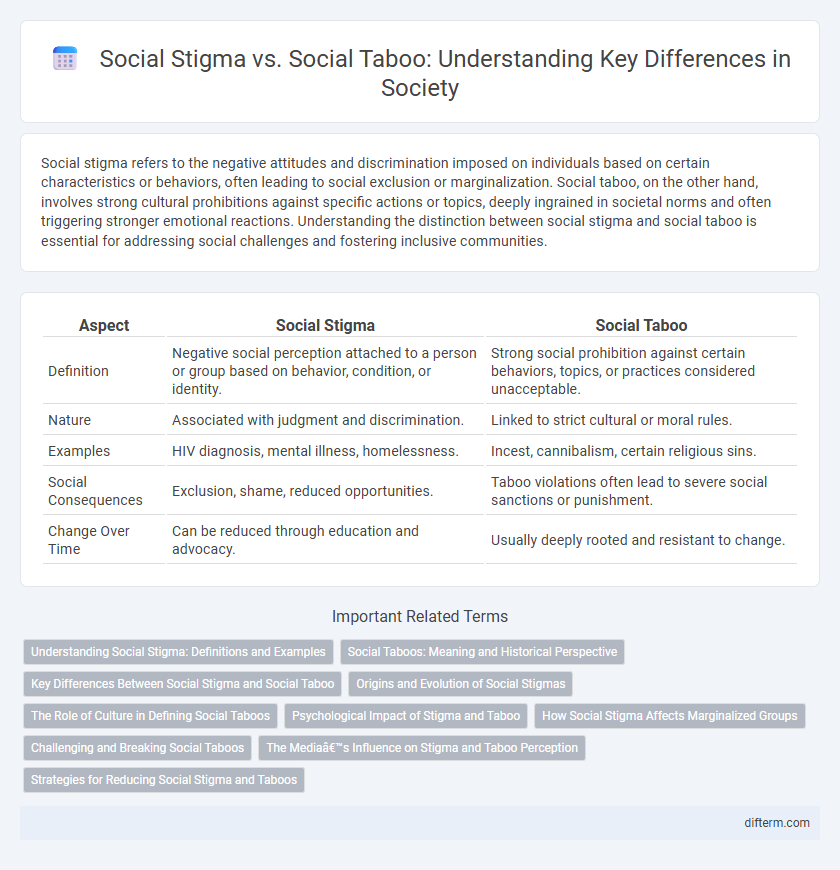
Social stigma refers to the negative attitudes and discrimination imposed on individuals based on certain characteristics or behaviors, often leading to social exclusion or marginalization. Social taboo, on the other hand, involves strong cultural prohibitions against specific actions or topics, deeply ingrained in societal norms and often triggering stronger emotional reactions. Understanding the distinction between social stigma and social taboo is essential for addressing social challenges and fostering inclusive communities.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Stigma | Social Taboo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Negative social perception attached to a person or group based on behavior, condition, or identity. | Strong social prohibition against certain behaviors, topics, or practices considered unacceptable. |
| Nature | Associated with judgment and discrimination. | Linked to strict cultural or moral rules. |
| Examples | HIV diagnosis, mental illness, homelessness. | Incest, cannibalism, certain religious sins. |
| Social Consequences | Exclusion, shame, reduced opportunities. | Taboo violations often lead to severe social sanctions or punishment. |
| Change Over Time | Can be reduced through education and advocacy. | Usually deeply rooted and resistant to change. |
Understanding Social Stigma: Definitions and Examples
Social stigma refers to the negative perception and discrimination directed toward individuals or groups based on characteristics such as race, mental health, or illness, often leading to exclusion and marginalization. Social taboo involves prohibitions against behaviors or topics considered morally or culturally unacceptable, such as discussing death openly or engaging in certain sexual practices. Understanding these concepts helps highlight how stigma affects personal identity and social interactions, while taboo shapes societal norms and boundaries.
