Social pet platforms foster social change by encouraging diverse interactions and reshaping traditional pet ownership dynamics. They challenge social stability by creating new communities that blur the lines between virtual and real-world relationships. These shifts promote inclusivity while simultaneously prompting adaptations in long-established social norms.
Table of Comparison
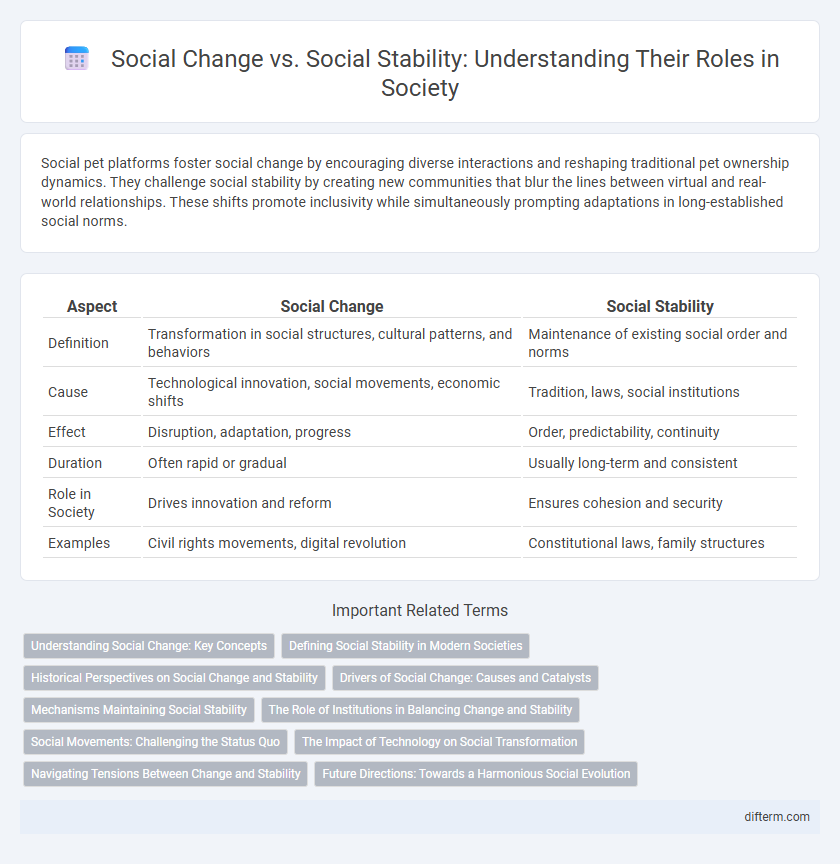
| Aspect | Social Change | Social Stability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transformation in social structures, cultural patterns, and behaviors | Maintenance of existing social order and norms |
| Cause | Technological innovation, social movements, economic shifts | Tradition, laws, social institutions |
| Effect | Disruption, adaptation, progress | Order, predictability, continuity |
| Duration | Often rapid or gradual | Usually long-term and consistent |
| Role in Society | Drives innovation and reform | Ensures cohesion and security |
| Examples | Civil rights movements, digital revolution | Constitutional laws, family structures |
Understanding Social Change: Key Concepts
Social change refers to significant shifts in societal structures, values, and cultural norms, driven by factors such as technological innovation, economic development, and social movements. Social stability emphasizes the maintenance of established social order, institutions, and traditions that provide continuity and predictability in society. Understanding social change requires analyzing the dynamic tension between forces promoting transformation and those resisting disruption to sustain equilibrium.
Defining Social Stability in Modern Societies
Social stability in modern societies refers to the consistent functioning of social institutions, norms, and roles that maintain order and predictability within communities. It ensures the continuity of cultural values, legal frameworks, and economic systems, preventing abrupt disruptions that could lead to chaos or conflict. Stable societies foster trust, cooperation, and social cohesion, enabling sustainable development and collective well-being amidst ongoing changes.
Historical Perspectives on Social Change and Stability
Historical perspectives on social change and stability highlight the dynamic interplay between transformative movements and enduring institutions. The Industrial Revolution exemplifies rapid social change through technological innovation, reshaping economic and social structures, while traditional agrarian societies demonstrate social stability with established customs and hierarchies. Sociologists like Emile Durkheim emphasize the importance of social cohesion for stability, whereas Karl Marx's theories focus on conflict-driven social change rooted in class struggles.
Drivers of Social Change: Causes and Catalysts
Technological advancements, economic shifts, and cultural exchanges serve as primary drivers of social change by altering how societies function and interact. Social movements and political reforms act as catalysts, accelerating transformations in norms, values, and institutions. Environmental factors and demographic trends also influence social stability, either reinforcing existing structures or prompting adaptation.
Mechanisms Maintaining Social Stability
Social stability is maintained through mechanisms such as social norms, institutions, and law enforcement that reinforce predictable behavior and collective order. Cultural traditions and shared values promote social cohesion by encouraging conformity and reducing conflicts. Socialization processes within families and educational systems transmit these norms, ensuring continuity across generations.
The Role of Institutions in Balancing Change and Stability
Institutions such as governments, educational systems, and legal frameworks play a crucial role in balancing social change and stability by providing structured mechanisms for adaptation and continuity. These entities mediate societal transformations through policy reforms, social norms enforcement, and conflict resolution, ensuring that change occurs without disrupting social order. Effective institutional functioning fosters resilience, allowing societies to evolve while maintaining core values and cohesion.
Social Movements: Challenging the Status Quo
Social movements play a crucial role in challenging the status quo by mobilizing collective action to address social inequalities and demand systemic reforms. These movements disrupt social stability to create awareness, influence policy, and shift cultural norms, often leading to significant societal transformation. The dynamic tension between social change and social stability highlights the persistent negotiation between innovation and preservation within societies.
The Impact of Technology on Social Transformation
Technology accelerates social transformation by enabling rapid communication, access to information, and new forms of social interaction, thereby challenging traditional social structures. Digital platforms foster social mobilization and activism, reshaping cultural norms and power dynamics across global communities. Despite its disruptive potential, technology also supports social stability by facilitating economic growth, education, and governance through enhanced connectivity.
Navigating Tensions Between Change and Stability
Navigating tensions between social change and social stability requires balancing innovation with tradition to maintain societal cohesion. Social change drives progress through movements, technological advancements, and shifting cultural norms, while social stability preserves institutions, legal frameworks, and shared values that sustain order. Understanding this dynamic interplay enables policymakers and communities to foster inclusive development without triggering social disruption.
Future Directions: Towards a Harmonious Social Evolution
Societies must balance social change and social stability to achieve harmonious social evolution, fostering adaptive policies that respond to emerging technological and environmental challenges. Emphasizing inclusive governance and community engagement promotes resilience and equitable progress. Future directions prioritize integrative frameworks that harmonize innovation with cultural preservation to sustain social cohesion.
social change vs social stability Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com