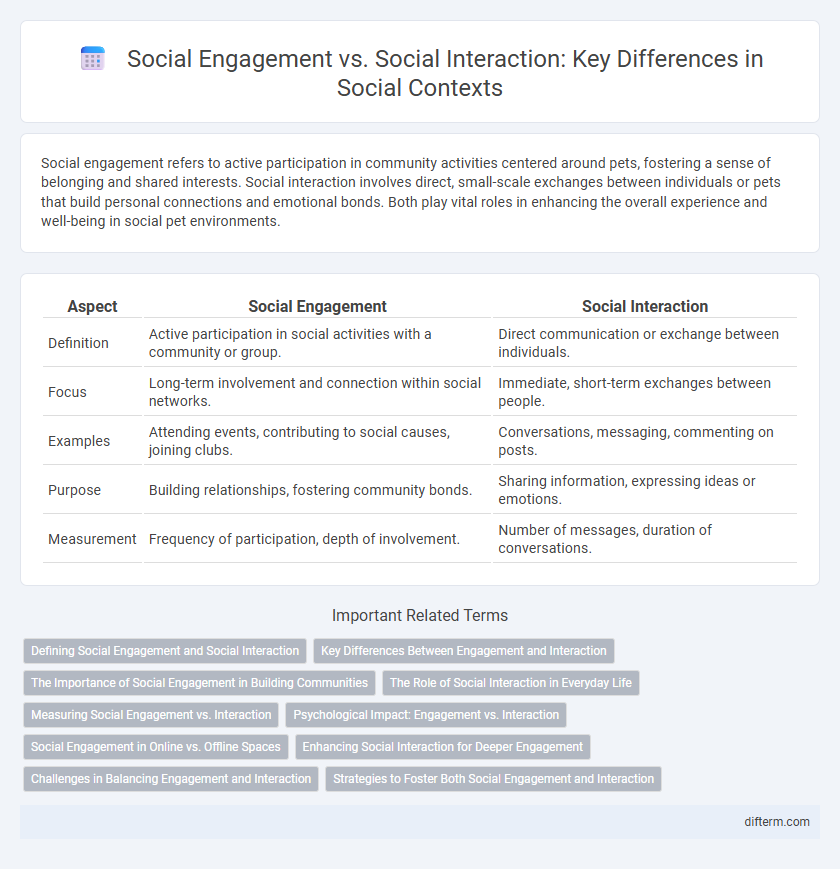
Social engagement refers to active participation in community activities centered around pets, fostering a sense of belonging and shared interests. Social interaction involves direct, small-scale exchanges between individuals or pets that build personal connections and emotional bonds. Both play vital roles in enhancing the overall experience and well-being in social pet environments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Engagement | Social Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active participation in social activities with a community or group. | Direct communication or exchange between individuals. |
| Focus | Long-term involvement and connection within social networks. | Immediate, short-term exchanges between people. |
| Examples | Attending events, contributing to social causes, joining clubs. | Conversations, messaging, commenting on posts. |
| Purpose | Building relationships, fostering community bonds. | Sharing information, expressing ideas or emotions. |
| Measurement | Frequency of participation, depth of involvement. | Number of messages, duration of conversations. |
Defining Social Engagement and Social Interaction
Social engagement refers to the active participation and involvement in community activities, fostering deeper connections and a sense of belonging within a social group. Social interaction involves the exchange of communication and behaviors between individuals, often occurring in spontaneous or casual settings. Understanding the distinction is crucial for developing strategies that enhance community cohesion and interpersonal relationships.
Key Differences Between Engagement and Interaction
Social engagement involves sustained participation and emotional investment in activities or communities, reflecting commitment and ongoing involvement. Social interaction refers to the immediate exchange of information, communication, or behaviors between individuals or groups in real-time contexts. Key differences lie in engagement's depth and duration versus interaction's immediacy and frequency.
The Importance of Social Engagement in Building Communities
Social engagement drives meaningful participation within communities, fostering shared goals and collective action that strengthen social cohesion. Unlike casual social interaction, social engagement involves active contribution to community development, enhancing trust and mutual support among members. Robust social engagement improves community resilience and promotes a sense of belonging essential for sustainable societal growth.
The Role of Social Interaction in Everyday Life
Social interaction forms the foundation of social engagement by facilitating meaningful connections and shared experiences that enhance community cohesion. Everyday social interactions contribute to emotional well-being, improve communication skills, and foster a sense of belonging. Understanding these interactions helps in designing environments and policies that promote positive social engagement and mental health.
Measuring Social Engagement vs. Interaction
Measuring social engagement involves quantifying user actions such as likes, shares, and comments to assess content impact and audience investment. Social interaction metrics focus on real-time conversations and reciprocal communication patterns, revealing the depth of user relationships. Effective analysis combines engagement rates with interaction quality to provide a comprehensive understanding of social behavior dynamics.
Psychological Impact: Engagement vs. Interaction
Social engagement, characterized by sustained and meaningful involvement in community activities, significantly enhances psychological well-being by fostering a sense of belonging and purpose. In contrast, social interaction, often brief and superficial, offers limited emotional support and may not contribute deeply to mental health. Research indicates that higher levels of social engagement correlate with reduced stress, lower depression rates, and improved cognitive functioning.
Social Engagement in Online vs. Offline Spaces
Social engagement in online spaces enables broader participation through digital platforms, enhancing community building and real-time collaboration across diverse demographics. Offline social engagement fosters deeper emotional connections and trust through face-to-face interactions, critical for sustaining long-term relationships and local networks. Balancing online and offline social engagement maximizes both reach and relational depth, leveraging technology while maintaining authentic human connections.
Enhancing Social Interaction for Deeper Engagement
Enhancing social interaction through meaningful conversations and active listening significantly boosts social engagement by fostering genuine connections and trust among participants. Utilizing interactive platforms and real-time communication tools encourages participation, making interactions more dynamic and impactful. Prioritizing quality over quantity in social exchanges leads to deeper emotional involvement and sustained community growth.
Challenges in Balancing Engagement and Interaction
Balancing social engagement and social interaction presents challenges such as maintaining genuine connections without overwhelming participants or causing engagement fatigue. Digital platforms often amplify interaction volume but can dilute the quality of engagement, leading to superficial relationships. Effective strategies must prioritize meaningful interactions while managing the quantity and intensity of social participation to foster sustained community involvement.
Strategies to Foster Both Social Engagement and Interaction
Effective strategies to foster social engagement and interaction include creating inclusive environments that encourage active participation through group activities and collaborative projects. Leveraging digital platforms to facilitate meaningful connections and real-time communication enhances interaction while maintaining consistent feedback loops to motivate continued social involvement. Implementing structured programs like peer mentoring and community events supports sustained engagement by building trust and shared purpose among participants.
social engagement vs social interaction Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com