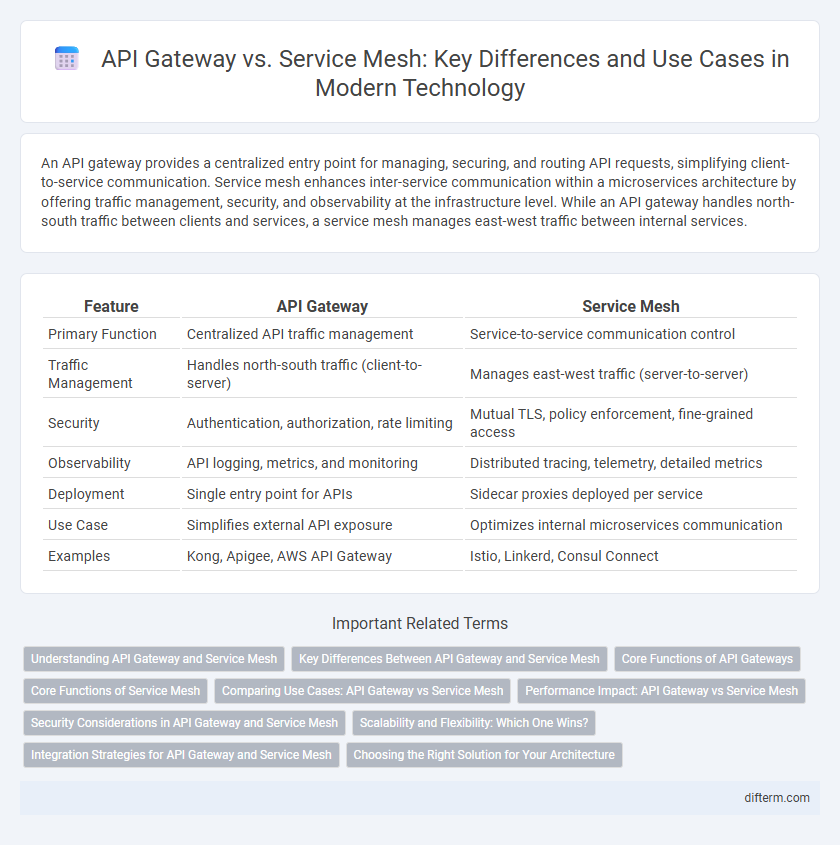
An API gateway provides a centralized entry point for managing, securing, and routing API requests, simplifying client-to-service communication. Service mesh enhances inter-service communication within a microservices architecture by offering traffic management, security, and observability at the infrastructure level. While an API gateway handles north-south traffic between clients and services, a service mesh manages east-west traffic between internal services.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | API Gateway | Service Mesh |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Centralized API traffic management | Service-to-service communication control |
| Traffic Management | Handles north-south traffic (client-to-server) | Manages east-west traffic (server-to-server) |
| Security | Authentication, authorization, rate limiting | Mutual TLS, policy enforcement, fine-grained access |
| Observability | API logging, metrics, and monitoring | Distributed tracing, telemetry, detailed metrics |
| Deployment | Single entry point for APIs | Sidecar proxies deployed per service |
| Use Case | Simplifies external API exposure | Optimizes internal microservices communication |
| Examples | Kong, Apigee, AWS API Gateway | Istio, Linkerd, Consul Connect |
Understanding API Gateway and Service Mesh
API Gateway serves as a centralized entry point that manages, routes, and secures client requests to backend services, optimizing traffic through features like rate limiting, authentication, and protocol translation. Service Mesh operates at the network level, managing service-to-service communication with capabilities such as load balancing, service discovery, and observability by injecting proxies alongside microservices. Understanding these roles is crucial for architects designing scalable, secure, and reliable microservices infrastructure.
Key Differences Between API Gateway and Service Mesh
API gateways primarily manage external client requests by routing, authentication, and rate limiting, whereas service meshes handle internal service-to-service communication with features like load balancing, service discovery, and security. API gateways operate at the edge, providing a unified entry point for APIs, while service meshes function within the infrastructure to enhance microservices networking and observability. The key difference lies in their scope: API gateways focus on managing traffic between clients and services, whereas service meshes optimize and secure interactions among microservices themselves.
Core Functions of API Gateways
API gateways primarily handle request routing, protocol translation, and security enforcement by managing authentication, authorization, and rate limiting for APIs. They act as a centralized entry point, simplifying client interactions with multiple backend services through functions like load balancing and request aggregation. Core functions also include traffic monitoring, analytics, and caching, which optimize performance and enhance API management in microservices architectures.
Core Functions of Service Mesh
Service mesh primarily manages service-to-service communication within microservices architectures by providing traffic routing, load balancing, and secure inter-service communication. It offers observability features such as monitoring, tracing, and logging to simplify debugging and performance optimization. Core functions include service discovery, failure recovery, and enforcing policies like authentication, authorization, and encryption at the network layer.
Comparing Use Cases: API Gateway vs Service Mesh
API gateways excel in managing external client requests, providing features like request routing, rate limiting, and authentication for microservices exposed to the internet. Service meshes specialize in handling internal service-to-service communication within a microservices architecture, offering advanced features such as load balancing, service discovery, and security policies at the network level. Organizations often use API gateways for ingress traffic control and service meshes for observability and resilience in complex, distributed systems.
Performance Impact: API Gateway vs Service Mesh
API gateways centralize request routing, often introducing minimal latency by handling authentication, rate limiting, and protocol translation at the edge. Service meshes distribute communication control across microservices, enabling fine-grained observability and security but potentially increasing inter-service communication overhead due to sidecar proxies. Performance impact varies with system scale; API gateways optimize external traffic flow, while service meshes enhance internal service-to-service performance monitoring, sometimes at the cost of added resource consumption.
Security Considerations in API Gateway and Service Mesh
API gateways centralize security by enforcing authentication, authorization, and rate limiting at the entry point, providing a unified security model. Service meshes enhance security with fine-grained, mutual TLS encryption between services, enabling secure, encrypted communication within microservices architectures. Combining both allows comprehensive security by managing external access through API gateways and securing internal service-to-service traffic via service meshes.
Scalability and Flexibility: Which One Wins?
API gateways offer scalability by managing request routing, authentication, and rate limiting, making them ideal for handling external client traffic with simplicity. Service meshes provide greater flexibility and fine-grained control over inter-service communication within microservices architectures, enabling dynamic load balancing, observability, and security policies at the network level. For large-scale, complex environments requiring advanced traffic management and resilience, service meshes typically outperform API gateways in scalability and flexibility.
Integration Strategies for API Gateway and Service Mesh
API gateways streamline integration by centralizing API request routing, authentication, and rate limiting, ideal for external client interactions and single-entry points. Service meshes provide a granular, infrastructure-layer integration for microservices communication, enabling features like load balancing, encryption, and observability within distributed applications. Combining API gateways with service meshes enhances overall integration by leveraging the gateway's edge routing capabilities alongside the mesh's internal service-to-service communication management.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Architecture
API gateways centralize request routing, security, and traffic management, making them ideal for managing client-to-service communication and simplifying external API exposure. Service meshes provide fine-grained control over service-to-service interactions, offering advanced features like load balancing, encryption, and observability within microservices architectures. Selecting the right solution depends on your architecture's complexity, with API gateways suited for edge management and service meshes optimized for internal service communication and resilience.
API gateway vs Service mesh Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com