Web scraping extracts specific data from websites by parsing HTML content, enabling targeted information retrieval for analysis or use in applications. Web crawling systematically scans and indexes entire websites or the web at large, facilitating efficient data collection for search engines or large-scale data aggregation. Understanding the distinction helps businesses implement appropriate strategies for data acquisition and content monitoring.
Table of Comparison
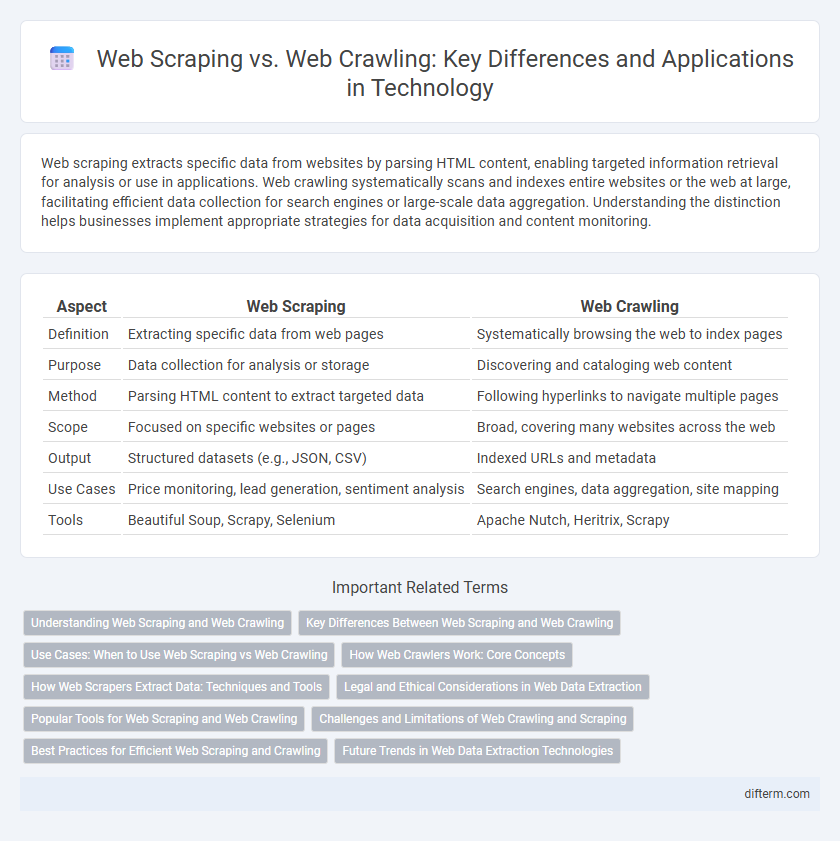
| Aspect | Web Scraping | Web Crawling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Extracting specific data from web pages | Systematically browsing the web to index pages |
| Purpose | Data collection for analysis or storage | Discovering and cataloging web content |
| Method | Parsing HTML content to extract targeted data | Following hyperlinks to navigate multiple pages |
| Scope | Focused on specific websites or pages | Broad, covering many websites across the web |
| Output | Structured datasets (e.g., JSON, CSV) | Indexed URLs and metadata |
| Use Cases | Price monitoring, lead generation, sentiment analysis | Search engines, data aggregation, site mapping |
| Tools | Beautiful Soup, Scrapy, Selenium | Apache Nutch, Heritrix, Scrapy |
Understanding Web Scraping and Web Crawling
Web scraping involves extracting specific data from web pages using automated scripts or tools, focusing on retrieving targeted information such as prices, reviews, or contact details. Web crawling refers to the process of systematically browsing and indexing entire websites or vast portions of the internet, enabling search engines to catalog pages and build searchable databases. Understanding the technical distinctions and use cases between web scraping and web crawling is essential for optimizing data collection strategies in technology-driven projects.
Key Differences Between Web Scraping and Web Crawling
Web scraping extracts specific data from web pages, transforming unstructured information into structured datasets, while web crawling systematically navigates through websites to index content for search engines or data discovery. Web scraping targets particular elements or data points, often for data analysis, whereas web crawling focuses on broad data collection and link discovery across multiple web domains. The technological distinction lies in scraping's emphasis on data parsing and extraction, contrasted with crawling's priority on automated, large-scale web traversal and metadata compilation.
Use Cases: When to Use Web Scraping vs Web Crawling
Web scraping is ideal for extracting specific data from targeted websites, such as product prices or user reviews, to support competitive analysis and market research. Web crawling suits scenarios requiring comprehensive indexing of multiple web pages, like search engines or data aggregation platforms that need to systematically explore entire domains. Choosing between web scraping and web crawling depends on whether the goal is data collection from select pages or creating a broad map of interconnected web content.
How Web Crawlers Work: Core Concepts
Web crawlers systematically browse the internet by following links from one webpage to another, using algorithms to index and map vast amounts of online content. They start with a list of URLs, fetch their HTML content, extract hyperlinks, and recursively visit these links to discover new pages while respecting rules defined in robots.txt files. Efficient crawling strategies manage bandwidth and server load, ensuring comprehensive, up-to-date datasets crucial for search engines and data mining applications.
How Web Scrapers Extract Data: Techniques and Tools
Web scrapers extract data using techniques like DOM parsing, XPath queries, and CSS selectors to target specific elements within web pages. Tools such as Beautiful Soup, Scrapy, and Selenium automate data extraction by navigating HTML structures and handling dynamic content rendered by JavaScript. These methods enable efficient retrieval of structured data, enabling applications like price comparison, market research, and sentiment analysis.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Web Data Extraction
Web scraping involves extracting specific data from websites, often raising legal concerns related to copyright infringement and terms of service violations, whereas web crawling systematically indexes site content for search engines, generally operating under clearer regulatory frameworks. Ethical considerations emphasize respecting robots.txt directives and user privacy to avoid unauthorized data harvesting and potential harms caused by overloading servers. Compliance with laws such as the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) in the US and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe is critical to ensure lawful web data extraction practices.
Popular Tools for Web Scraping and Web Crawling
Popular tools for web scraping include Beautiful Soup, Scrapy, and Octoparse, which excel at extracting data from HTML pages with ease. Web crawling relies on frameworks like Apache Nutch, Heritrix, and Scrapy, designed to systematically browse and index large volumes of web pages. Each tool offers unique features optimized for specific tasks in data extraction and web navigation, supporting efficient handling of diverse web data needs.
Challenges and Limitations of Web Crawling and Scraping
Web crawling faces challenges like handling dynamic content, managing large-scale data extraction, and respecting site restrictions such as robots.txt protocols. Web scraping encounters limitations including IP blocking, CAPTCHA challenges, and frequent website structural changes that require constant adaptation. Both processes demand sophisticated tools to maintain data accuracy and comply with legal and ethical guidelines.
Best Practices for Efficient Web Scraping and Crawling
Effective web scraping and crawling require respecting website robots.txt files to avoid legal issues and server overload. Using randomized request intervals and rotating user agents help mimic human behavior, reducing the risk of IP blocking. Employing asynchronous processing and prioritizing URLs based on relevance significantly enhances the efficiency of data extraction tasks.
Future Trends in Web Data Extraction Technologies
Future trends in web data extraction technologies emphasize the integration of AI-driven algorithms to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of both web scraping and web crawling. Advances in natural language processing and machine learning enable more sophisticated data parsing and real-time adaptation to dynamic web content. Scalability improvements coupled with robust anti-bot detection methods will define the next generation of web data extraction tools.
Web scraping vs Web crawling Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com