Social cohesion in the context of social pets emphasizes fostering positive interactions and emotional bonds among animals, enhancing their overall well-being and group harmony. Social control, however, involves mechanisms that regulate behavior and maintain order within animal groups, often through dominance hierarchies or behavioral cues. Balancing social cohesion with social control is essential to promote a healthy, stable social environment that supports both individual and group dynamics.
Table of Comparison
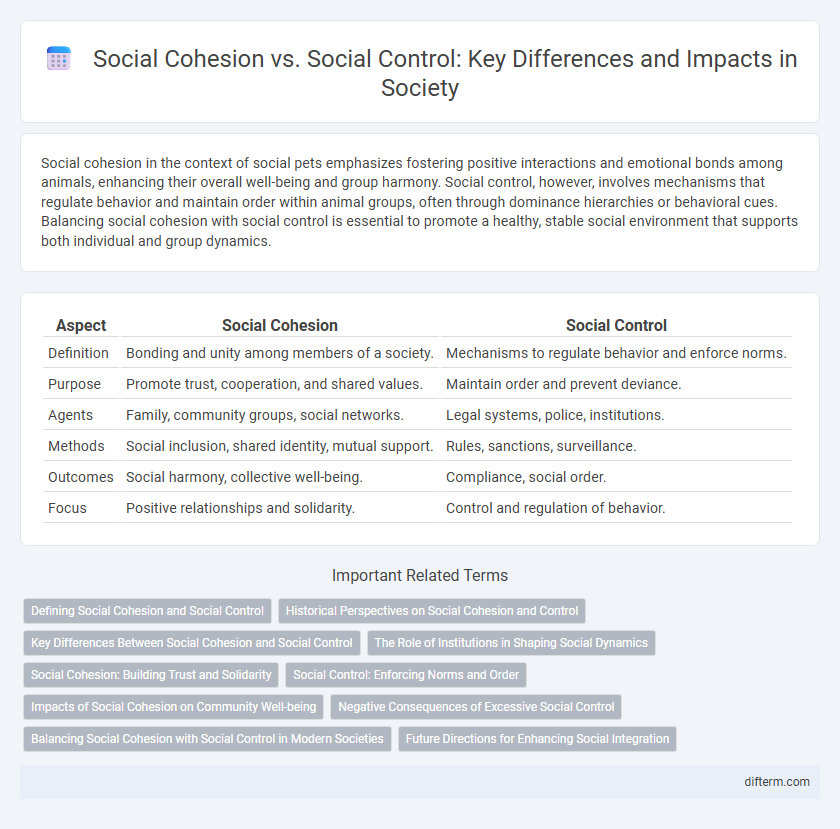
| Aspect | Social Cohesion | Social Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bonding and unity among members of a society. | Mechanisms to regulate behavior and enforce norms. |
| Purpose | Promote trust, cooperation, and shared values. | Maintain order and prevent deviance. |
| Agents | Family, community groups, social networks. | Legal systems, police, institutions. |
| Methods | Social inclusion, shared identity, mutual support. | Rules, sanctions, surveillance. |
| Outcomes | Social harmony, collective well-being. | Compliance, social order. |
| Focus | Positive relationships and solidarity. | Control and regulation of behavior. |
Defining Social Cohesion and Social Control
Social cohesion refers to the strength of relationships and sense of solidarity among members of a community, fostering trust, cooperation, and shared values. Social control encompasses the mechanisms, including laws, norms, and sanctions, that regulate individual and group behavior to maintain order and conformity within society. Understanding the distinction between social cohesion as a positive, unifying force and social control as a regulatory tool clarifies their complementary roles in sustaining social stability.
Historical Perspectives on Social Cohesion and Control
Historical perspectives on social cohesion emphasize the collective bonds formed through shared norms, values, and cultural practices that foster unity within societies. In contrast, social control mechanisms, such as laws, sanctions, and institutional regulations, have historically functioned to maintain order and regulate individual behavior, often reflecting power dynamics. The evolution of social cohesion and control reveals their intertwined role in shaping societal stability and addressing conflicts throughout history.
Key Differences Between Social Cohesion and Social Control
Social cohesion refers to the strength of relationships and the sense of solidarity among members of a community, emphasizing shared values and trust that foster cooperation. Social control involves mechanisms, such as laws and norms, used to regulate individual and group behavior to maintain order and prevent deviance. The key difference lies in social cohesion promoting unity through positive bonds, while social control enforces conformity often through external pressure or sanctions.
The Role of Institutions in Shaping Social Dynamics
Institutions such as schools, law enforcement, and religious organizations play a crucial role in fostering social cohesion by promoting shared values, norms, and collective identity. These entities also exercise social control through regulations, sanctions, and surveillance to maintain order and prevent deviance. The balance between these functions shapes social dynamics by influencing trust, cooperation, and conformity within communities.
Social Cohesion: Building Trust and Solidarity
Social cohesion fosters strong community bonds by promoting trust, shared values, and mutual support among members, which enhances collective well-being and reduces social disparities. Building trust involves inclusive dialogue, equitable resource distribution, and active participation in community activities, creating a sense of belonging and solidarity. Strengthened social cohesion improves resilience to social tensions and facilitates collaborative solutions to common challenges.
Social Control: Enforcing Norms and Order
Social control plays a crucial role in enforcing norms and maintaining order within communities by establishing rules and mechanisms that regulate individual behavior. Institutions such as law enforcement, educational systems, and family structures implement sanctions that deter deviance, ensuring social stability and cohesion. Effective social control reduces conflict, promotes predictability, and supports collective well-being in diverse societies.
Impacts of Social Cohesion on Community Well-being
Social cohesion enhances community well-being by fostering trust, mutual support, and shared values among residents, leading to improved mental health and reduced crime rates. Strong social networks promote collaboration in addressing local challenges and increase collective efficacy. Higher levels of social cohesion also contribute to greater economic stability and resilience in communities.
Negative Consequences of Excessive Social Control
Excessive social control can undermine social cohesion by fostering mistrust and resentment among community members, leading to social fragmentation. Overregulation often suppresses individual freedoms, resulting in decreased civic engagement and weakening collective identity. Such rigidity may provoke resistance and social unrest, further disrupting societal harmony.
Balancing Social Cohesion with Social Control in Modern Societies
Balancing social cohesion with social control in modern societies involves fostering trust, cooperation, and shared values while implementing regulations that ensure public safety and order. Effective social cohesion enhances community resilience and collective identity, whereas social control mechanisms prevent deviance and maintain stability. Achieving this balance requires inclusive policies that promote social integration without excessive authoritarianism.
Future Directions for Enhancing Social Integration
Future directions for enhancing social integration include leveraging community-driven initiatives that foster trust and mutual respect among diverse groups, thereby strengthening social cohesion. Implementing inclusive policies that balance social control with individual freedoms can promote greater participation and compliance within societies. Advancements in digital platforms enable real-time communication and collaboration, offering new opportunities to bridge social divides and reinforce collective identity.
social cohesion vs social control Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com