Stereotypes about social pets often paint them as overly dependent or needy, which can lead to unfair prejudices that overlook their unique personalities and benefits as companions. These generalized beliefs ignore the diverse behaviors and emotional intelligence that social pets exhibit in fostering human-animal bonds. Overcoming stereotype-based prejudice is essential to appreciate and support the positive role social pets play in emotional well-being.
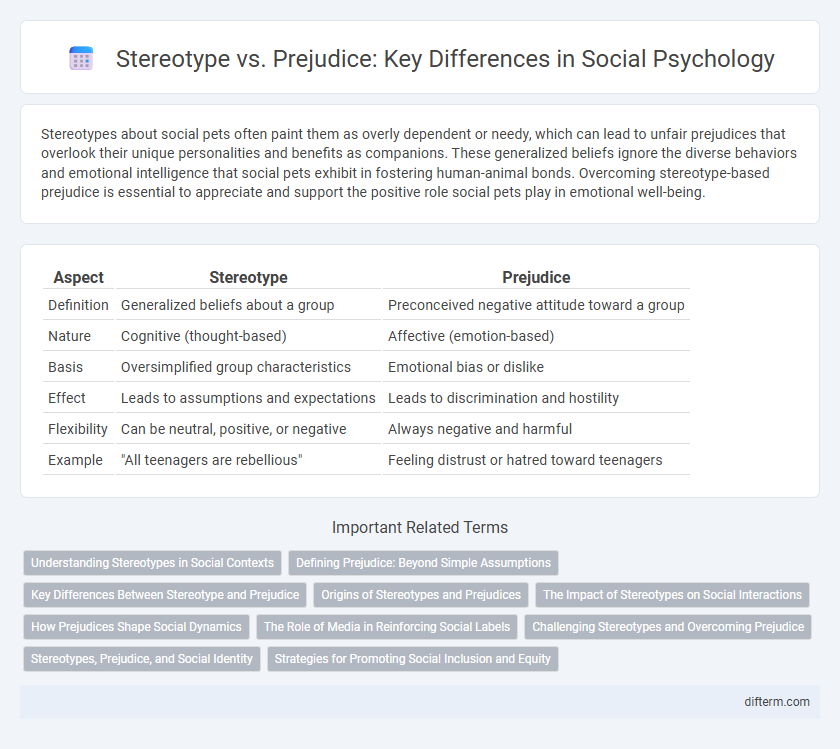
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Stereotype | Prejudice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generalized beliefs about a group | Preconceived negative attitude toward a group |
| Nature | Cognitive (thought-based) | Affective (emotion-based) |
| Basis | Oversimplified group characteristics | Emotional bias or dislike |
| Effect | Leads to assumptions and expectations | Leads to discrimination and hostility |
| Flexibility | Can be neutral, positive, or negative | Always negative and harmful |
| Example | "All teenagers are rebellious" | Feeling distrust or hatred toward teenagers |
Understanding Stereotypes in Social Contexts
Stereotypes are generalized beliefs about a group that simplify social perception but often lack accuracy, influencing how individuals interpret behaviors and traits. They function as cognitive shortcuts in social interactions, shaping expectations and guiding responses based on perceived group characteristics rather than personal experience. Understanding stereotypes is crucial for addressing biased behavior, as they differ from prejudices, which involve evaluative judgments and emotions linked to these generalized beliefs.
Defining Prejudice: Beyond Simple Assumptions
Prejudice involves preconceived opinions or feelings, often negative, directed toward individuals or groups based on characteristics such as race, gender, or ethnicity, without factual knowledge or experience. Unlike simple assumptions or stereotypes that categorize people broadly, prejudice implies an emotional bias and a readiness to discriminate or act against others. Understanding prejudice requires recognizing its deep-rooted social and psychological components that influence attitudes and behaviors beyond mere generalizations.
Key Differences Between Stereotype and Prejudice
Stereotypes are generalized beliefs or assumptions about a group of people based on perceived characteristics, often oversimplified and not necessarily negative. Prejudice involves preconceived, typically unfavorable judgments or attitudes toward individuals based on their group membership, reflecting emotional bias and discrimination potential. Key differences lie in stereotypes being cognitive schemas while prejudice encompasses affective responses, influencing social behavior and intergroup relations.
Origins of Stereotypes and Prejudices
Stereotypes originate from cognitive processes that simplify social perception by categorizing individuals based on group traits, often influenced by cultural narratives and media representation. Prejudices develop through emotional responses and social learning, reinforced by personal experiences and societal attitudes. Both stem from upbringing, historical context, and intergroup dynamics, shaping attitudes that impact social interactions and perpetuate discrimination.
The Impact of Stereotypes on Social Interactions
Stereotypes shape social interactions by creating generalized expectations about individuals based on group membership, often leading to miscommunication and reduced trust. These cognitive shortcuts influence behavior unconsciously, causing individuals to act in ways that may reinforce existing biases and social divisions. The persistent effect of stereotypes hampers authentic interpersonal connections and perpetuates social inequalities.
How Prejudices Shape Social Dynamics
Prejudices create rigid biases that influence group interactions and reinforce social hierarchies, limiting opportunities for marginalized communities. These preconceived negative judgments contribute to discrimination, impacting employment, education, and social inclusion. Persistent prejudices distort social perceptions, fostering division and obstructing social cohesion and equity.
The Role of Media in Reinforcing Social Labels
Media plays a critical role in reinforcing social labels by consistently portraying stereotypes that shape public perception and attitudes. Through repetitive imagery and narratives, media outlets often link specific groups to particular traits, which solidifies prejudiced beliefs and hinders social cohesion. This cycle of representation perpetuates societal divisions and influences discriminatory behavior on a broad scale.
Challenging Stereotypes and Overcoming Prejudice
Challenging stereotypes requires recognizing their oversimplified assumptions and actively seeking diverse perspectives to dismantle biased narratives. Overcoming prejudice involves fostering empathy through meaningful interactions and education that highlight individual experiences beyond generalized beliefs. Promoting awareness and inclusive dialogue creates environments where stereotypes lose influence and equitable social attitudes flourish.
Stereotypes, Prejudice, and Social Identity
Stereotypes are generalized beliefs about a group that influence social identity by categorizing individuals based on perceived traits, often leading to rigid assumptions. These mental shortcuts shape how people interpret social information and reinforce in-group favoritism while marginalizing out-groups. Prejudice stems from these stereotypes, producing negative attitudes that affect social interactions and group dynamics, impacting social cohesion and identity formation.
Strategies for Promoting Social Inclusion and Equity
Implementing education programs that increase awareness about the harmful effects of stereotypes and prejudice fosters empathy and reduces social biases. Creating inclusive policies that promote equal access to resources and opportunities helps dismantle systemic inequalities and supports marginalized communities. Encouraging diverse representation in media, workplaces, and institutions strengthens social cohesion and challenges ingrained discriminatory attitudes.
stereotype vs prejudice Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com