SaaS delivers ready-to-use applications over the internet, eliminating the need for installation or maintenance, making it ideal for end-users seeking convenience and accessibility. PaaS provides a development platform with tools and infrastructure, enabling developers to build, test, and deploy custom applications efficiently. Choosing between SaaS and PaaS depends on whether the primary requirement is immediate software access or a flexible environment for application development.
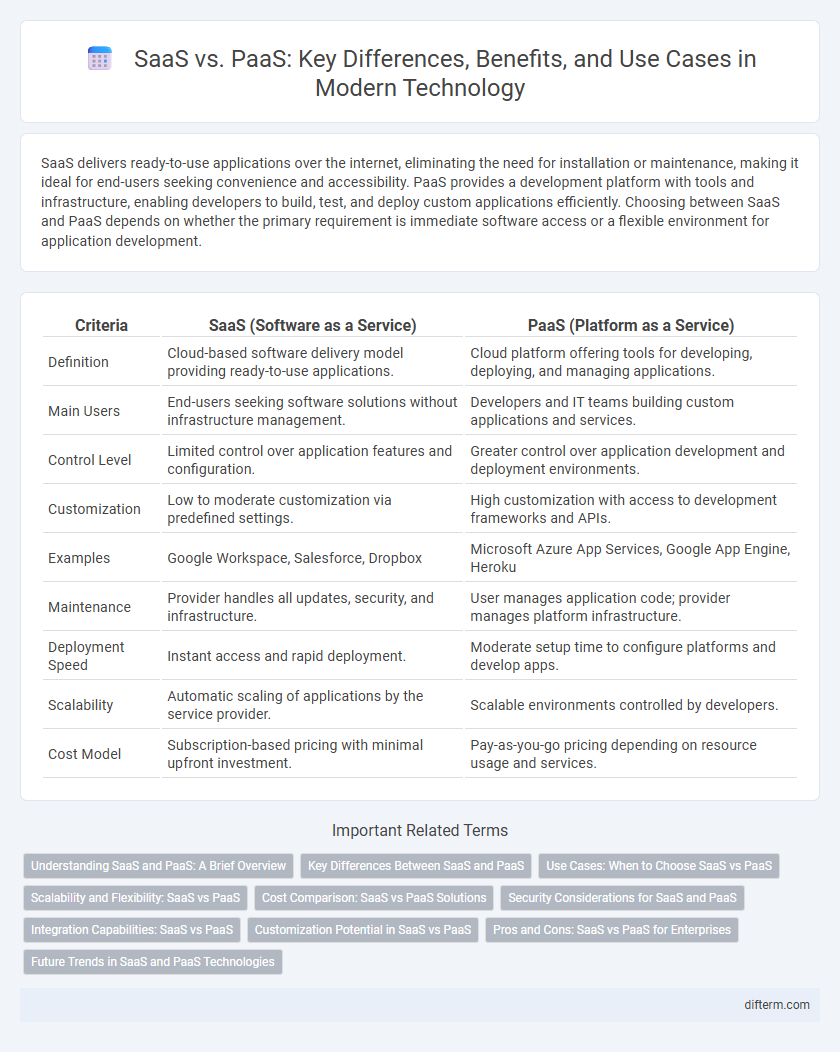
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | SaaS (Software as a Service) | PaaS (Platform as a Service) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud-based software delivery model providing ready-to-use applications. | Cloud platform offering tools for developing, deploying, and managing applications. |
| Main Users | End-users seeking software solutions without infrastructure management. | Developers and IT teams building custom applications and services. |
| Control Level | Limited control over application features and configuration. | Greater control over application development and deployment environments. |
| Customization | Low to moderate customization via predefined settings. | High customization with access to development frameworks and APIs. |
| Examples | Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox | Microsoft Azure App Services, Google App Engine, Heroku |
| Maintenance | Provider handles all updates, security, and infrastructure. | User manages application code; provider manages platform infrastructure. |
| Deployment Speed | Instant access and rapid deployment. | Moderate setup time to configure platforms and develop apps. |
| Scalability | Automatic scaling of applications by the service provider. | Scalable environments controlled by developers. |
| Cost Model | Subscription-based pricing with minimal upfront investment. | Pay-as-you-go pricing depending on resource usage and services. |
Understanding SaaS and PaaS: A Brief Overview
SaaS (Software as a Service) delivers fully developed applications over the internet, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance, enabling users to access software on-demand. PaaS (Platform as a Service) provides a cloud-based environment with tools and infrastructure for developers to build, test, and deploy custom applications efficiently. Both SaaS and PaaS enhance business agility, but SaaS offers ready-to-use software while PaaS supports scalable application development and customization.
