Open source technology allows users to access, modify, and distribute the software code freely, fostering innovation and collaboration within the pet tech community. Closed source technology restricts access to the source code, enabling companies to maintain control over their proprietary pet care solutions while limiting customization options. Choosing between open source and closed source pet technology depends on the desired balance between flexibility, security, and support.
Table of Comparison
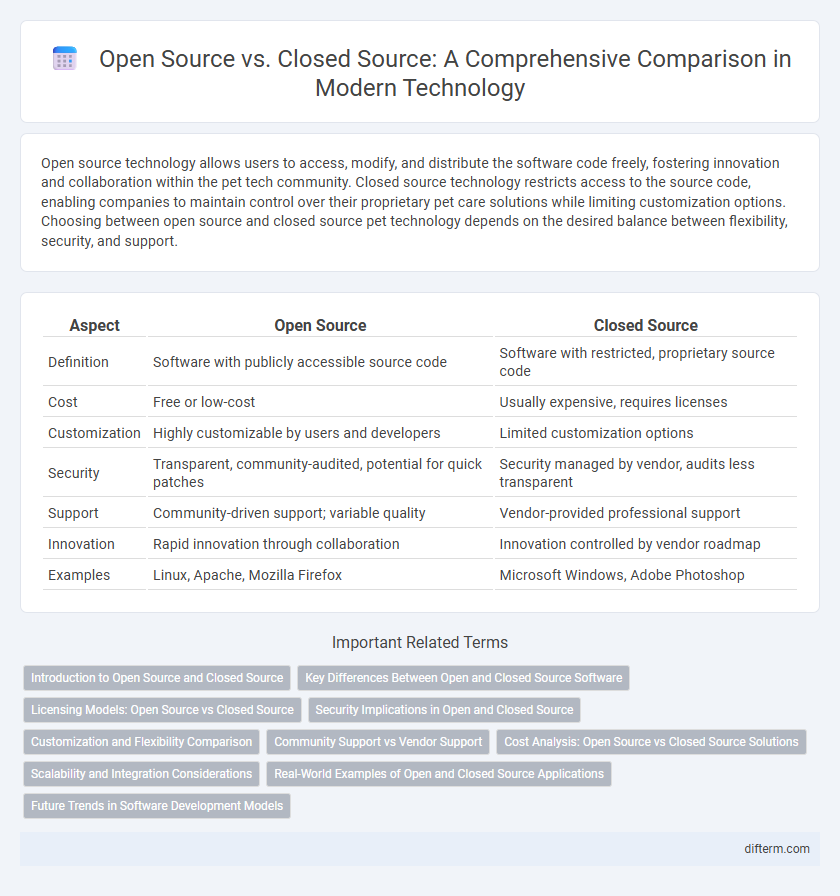
| Aspect | Open Source | Closed Source |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software with publicly accessible source code | Software with restricted, proprietary source code |
| Cost | Free or low-cost | Usually expensive, requires licenses |
| Customization | Highly customizable by users and developers | Limited customization options |
| Security | Transparent, community-audited, potential for quick patches | Security managed by vendor, audits less transparent |
| Support | Community-driven support; variable quality | Vendor-provided professional support |
| Innovation | Rapid innovation through collaboration | Innovation controlled by vendor roadmap |
| Examples | Linux, Apache, Mozilla Firefox | Microsoft Windows, Adobe Photoshop |
Introduction to Open Source and Closed Source
Open source software allows users to access, modify, and distribute the source code freely, promoting collaboration and innovation within the developer community. Closed source software restricts source code access, maintaining proprietary control for businesses to protect intellectual property and ensure consistent user experience. Understanding these fundamental differences is crucial for choosing the right development model based on transparency, customization, and licensing needs.
Key Differences Between Open and Closed Source Software
Open source software provides users with access to its source code, enabling customization, collaboration, and transparency, while closed source software restricts code access, prioritizing proprietary control and security. Open source projects benefit from community-driven development and faster issue resolution, contrasted with closed source's reliance on dedicated internal teams for updates and maintenance. Licensing models differ significantly, with open source using permissive or copyleft licenses and closed source employing restrictive, proprietary licenses limiting user modification and redistribution.
Licensing Models: Open Source vs Closed Source
Open source licensing models provide users with the freedom to access, modify, and distribute software code under licenses such as GPL, MIT, or Apache, fostering collaborative development and transparency. Closed source licensing restricts access to proprietary code, typically governed by End User License Agreements (EULAs), which limit usage, modification, and distribution rights to protect intellectual property. The choice between open and closed source licenses significantly impacts software innovation, community involvement, and commercial control within technology ecosystems.
Security Implications in Open and Closed Source
Open source software enables continuous public scrutiny, which often leads to faster identification and patching of security vulnerabilities compared to closed source solutions. Closed source software relies on limited internal teams to detect issues, potentially delaying vulnerability discovery and increasing risk exposure. The transparency in open source code fosters collaborative security improvements whereas closed source's proprietary nature can obscure vulnerabilities until exploited.
Customization and Flexibility Comparison
Open source software offers extensive customization and flexibility since its source code is openly accessible, allowing developers to modify and adapt the software to specific needs. Closed source software restricts access to the source code, limiting customization options and requiring users to rely on vendor-provided features and updates. This fundamental difference impacts the ability to tailor software solutions precisely in technology environments.
Community Support vs Vendor Support
Open source software thrives on robust community support, with developers worldwide contributing to rapid bug fixes, feature enhancements, and extensive documentation. Closed source software benefits from dedicated vendor support, offering professional help, structured updates, and accountability in service-level agreements. Community-driven forums and collaborative problem-solving contrast with vendor-provided customer service and official technical assistance.
Cost Analysis: Open Source vs Closed Source Solutions
Open source solutions typically reduce initial software acquisition costs since they are freely available, but they may incur expenses related to customization, integration, and ongoing community support. Closed source software often involves higher upfront licensing fees and proprietary vendor maintenance costs, however, it provides dedicated technical support and predictable expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership requires analyzing factors such as deployment scale, required feature sets, and long-term maintenance commitments.
Scalability and Integration Considerations
Open source software enables greater scalability due to its modular architecture and community-driven enhancements, allowing businesses to customize and scale solutions efficiently. Closed source platforms may limit scalability with proprietary constraints but often provide seamless integration with specific vendor ecosystems, ensuring stability and support. Integration considerations must weigh the flexibility of open APIs in open source against the streamlined, vendor-optimized integrations typical in closed source environments.
Real-World Examples of Open and Closed Source Applications
Linux and Firefox exemplify open-source applications, offering transparency, customizability, and community-driven improvements, which empower developers to adapt and enhance the software freely. Microsoft Windows and Adobe Photoshop represent closed-source software, delivering polished, proprietary features backed by dedicated corporate support but restricting user access to the source code. These real-world examples highlight the trade-offs between community collaboration and controlled development environments in software technology.
Future Trends in Software Development Models
Future trends in software development models emphasize the increasing integration of open source and closed source approaches to leverage their complementary strengths. Organizations prioritize hybrid development frameworks that combine open collaboration, transparency, and rapid innovation with proprietary security and intellectual property protections. Advances in AI-driven code generation and cloud-native platforms accelerate this convergence, shaping a dynamic ecosystem that supports scalability, customization, and robust software lifecycle management.
Open source vs Closed source Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com