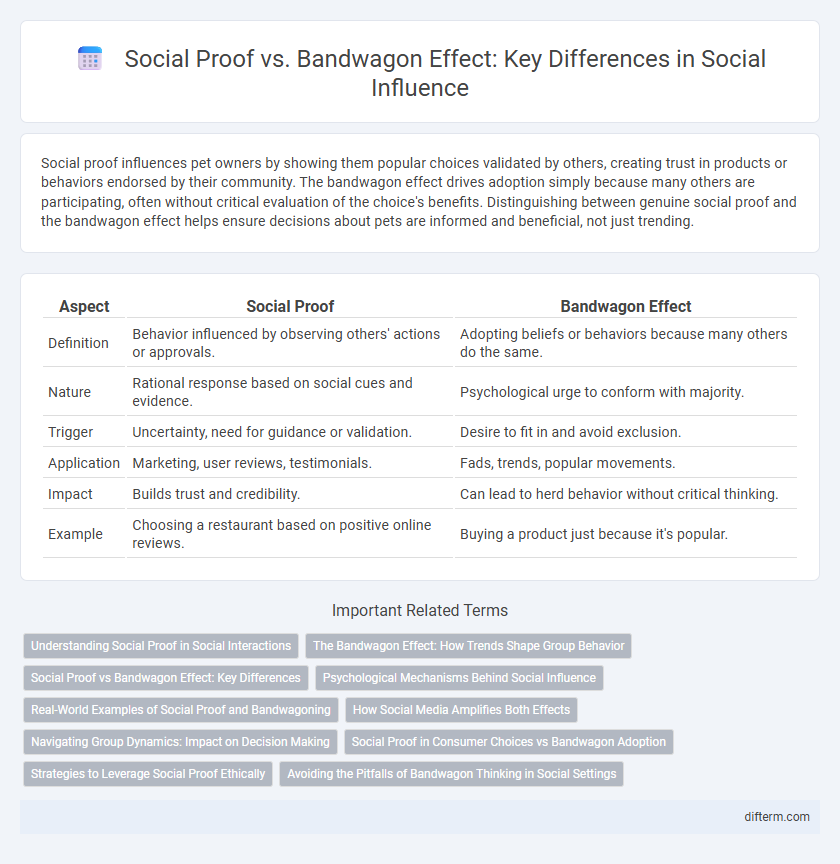
Social proof influences pet owners by showing them popular choices validated by others, creating trust in products or behaviors endorsed by their community. The bandwagon effect drives adoption simply because many others are participating, often without critical evaluation of the choice's benefits. Distinguishing between genuine social proof and the bandwagon effect helps ensure decisions about pets are informed and beneficial, not just trending.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Proof | Bandwagon Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Behavior influenced by observing others' actions or approvals. | Adopting beliefs or behaviors because many others do the same. |
| Nature | Rational response based on social cues and evidence. | Psychological urge to conform with majority. |
| Trigger | Uncertainty, need for guidance or validation. | Desire to fit in and avoid exclusion. |
| Application | Marketing, user reviews, testimonials. | Fads, trends, popular movements. |
| Impact | Builds trust and credibility. | Can lead to herd behavior without critical thinking. |
| Example | Choosing a restaurant based on positive online reviews. | Buying a product just because it's popular. |
Understanding Social Proof in Social Interactions
Social proof in social interactions occurs when individuals conform to the behaviors or opinions of others based on perceived credibility or expertise, enhancing trust and decision-making accuracy. Unlike the bandwagon effect, which involves following trends without critical evaluation, social proof relies on informed observation of social cues and context. Recognizing the difference improves awareness of influence dynamics in group behaviors and collective choices.
The Bandwagon Effect: How Trends Shape Group Behavior
The bandwagon effect drives individuals to adopt behaviors or beliefs primarily because others are doing so, amplifying the influence of popular trends within social groups. This phenomenon often results in rapid conformity as people seek social acceptance, regardless of their personal preferences. Unlike social proof, which relies on rational evaluation of others' actions, the bandwagon effect hinges more on emotional conformity and fear of exclusion.
Social Proof vs Bandwagon Effect: Key Differences
Social proof occurs when individuals imitate others' actions based on the belief that those actions are correct in a specific situation, leveraging perceived expertise or consensus. The bandwagon effect, in contrast, drives people to adopt behaviors or beliefs mainly because many others are doing so, emphasizing popularity over accuracy. Understanding these key differences highlights how social proof relies on informational influence while the bandwagon effect is rooted in normative influence.
Psychological Mechanisms Behind Social Influence
Social proof operates through informational social influence, where individuals conform because they believe others possess accurate knowledge, enhancing decision-making confidence. The bandwagon effect arises from normative social influence, driving conformity to gain social acceptance and avoid exclusion, regardless of the accuracy of others' behaviors. Both mechanisms leverage cognitive biases but differ in motivation: social proof seeks reliable information, while the bandwagon effect prioritizes social belonging.
Real-World Examples of Social Proof and Bandwagoning
Social proof is demonstrated when consumers rely on user reviews and ratings on platforms like Amazon or Yelp to make purchasing decisions, reflecting trust in collective experience. The bandwagon effect is evident in fashion trends, such as the rapid adoption of streetwear brands like Supreme, where the desire to fit in drives mass participation despite individual preferences. Both phenomena highlight the power of social influence, but social proof is grounded in credible evidence, whereas bandwagoning is fueled by perceived popularity independent of quality.
How Social Media Amplifies Both Effects
Social media platforms amplify social proof by enabling users to see real-time endorsements, likes, and shares, reinforcing trust in popular opinions or products. The bandwagon effect grows as viral trends and mass participation create perceived popularity, prompting others to join simply because many have already done so. Algorithms further intensify these effects by promoting content with high engagement, accelerating the spread of social validation and collective behavior.
Navigating Group Dynamics: Impact on Decision Making
Social proof influences decision making by signaling which behaviors or choices are deemed acceptable or successful within a group, often rooted in observed consensus or expert endorsement. The bandwagon effect drives individuals to adopt opinions or actions primarily because many others have done so, creating momentum that can amplify trends regardless of their intrinsic value. Understanding the subtle differences between social proof's informational guidance and the bandwagon effect's conformity pressure is crucial for effectively navigating group dynamics and making autonomous decisions.
Social Proof in Consumer Choices vs Bandwagon Adoption
Social proof influences consumer choices by encouraging individuals to follow behaviors demonstrated by others, especially when uncertainty exists. This psychological phenomenon relies on credible evidence from peers, reviews, and testimonials, enhancing trust and guiding purchasing decisions. In contrast, bandwagon adoption often stems from a desire to conform for social acceptance, regardless of the product's inherent value or quality.
Strategies to Leverage Social Proof Ethically
Leveraging social proof ethically involves showcasing genuine customer testimonials and verified reviews to build trust without manipulating perceptions. Transparent presentation of social validation, such as real-time user activity and authentic influencer endorsements, reinforces credibility while respecting consumer autonomy. Employing these strategies helps differentiate ethical social proof from the bandwagon effect, which often relies on herd mentality rather than truthful influence.
Avoiding the Pitfalls of Bandwagon Thinking in Social Settings
Bandwagon effect causes individuals to adopt behaviors or opinions primarily because others do, often leading to shallow consensus without critical evaluation. Social proof, when used effectively, provides genuine validation through credible sources and authentic experiences that guide informed decisions. Avoiding bandwagon thinking requires cultivating awareness of personal values and encouraging diverse perspectives to foster authentic social interactions.
social proof vs bandwagon effect Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com