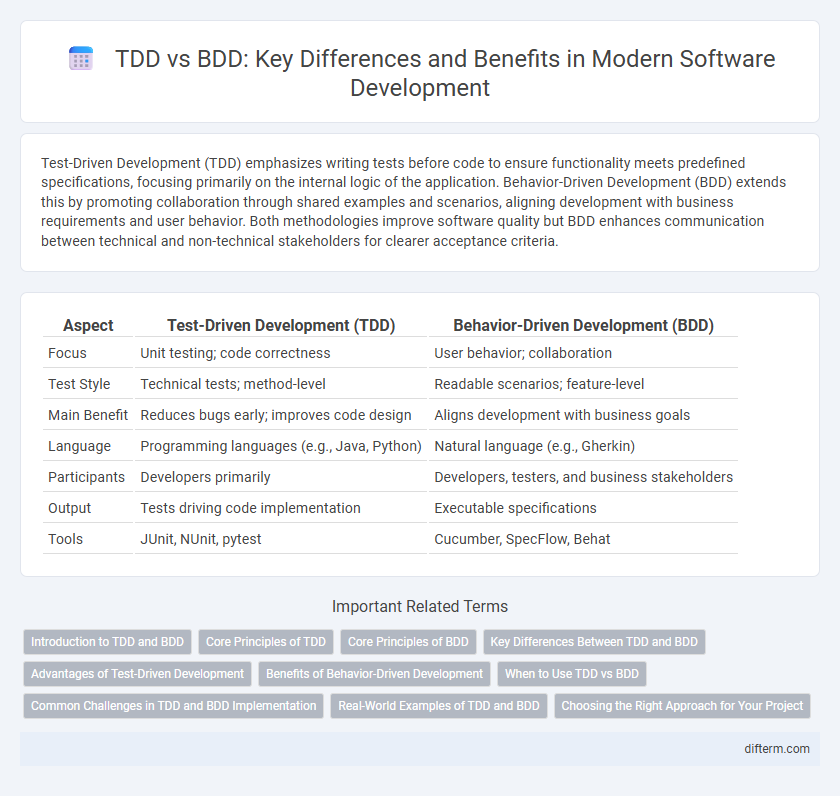
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Test-Driven Development (TDD) | Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Unit testing; code correctness | User behavior; collaboration |
| Test Style | Technical tests; method-level | Readable scenarios; feature-level |
| Main Benefit | Reduces bugs early; improves code design | Aligns development with business goals |
| Language | Programming languages (e.g., Java, Python) | Natural language (e.g., Gherkin) |
| Participants | Developers primarily | Developers, testers, and business stakeholders |
| Output | Tests driving code implementation | Executable specifications |
| Tools | JUnit, NUnit, pytest | Cucumber, SpecFlow, Behat |
Introduction to TDD and BDD
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a software development approach where developers write unit tests before coding functionality, ensuring code reliability and facilitating refactoring. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) extends TDD by emphasizing collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders through natural language scenarios that define application behavior. Both methodologies enhance software quality but differ in focus: TDD centers on technical correctness, while BDD prioritizes business-centric outcomes.
Core Principles of TDD
Test-Driven Development (TDD) revolves around the core principle of writing automated test cases before actual code implementation, ensuring that development aligns strictly with predefined requirements. This approach emphasizes a short, iterative cycle of writing a failing test, developing minimal code to pass the test, and then refactoring for optimization and clarity. TDD fosters robust, maintainable code by driving design decisions through test scenarios that validate functionality at a granular level.
Core Principles of BDD
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) centers on enhancing collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders through a shared language that defines application behavior in clear, executable examples. Its core principles emphasize writing scenarios in a human-readable format that captures requirements as user stories, promoting communication and reducing misunderstandings throughout the development cycle. By focusing on specifying expected behavior rather than implementation details, BDD supports creating more maintainable, testable, and business-aligned software solutions.
Key Differences Between TDD and BDD
Test-Driven Development (TDD) emphasizes writing tests based on technical specifications before coding, focusing on unit tests and developer-centric validation. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) extends TDD by incorporating natural language scenarios to define application behavior, promoting collaboration between developers, testers, and non-technical stakeholders. The key difference lies in TDD's focus on implementation correctness, while BDD prioritizes defining and verifying system behavior from a user perspective.
Advantages of Test-Driven Development
Test-Driven Development (TDD) accelerates the identification of defects by enforcing writing tests before code implementation, which enhances software quality and reliability. It promotes modular, maintainable code structures through continuous refactoring guided by failing tests. TDD facilitates better developer productivity and reduces debugging time, resulting in efficient, robust software delivery cycles.
Benefits of Behavior-Driven Development
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) enhances collaboration between developers, testers, and non-technical stakeholders through shared, natural language specifications that improve communication and reduce misunderstandings. BDD encourages the creation of executable specifications that serve as living documentation, increasing maintainability and ensuring alignment with business requirements. This approach accelerates feedback loops, facilitates early defect detection, and improves overall software quality by integrating automated tests that reflect real user behaviors.
When to Use TDD vs BDD
TDD (Test-Driven Development) is ideal for developers aiming to ensure code functionality through low-level unit tests, especially in complex algorithms or backend logic where precision is critical. BDD (Behavior-Driven Development) suits cross-functional teams focusing on user behavior and acceptance criteria, improving collaboration between developers, testers, and non-technical stakeholders during feature development. Choose TDD when emphasizing code quality and reliability, and BDD when aligning development with business requirements and enhancing communication across roles.
Common Challenges in TDD and BDD Implementation
Common challenges in Test-Driven Development (TDD) and Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) implementation include maintaining clear communication between developers and stakeholders to ensure accurate requirement understanding. Both methodologies face difficulties in writing comprehensive test cases that cover evolving application behavior while avoiding test fragility and excessive maintenance overhead. Ensuring consistent collaboration and integrating automated testing tools effectively remain critical hurdles for successful adoption of TDD and BDD practices.
Real-World Examples of TDD and BDD
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is widely used in software projects like Google's Kubernetes, where automated unit tests define precise functionality before implementation. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) finds strong application in e-commerce platforms like Shopify, enabling collaboration between developers and non-technical stakeholders through user-readable test scenarios. Both methodologies enhance code quality and reduce bugs, but TDD emphasizes internal code correctness while BDD focuses on user behavior and acceptance criteria.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
TDD (Test-Driven Development) emphasizes writing tests before code to ensure functionality aligns with requirements, making it ideal for projects needing robust unit test coverage and early bug detection. BDD (Behavior-Driven Development) focuses on defining behavior through user stories and collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders, enhancing communication and delivering features that meet user expectations. Selecting between TDD and BDD depends on project goals, team collaboration level, and focus on either technical correctness or business behavior clarity.
TDD vs BDD Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com