Social exclusion occurs when individuals are ignored or excluded by a group, leading to feelings of isolation without explicit negative judgment. Social rejection involves active disapproval or dismissal, causing more intense emotional pain and damage to self-esteem. Understanding the nuances between these concepts helps in addressing the psychological impact on pets and improving their social well-being.
Table of Comparison
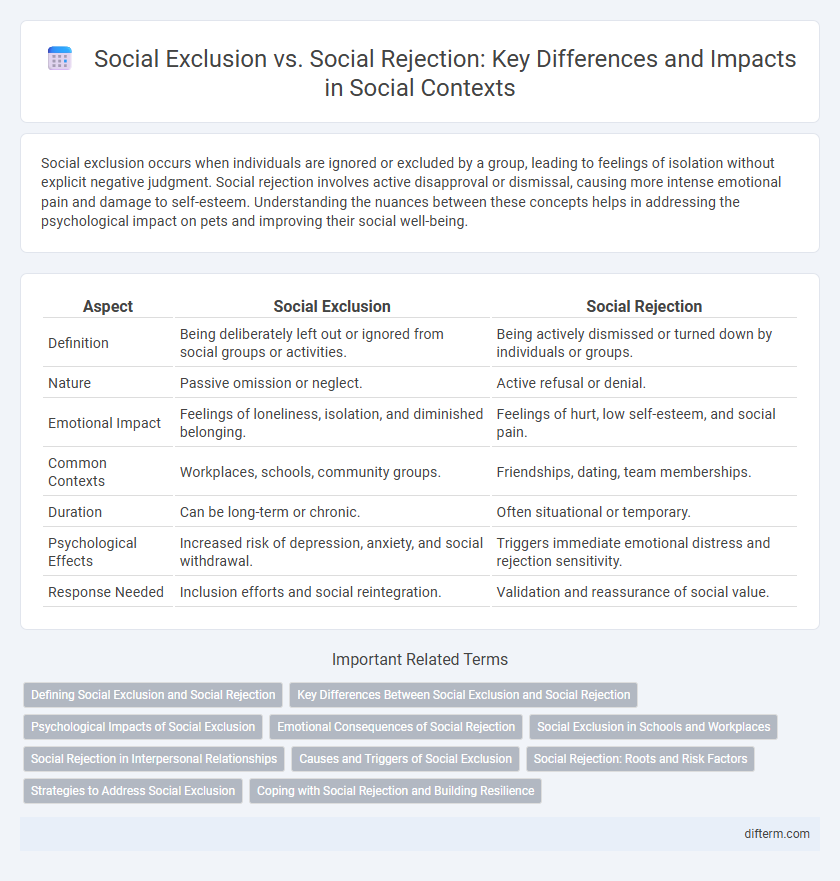
| Aspect | Social Exclusion | Social Rejection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Being deliberately left out or ignored from social groups or activities. | Being actively dismissed or turned down by individuals or groups. |
| Nature | Passive omission or neglect. | Active refusal or denial. |
| Emotional Impact | Feelings of loneliness, isolation, and diminished belonging. | Feelings of hurt, low self-esteem, and social pain. |
| Common Contexts | Workplaces, schools, community groups. | Friendships, dating, team memberships. |
| Duration | Can be long-term or chronic. | Often situational or temporary. |
| Psychological Effects | Increased risk of depression, anxiety, and social withdrawal. | Triggers immediate emotional distress and rejection sensitivity. |
| Response Needed | Inclusion efforts and social reintegration. | Validation and reassurance of social value. |
Defining Social Exclusion and Social Rejection
Social exclusion refers to the systemic process by which individuals or groups are marginalized from social, economic, political, and cultural participation, leading to limited access to resources and opportunities. Social rejection, on the other hand, is an interpersonal phenomenon where an individual is deliberately dismissed or ignored by others within a social context, often resulting in feelings of isolation and diminished self-worth. Both concepts significantly impact mental health and societal cohesion but operate at different levels of social interaction.
Key Differences Between Social Exclusion and Social Rejection
Social exclusion involves the systematic process of denying individuals or groups access to resources, rights, and social participation, often leading to isolation and marginalization. Social rejection, on the other hand, refers to individual or group responses where a person is actively dismissed or ignored during social interactions, affecting emotional well-being. Key differences include the broader, structural nature of social exclusion versus the immediate, interpersonal dynamics of social rejection.
Psychological Impacts of Social Exclusion
Social exclusion triggers significant psychological impacts, including heightened anxiety, depression, and feelings of loneliness, which stem from the innate human need for belonging. Neuroimaging studies reveal that social exclusion activates brain regions associated with physical pain, such as the anterior cingulate cortex, underscoring its profound emotional toll. Prolonged exclusion can impair self-esteem and cognitive function, increasing vulnerability to mental health disorders and impairing social interactions.
Emotional Consequences of Social Rejection
Social rejection often leads to profound emotional consequences such as increased feelings of loneliness, decreased self-esteem, and heightened anxiety. These emotional responses can trigger stress-related physiological changes and contribute to long-term mental health issues like depression. Unlike social exclusion, which involves being left out or ignored, social rejection explicitly communicates personal disapproval, intensifying its impact on emotional well-being.
Social Exclusion in Schools and Workplaces
Social exclusion in schools and workplaces often manifests as isolation from group activities, limited access to resources, and persistent marginalization, severely impacting individuals' mental health and productivity. This form of exclusion differs from social rejection by being more systemic and indirect, embedded in policies or group dynamics rather than overt actions. Addressing social exclusion requires targeted interventions to promote inclusivity, equitable participation, and supportive environments, fostering well-being and collaboration.
Social Rejection in Interpersonal Relationships
Social rejection in interpersonal relationships occurs when individuals are deliberately excluded or dismissed by others, leading to feelings of humiliation, loneliness, and decreased self-esteem. Unlike social exclusion, which is often passive and unintentional, social rejection involves active negative judgment or criticism targeted at specific behaviors or traits. This form of rejection impacts emotional regulation and can increase vulnerability to mental health issues such as anxiety and depression.
Causes and Triggers of Social Exclusion
Social exclusion often stems from systemic inequalities such as poverty, discrimination, and lack of access to education or employment opportunities, reinforcing marginalization within communities. Triggered by factors like cultural differences, stigmatization, and social stereotypes, exclusion intensifies when individuals or groups deviate from perceived social norms. These causes create barriers to participation, resulting in diminished social support networks and increased feelings of isolation.
Social Rejection: Roots and Risk Factors
Social rejection stems from perceived violations of social norms, differences in values, or lack of social skills, triggering exclusion by peers and communities. Key risk factors include low self-esteem, previous experiences of rejection, and social anxiety, which intensify the negative impact and hinder social integration. Neurobiological responses to rejection activate brain regions linked to physical pain, emphasizing its profound emotional and psychological effects.
Strategies to Address Social Exclusion
Combating social exclusion requires implementing inclusive policies that promote equal access to education, employment, and healthcare services for marginalized groups. Community engagement initiatives foster social cohesion by encouraging interaction and shared activities among diverse populations. Support programs offering counseling and skill-building workshops empower individuals to overcome barriers and actively participate in society.
Coping with Social Rejection and Building Resilience
Coping with social rejection involves developing emotional regulation strategies and seeking supportive social networks to mitigate feelings of isolation and maintain mental well-being. Building resilience requires consistent practice of self-compassion, cognitive reframing to challenge negative beliefs, and engagement in activities fostering a sense of belonging and purpose. Research highlights that individuals with strong resilience exhibit lower cortisol levels and reduced risk of depression following experiences of social exclusion or rejection.
social exclusion vs social rejection Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com