Social influence involves the subtle, often unconscious changes in an individual's behavior or attitudes due to the presence or actions of others, shaping decisions through conformity and social norms. Social persuasion, on the other hand, is a deliberate attempt to change someone's beliefs or behaviors by presenting arguments, appeals, or emotional triggers. Understanding the distinction between these mechanisms is crucial for effectively engaging audiences in social pet communities and driving positive behavioral change.
Table of Comparison
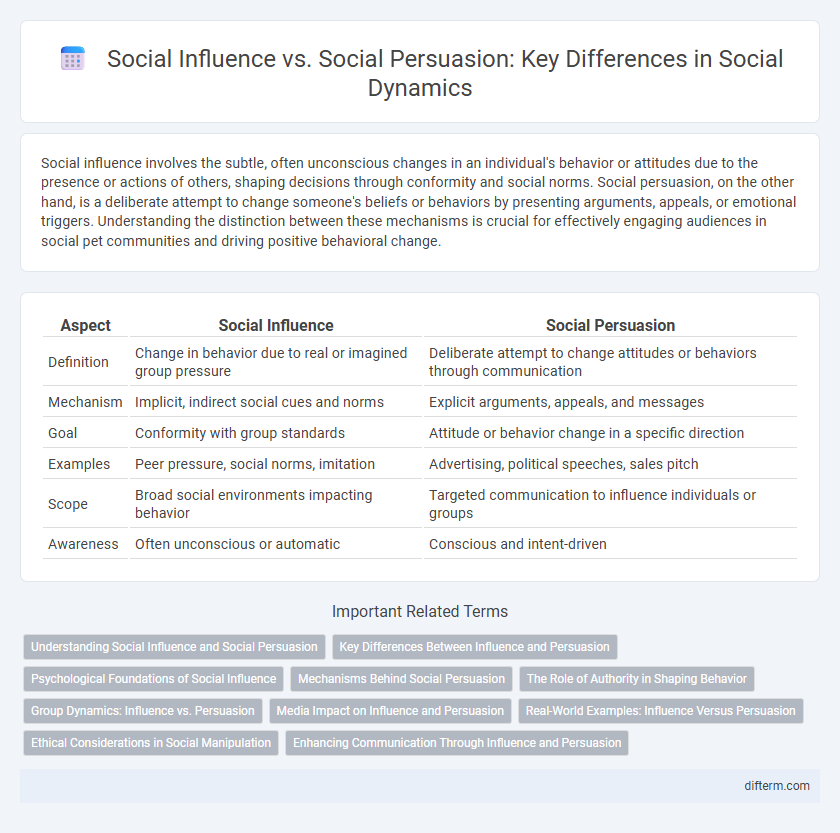
| Aspect | Social Influence | Social Persuasion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Change in behavior due to real or imagined group pressure | Deliberate attempt to change attitudes or behaviors through communication |
| Mechanism | Implicit, indirect social cues and norms | Explicit arguments, appeals, and messages |
| Goal | Conformity with group standards | Attitude or behavior change in a specific direction |
| Examples | Peer pressure, social norms, imitation | Advertising, political speeches, sales pitch |
| Scope | Broad social environments impacting behavior | Targeted communication to influence individuals or groups |
| Awareness | Often unconscious or automatic | Conscious and intent-driven |
Understanding Social Influence and Social Persuasion
Social influence involves the ways individuals change their behavior to meet group norms or expectations, encompassing conformity, compliance, and obedience. Social persuasion specifically targets changing attitudes or behaviors through communication techniques such as appeals, messaging strategies, and rhetoric. Understanding both concepts reveals the mechanisms behind group dynamics and decision-making processes in social environments.
Key Differences Between Influence and Persuasion
Social influence involves the subtle, often unconscious effects that others have on an individual's attitudes, beliefs, or behaviors through social norms, modeling, or conformity. Social persuasion is a deliberate, strategic effort to change a person's attitudes or behavior using communication techniques such as argumentation, appeals, or negotiation. Key differences include the intentionality behind persuasion versus the more automatic nature of influence, and persuasion's reliance on explicit messaging compared to influence's more implicit social cues.
Psychological Foundations of Social Influence
Social influence is rooted in the psychological foundations of group dynamics, conformity, and normative social behavior, where individuals adapt their actions to align with group expectations. Social persuasion relies on cognitive processes like attitude change, motivation, and credibility of the source, leveraging techniques such as reciprocity, authority, and social proof. Understanding these mechanisms reveals how social influence shapes behavior passively through implicit social norms, while social persuasion actively targets belief systems to modify attitudes and decisions.
Mechanisms Behind Social Persuasion
Social persuasion operates through mechanisms such as emotional appeal, social proof, and authority, which influence individuals by leveraging cognitive biases and trust in credible sources. These processes activate neural pathways linked to decision-making, enhancing message acceptance and behavioral change. In contrast to general social influence, persuasion specifically targets attitude modification through strategic communication tactics and psychological triggers.
The Role of Authority in Shaping Behavior
Authority significantly shapes social behavior by leveraging perceived expertise and power to influence decision-making and actions. Social influence often operates through normative pressures and conformity, while social persuasion strategically employs authoritative appeals to establish credibility and trust. Understanding the distinct impact of authority within these mechanisms enhances effective communication and behavioral change strategies.
Group Dynamics: Influence vs. Persuasion
Group dynamics shape social influence by promoting conformity and normative behavior through implicit social pressures within cohesive groups. Social persuasion relies on explicit communication techniques, appealing to emotions and logic to change group members' attitudes or decisions. Understanding the distinction between influence as passive alignment and persuasion as active convincing is essential for effective group leadership and decision-making.
Media Impact on Influence and Persuasion
Media channels shape social influence by amplifying norms and behaviors through widespread exposure, enhancing conformity within peer networks. Social persuasion is strategically driven by targeted messaging in digital platforms, utilizing emotional appeals and credibility cues to modify attitudes and decision-making. The pervasive role of social media algorithms intensifies both influence and persuasion by curating content that reinforces existing beliefs and prompts behavioral change.
Real-World Examples: Influence Versus Persuasion
Social influence often manifests in subtle, pervasive ways such as peer pressure encouraging teenagers to adopt fashion trends without explicit requests, whereas social persuasion involves direct communication tactics like a political candidate delivering compelling speeches to sway voter opinions. For instance, viral social media challenges leverage influence by creating a bandwagon effect, while persuasive advertisements use targeted messages and emotional appeals to drive consumer behavior. These real-world examples highlight that social influence operates through implicit social norms and behaviors, whereas social persuasion relies on intentional, strategic efforts to change attitudes or actions.
Ethical Considerations in Social Manipulation
Social influence leverages subtle cues and social norms to shape behavior without overt coercion, emphasizing respect for autonomy and informed consent. Social persuasion involves deliberate communication strategies aimed at changing attitudes or behaviors, requiring transparency to avoid deception and manipulation. Ethical considerations prioritize protecting individuals from exploitation, maintaining trust, and ensuring that influence or persuasion aligns with moral standards and respects personal agency.
Enhancing Communication Through Influence and Persuasion
Social influence shapes attitudes and behaviors through subtle cues and group dynamics, while social persuasion involves deliberate strategies to change opinions and motivate actions. Enhancing communication relies on understanding the psychological principles behind both processes, such as reciprocity, social proof, and authority, to effectively engage and inspire audiences. Mastering these techniques improves interpersonal connections and drives meaningful social change in communities and organizations.
social influence vs social persuasion Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com