Public blockchains offer decentralized, transparent networks accessible to anyone, ensuring high security through consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work or proof-of-stake. Private blockchains restrict access to selected participants, enhancing privacy, control, and faster transaction speeds but sacrificing some decentralization. Both models serve unique technology pet applications, balancing transparency and confidentiality based on specific needs.
Table of Comparison
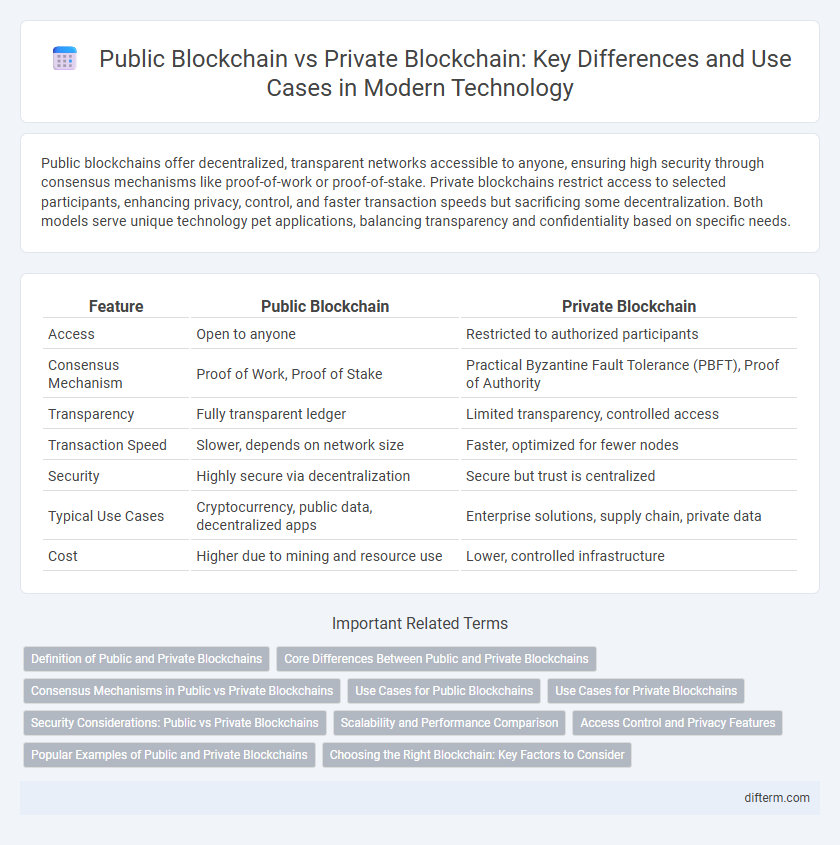
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Open to anyone | Restricted to authorized participants |
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof of Work, Proof of Stake | Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), Proof of Authority |
| Transparency | Fully transparent ledger | Limited transparency, controlled access |
| Transaction Speed | Slower, depends on network size | Faster, optimized for fewer nodes |
| Security | Highly secure via decentralization | Secure but trust is centralized |
| Typical Use Cases | Cryptocurrency, public data, decentralized apps | Enterprise solutions, supply chain, private data |
| Cost | Higher due to mining and resource use | Lower, controlled infrastructure |
Definition of Public and Private Blockchains
Public blockchains operate on decentralized networks where anyone can participate, validate transactions, and access the ledger, exemplified by Bitcoin and Ethereum. Private blockchains restrict network access to authorized participants, providing controlled and secure environments often used by enterprises for internal processes. The core distinction lies in decentralization and accessibility, with public blockchains promoting transparency and private blockchains emphasizing privacy and permissioned control.
Core Differences Between Public and Private Blockchains
Public blockchains operate on decentralized networks with open access, allowing anyone to participate in validating transactions and maintaining consensus, ensuring transparency and security through distributed trust. Private blockchains restrict access to selected participants, enabling faster transaction speeds and enhanced privacy by operating within a controlled environment, often preferred for enterprise applications. The core differences lie in governance, accessibility, consensus mechanisms, and scalability, where public blockchains prioritize openness and trustlessness, while private blockchains emphasize efficiency and confidentiality.
Consensus Mechanisms in Public vs Private Blockchains
Public blockchains utilize consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) to ensure decentralized verification and security, allowing anyone to participate in the network. Private blockchains employ consensus algorithms such as Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) and Raft, which prioritize speed and permissioned access by restricting validation to trusted nodes. The differing consensus mechanisms in public and private blockchains directly impact scalability, security, and network participation levels.
Use Cases for Public Blockchains
Public blockchains excel in decentralized applications, cryptocurrency transactions like Bitcoin and Ethereum, and transparent supply chain tracking, enabling trust without intermediaries. Their open nature supports secure voting systems, tokenized digital assets, and global identity verification, where accessibility and immutability are critical. Enterprises leverage public blockchains for decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, fostering innovation through smart contract automation and peer-to-peer exchanges.
Use Cases for Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are specifically designed for enterprise use, offering enhanced security and control by restricting access to authorized participants, making them ideal for supply chain management, financial services, and healthcare data sharing. These blockchains enable streamlined transactions, improved data privacy, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Use cases include interbank settlements, secure medical record exchange, and confidential contract execution within trusted consortiums.
Security Considerations: Public vs Private Blockchains
Public blockchains offer robust security through decentralized consensus mechanisms and widespread network validation, reducing risks of single points of failure and censorship. Private blockchains prioritize controlled access and permissioned participants, enhancing data privacy and transaction confidentiality but depending heavily on trust in network administrators. Security vulnerabilities in private blockchains often arise from centralized control, whereas public blockchains face threats like 51% attacks but benefit from transparency and collective scrutiny.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
Public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum face scalability challenges due to decentralized consensus mechanisms, limiting transaction throughput to around 7-15 TPS and causing higher latency. Private blockchains, such as Hyperledger Fabric, leverage permissioned networks with fewer nodes and optimized consensus algorithms, achieving higher scalability with thousands of TPS and lower latency. Performance in private blockchains benefits from controlled access and reduced computational overhead, making them suitable for enterprise applications requiring faster processing and scalability.
Access Control and Privacy Features
Public blockchains offer open access where anyone can join, validate transactions, and maintain transparency, making them ideal for decentralized applications requiring high trust. Private blockchains implement strict access control through permissioned networks, restricting participation to authorized entities, which enhances privacy and confidentiality. These privacy features in private blockchains support use cases like enterprise consortia and sensitive data management by preventing unauthorized data exposure.
Popular Examples of Public and Private Blockchains
Ethereum, Bitcoin, and Cardano represent some of the most popular public blockchains known for their decentralized and permissionless networks. In contrast, private blockchains such as Hyperledger Fabric and R3 Corda cater to enterprise needs by offering controlled access and enhanced privacy features. These platforms illustrate the key differences in accessibility, consensus mechanisms, and use cases between public and private blockchain technologies.
Choosing the Right Blockchain: Key Factors to Consider
Choosing the right blockchain involves evaluating security, scalability, and transparency requirements specific to each use case. Public blockchains offer decentralized trust and immutability, ideal for open networks and cryptocurrency applications, while private blockchains provide controlled access and faster transaction speeds suited for enterprise solutions. Assessing consensus mechanisms, compliance needs, and integration capabilities helps determine the optimal blockchain type for business objectives.
Public blockchain vs Private blockchain Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com