Key Differences Between SaaS and PaaS
SaaS (Software as a Service) delivers fully functional applications over the internet, allowing users to access software without managing underlying infrastructure. PaaS (Platform as a Service) provides a development environment where developers can build, deploy, and manage custom applications without handling hardware or operating systems. Key differences include SaaS offering ready-to-use software for end-users, while PaaS focuses on providing tools and frameworks for developers to create applications.
Use Cases: When to Choose SaaS vs PaaS
SaaS is ideal for businesses seeking ready-to-use applications like email, CRM, or collaboration tools with minimal customization, enabling rapid deployment and reduced IT management. PaaS suits developers needing a comprehensive environment for building, testing, and deploying custom applications, offering flexibility in programming languages, middleware, and infrastructure control. Organizations choose SaaS for standardized solutions, while PaaS supports innovation through scalable, tailored application development.
Scalability and Flexibility: SaaS vs PaaS
SaaS platforms offer scalability through pre-built applications that automatically adjust to user demand without requiring infrastructure management, making them ideal for businesses seeking quick deployment. PaaS provides greater flexibility by allowing developers to build, customize, and scale applications on a managed platform, facilitating tailored solutions that can evolve with specific requirements. Both models support scalability, but PaaS enables deeper customization and control over resources, while SaaS prioritizes ease of use and rapid scalability.
Cost Comparison: SaaS vs PaaS Solutions
SaaS solutions typically offer lower upfront costs since they provide ready-to-use software hosted on the provider's infrastructure, eliminating the need for extensive hardware investments or ongoing maintenance expenses. PaaS platforms involve higher initial expenses due to the development environment and customization capabilities but can reduce long-term costs by enabling faster application development and scalability without added infrastructure management. Evaluating total cost of ownership (TCO), businesses should consider subscription fees, development costs, integration complexity, and potential savings from reduced IT operational overhead when comparing SaaS and PaaS models.
Security Considerations for SaaS and PaaS
SaaS security primarily relies on the provider for data protection, access control, and regular updates, making it essential to evaluate the vendor's compliance with standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and GDPR. PaaS offers greater control over application security, allowing developers to implement custom encryption, authentication, and threat detection mechanisms, while still depending on the platform provider for underlying infrastructure security. Both models require rigorous identity and access management (IAM), regular vulnerability assessments, and secure API integrations to mitigate risks in cloud environments.
Integration Capabilities: SaaS vs PaaS
SaaS platforms offer pre-built integration capabilities with popular applications and services, enabling quick deployment and seamless connectivity for end-users. PaaS solutions provide extensive customization and flexibility, allowing developers to build tailored integration workflows using APIs, middleware, and connectors. While SaaS excels in out-of-the-box integration efficiency, PaaS is preferred for scalable, complex, and bespoke integration requirements in enterprise environments.
Customization Potential in SaaS vs PaaS
SaaS platforms offer limited customization options typically confined to user interface settings and predefined configurations, prioritizing ease of use and rapid deployment. In contrast, PaaS solutions provide extensive customization potential by allowing developers to build, deploy, and optimize applications with full control over the software stack and integrated development tools. This flexibility in PaaS supports tailored workflows and complex integrations, making it ideal for organizations with specific functional requirements.
Pros and Cons: SaaS vs PaaS for Enterprises
SaaS offers enterprises rapid deployment, lower upfront costs, and ease of use with ready-made applications, but it limits customization and may pose integration challenges with existing systems. PaaS provides greater flexibility and control over application development and scaling, enabling enterprises to tailor solutions to specific needs while requiring more technical expertise and longer deployment times. Choosing between SaaS and PaaS depends on an enterprise's need for customization, development resources, and time-to-market priorities.
Future Trends in SaaS and PaaS Technologies
Future trends in SaaS and PaaS technologies emphasize increased integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance automation and predictive analytics. The rise of multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies is driving greater interoperability and flexibility between SaaS and PaaS platforms. Advancements in low-code and no-code development environments within PaaS are enabling faster application deployment and democratizing software creation across industries.
SaaS vs PaaS Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com