SQL databases excel in structured data environments with complex queries and ACID compliance, making them ideal for applications requiring transaction reliability and consistency. NoSQL databases offer flexible schema designs, horizontal scalability, and high performance, suitable for handling large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data in pet technology systems. Choosing between SQL and NoSQL depends on the specific data types, scalability needs, and consistency requirements of the pet technology application.
Table of Comparison
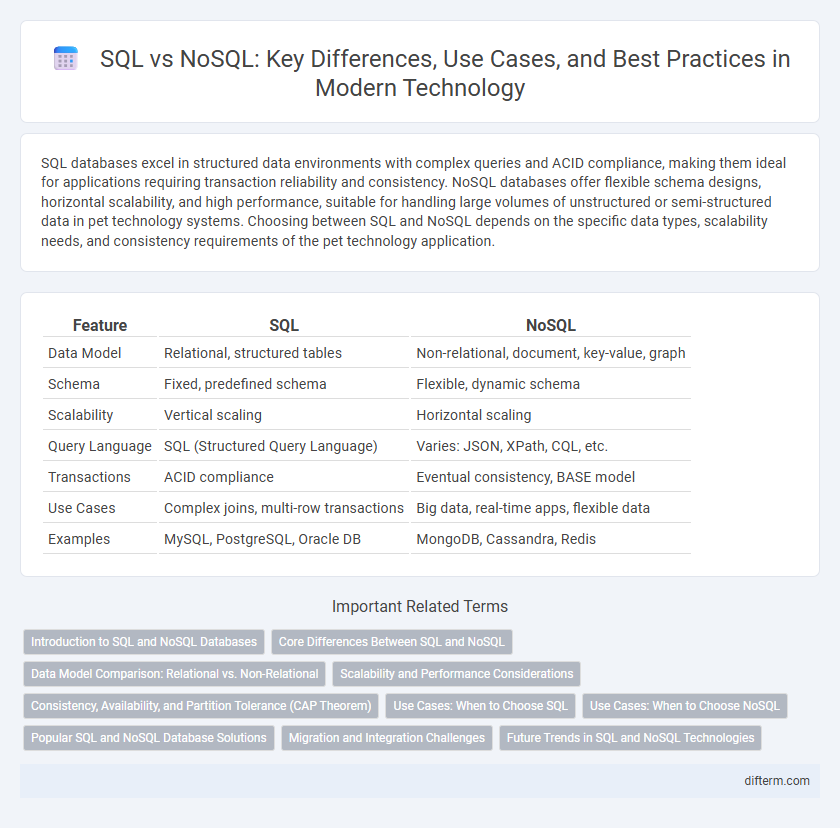
| Feature | SQL | NoSQL |
|---|---|---|
| Data Model | Relational, structured tables | Non-relational, document, key-value, graph |
| Schema | Fixed, predefined schema | Flexible, dynamic schema |
| Scalability | Vertical scaling | Horizontal scaling |
| Query Language | SQL (Structured Query Language) | Varies: JSON, XPath, CQL, etc. |
| Transactions | ACID compliance | Eventual consistency, BASE model |
| Use Cases | Complex joins, multi-row transactions | Big data, real-time apps, flexible data |
| Examples | MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle DB | MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis |
Introduction to SQL and NoSQL Databases
SQL databases are structured around relational models using tables with predefined schemas, making them ideal for complex queries and transactions requiring data consistency. NoSQL databases support flexible, schema-less data storage formats such as key-value, document, column-family, and graph, enabling high scalability and performance for unstructured or semi-structured data. Both database types cater to distinct use cases, with SQL excelling in transactional systems and NoSQL preferred for big data and real-time web applications.
Core Differences Between SQL and NoSQL
SQL databases use structured query language for defining and manipulating data, relying on a fixed schema and table-based relational model that ensures ACID compliance for transactional integrity. NoSQL databases offer flexible schema designs with document, key-value, column-family, or graph data models, supporting horizontal scalability and handling unstructured or semi-structured data efficiently. Performance in SQL shines with complex queries and transactions, while NoSQL excels in distributed environments requiring high availability and rapid, large-scale data processing.
Data Model Comparison: Relational vs. Non-Relational
SQL databases utilize a structured, relational data model based on tables with predefined schemas, enforcing ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties for transaction reliability. NoSQL databases adopt a flexible, non-relational data model that supports document, key-value, wide-column, or graph formats, enabling schema-less data storage and horizontal scalability. This fundamental difference impacts query languages, data consistency, and performance optimization, with SQL excelling in complex joins and transactions, while NoSQL suits unstructured, large-scale, or evolving datasets.
Scalability and Performance Considerations
SQL databases excel in complex query processing and transactional consistency but often face scalability challenges when handling large-scale, distributed systems due to vertical scaling limitations. NoSQL databases, designed with horizontal scalability in mind, offer high performance for big data and real-time web applications by distributing data across multiple nodes. Performance in NoSQL systems is enhanced through flexible schema design and eventual consistency models, making them ideal for dynamic, high-throughput environments.
Consistency, Availability, and Partition Tolerance (CAP Theorem)
SQL databases prioritize consistency and partition tolerance, ensuring reliable transactions and data integrity across distributed networks, but often at the expense of availability during network partitions. NoSQL databases emphasize availability and partition tolerance, maintaining service responsiveness under network failures while allowing eventual consistency models. The choice between SQL and NoSQL depends on the specific application requirements for strict consistency versus high availability in distributed systems.
Use Cases: When to Choose SQL
SQL databases excel in applications requiring complex queries, structured data models, and ACID compliance, such as financial systems, enterprise resource planning, and customer relationship management. They are ideal for scenarios with a fixed schema and relationships that demand data integrity and consistency, enabling reliable transaction management. Selecting SQL is advantageous when the use case involves intricate joins, reporting, and a need for standardized query language support.
Use Cases: When to Choose NoSQL
NoSQL databases excel in handling large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data, making them ideal for real-time analytics, content management systems, and IoT applications. Use NoSQL when scalability, high availability, and flexible schema design are critical, especially in big data and cloud-native environments. NoSQL solutions like MongoDB, Cassandra, and Couchbase outperform traditional SQL databases in horizontal scaling and rapid iteration of evolving data models.
Popular SQL and NoSQL Database Solutions
Popular SQL database solutions include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server, known for their structured query language and ACID compliance. In contrast, prominent NoSQL databases such as MongoDB, Cassandra, and Redis offer flexible schema designs, scalability, and high performance for unstructured or semi-structured data. Choosing between SQL and NoSQL depends on data consistency requirements, scalability needs, and specific application use cases in technology development.
Migration and Integration Challenges
Migrating from SQL to NoSQL databases involves complex data model transformations due to relational schemas versus flexible, schema-less structures in NoSQL. Integration challenges arise from differing query languages like SQL's standardized syntax compared to NoSQL's diverse APIs and consistency models. Ensuring data integrity and seamless interoperability across hybrid environments requires robust data mapping tools and middleware solutions.
Future Trends in SQL and NoSQL Technologies
SQL databases are evolving with advanced features like automated query optimization, enhanced support for JSON data, and improved horizontal scalability through distributed SQL systems. NoSQL technologies are increasingly integrating multi-model capabilities, real-time analytics, and AI-driven indexing to handle diverse and unstructured data at scale. The convergence of SQL and NoSQL functionalities is driving hybrid database platforms that offer flexibility, performance, and strong consistency for next-generation applications.
SQL vs NoSQL Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com