Social pets often experience status consistency when their rank or role within a group aligns with their behavior and social expectations, leading to stable relationships and clear social hierarchies. In contrast, status inconsistency arises when a pet's perceived status conflicts with its actual behavior or group position, causing confusion and tension in social interactions. Understanding these dynamics helps improve pet socialization and reduces stress in multi-pet households.
Table of Comparison
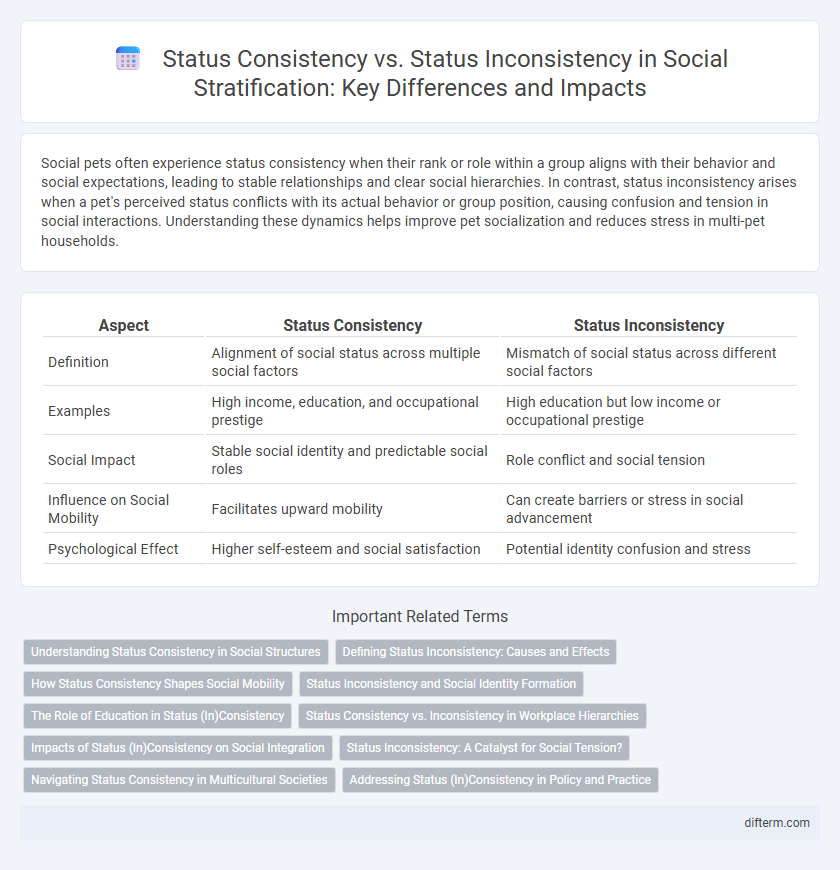
| Aspect | Status Consistency | Status Inconsistency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alignment of social status across multiple social factors | Mismatch of social status across different social factors |
| Examples | High income, education, and occupational prestige | High education but low income or occupational prestige |
| Social Impact | Stable social identity and predictable social roles | Role conflict and social tension |
| Influence on Social Mobility | Facilitates upward mobility | Can create barriers or stress in social advancement |
| Psychological Effect | Higher self-esteem and social satisfaction | Potential identity confusion and stress |
Understanding Status Consistency in Social Structures
Status consistency refers to the alignment of an individual's social status across multiple dimensions such as income, education, and occupational prestige, creating a coherent and stable social position. Status inconsistency occurs when these dimensions conflict, for example, holding a high education level but a low-income job, leading to social tension and identity challenges. Understanding status consistency aids in analyzing social cohesion and the dynamics of social inequality within structured communities.
Defining Status Inconsistency: Causes and Effects
Status inconsistency occurs when an individual's social positions have conflicting levels of prestige, income, or power, leading to a mismatch in social status. Common causes include disparities between educational attainment and occupational prestige or income level and social class background. The effects of status inconsistency often involve psychological stress, social tension, and challenges in social interactions due to ambiguous or contested social standing.
How Status Consistency Shapes Social Mobility
Status consistency, where an individual's social rankings across factors like education, income, and occupation align, facilitates smoother social mobility by providing stable resources and social networks. In contrast, status inconsistency, marked by conflicting rankings such as high education but low income, creates barriers to upward mobility due to conflicting social signals and reduced social capital. Consistent status enhances predictability in social interactions and access to opportunities, driving greater upward mobility within social hierarchies.
Status Inconsistency and Social Identity Formation
Status inconsistency occurs when an individual holds differing levels of social status across various dimensions such as occupation, education, and income, leading to conflicting social identities. This inconsistency complicates social identity formation by generating internal tension and ambiguity, influencing how individuals perceive themselves and how they are perceived by society. Research shows that status inconsistency often results in psychological stress and can affect social behavior, group affiliation, and identity negotiation processes.
The Role of Education in Status (In)Consistency
Education plays a critical role in shaping status consistency by aligning an individual's occupational position with their socioeconomic background, which reinforces social stability. When educational attainment surpasses or falls short of family status, it creates status inconsistency, leading to shifts in social mobility and identity conflict. Understanding the impact of education on status (in)consistency reveals how credentials influence both personal social standing and broader societal stratification.
Status Consistency vs. Inconsistency in Workplace Hierarchies
Status consistency in workplace hierarchies occurs when an individual's rank, income, and authority align uniformly, fostering clear role expectations and smoother organizational functioning. In contrast, status inconsistency arises when discrepancies exist among these dimensions, potentially leading to conflicts, reduced job satisfaction, and challenges in team dynamics. Understanding the impact of status alignment helps organizations design more cohesive leadership structures and improve employee engagement.
Impacts of Status (In)Consistency on Social Integration
Status consistency promotes social integration by aligning an individual's socioeconomic indicators such as education, income, and occupation, fostering stability and acceptance within social groups. Status inconsistency, where disparities exist among these indicators, often leads to social tension and challenges in group cohesion due to conflicting expectations and perceived inequalities. The resulting impact on social integration can manifest as reduced social trust, fragmented networks, and increased potential for social conflict.
Status Inconsistency: A Catalyst for Social Tension?
Status inconsistency occurs when an individual's social positions have both high and low rankings across different status dimensions, such as income, education, or occupation, generating conflicting social signals. This inconsistency can act as a catalyst for social tension by fostering feelings of relative deprivation, frustration, and resentment both within individuals and between social groups. Research indicates that status inconsistency correlates with increased stress levels, diminished social cohesion, and heightened potential for conflict in communities.
Navigating Status Consistency in Multicultural Societies
Status consistency fosters social harmony by aligning an individual's social, economic, and cultural ranks, reducing conflicts in multicultural societies. Navigating status inconsistency requires recognizing diverse value systems and promoting inclusive policies that respect differing social hierarchies. Effective multicultural integration depends on balancing these status dynamics to enhance cohesion and equal opportunity across cultural groups.
Addressing Status (In)Consistency in Policy and Practice
Addressing status consistency and inconsistency in policy and practice requires recognizing the complex interplay between individuals' social, economic, and occupational positions to promote equitable outcomes. Policies must integrate multidimensional indicators such as income, education, and occupational prestige to accurately reflect status disparities and guide targeted interventions. Effective practice involves continuous monitoring and adaptive strategies to mitigate the adverse effects of status inconsistency on social cohesion and individual well-being.
status consistency vs status inconsistency Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com