Social Taboos: Meaning and Historical Perspective
Social taboos are deeply rooted prohibitions against behaviors or discussions considered sacred or forbidden within a culture, often enforced through implicit social sanctions. Historically, these taboos have shaped societal norms by delineating boundaries that preserve communal values, such as prohibitions on incest, cannibalism, or certain religious practices. Unlike social stigma, which attaches negative perceptions to individuals or groups, social taboos define collective moral constraints that are resistant to change over time.
Key Differences Between Social Stigma and Social Taboo
Social stigma refers to the negative perception and discrimination directed at individuals or groups based on characteristics perceived as deviant, often leading to social exclusion and shame. Social taboo involves deeply entrenched prohibitions against certain behaviors or topics, rooted in cultural or moral beliefs, and violating them can result in severe social rejection or punishment. Key differences include stigma targeting identity or behavior with a focus on social disapproval, whereas taboo enforces cultural norms by forbidding specific acts considered sacred or harmful.
Origins and Evolution of Social Stigmas
Social stigmas originate from deeply rooted cultural beliefs and historical prejudices that label certain traits or behaviors as undesirable, often evolving through repeated social reinforcement across generations. These stigmas develop as mechanisms to enforce conformity and maintain social hierarchies, frequently linked to identity markers such as race, gender, or socioeconomic status. Over time, social stigmas can solidify into institutionalized discrimination, whereas changing social values and increased awareness may gradually diminish their influence.
The Role of Culture in Defining Social Taboos
Culture profoundly shapes social taboos by establishing collective norms that dictate forbidden behaviors and beliefs unique to each society. These taboos often reflect deep-rooted values, religious doctrines, and historical experiences that communities strive to preserve. Understanding cultural contexts is essential for interpreting why certain actions are deemed unacceptable and how social cohesion is maintained through these prohibitions.
Psychological Impact of Stigma and Taboo
Social stigma triggers feelings of shame, isolation, and low self-esteem, significantly affecting mental health by fostering anxiety and depression. Social taboos, tied to deeply ingrained cultural norms, create intense fear of social rejection and harsh internalized guilt, often leading to psychological distress. Both stigma and taboo interfere with open communication, hindering emotional support and access to mental health resources.
How Social Stigma Affects Marginalized Groups
Social stigma imposes negative stereotypes and discrimination on marginalized groups, limiting their access to resources, opportunities, and social acceptance. This exclusion exacerbates inequalities in health, education, and employment, creating systemic barriers that hinder social mobility. Persistent stigmatization fosters internalized shame and social isolation, significantly impacting the mental well-being of affected individuals.
Challenging and Breaking Social Taboos
Challenging and breaking social taboos requires confronting deeply ingrained cultural beliefs that often dictate unacceptable behaviors or topics, such as those related to sexuality, mental health, or death. Activists and educators play a critical role in raising awareness and fostering open dialogue to dismantle these prohibitions, reducing fear and misinformation. Overcoming social taboos can lead to greater social acceptance, inclusivity, and mental well-being across diverse communities.
The Media’s Influence on Stigma and Taboo Perception
The media plays a pivotal role in shaping public perception of social stigma and taboo by framing certain behaviors and identities as deviant or unacceptable. News outlets and entertainment platforms often reinforce stereotypes, contributing to the persistence of stigma surrounding mental health, LGBTQ+ issues, and marginalized communities. By selectively highlighting or ignoring specific topics, the media influences societal norms and either perpetuates or challenges existing social taboos.
Strategies for Reducing Social Stigma and Taboos
Effective strategies for reducing social stigma and taboos involve education campaigns that promote awareness and empathy towards marginalized groups. Community engagement initiatives foster open dialogue, challenging misconceptions and encouraging inclusive attitudes. Policy reforms ensuring equal rights and anti-discrimination laws further dismantle systemic barriers that perpetuate stigma and taboo.
social stigma vs social taboo Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com