Social policy focuses on addressing the needs and well-being of individuals and communities by implementing programs related to health, education, and welfare. Public policy encompasses a broader scope, including social policy but also covering economic, environmental, and governance issues set by government authorities. Understanding the distinction helps in analyzing how specific social objectives are integrated within wider governmental strategies.
Table of Comparison
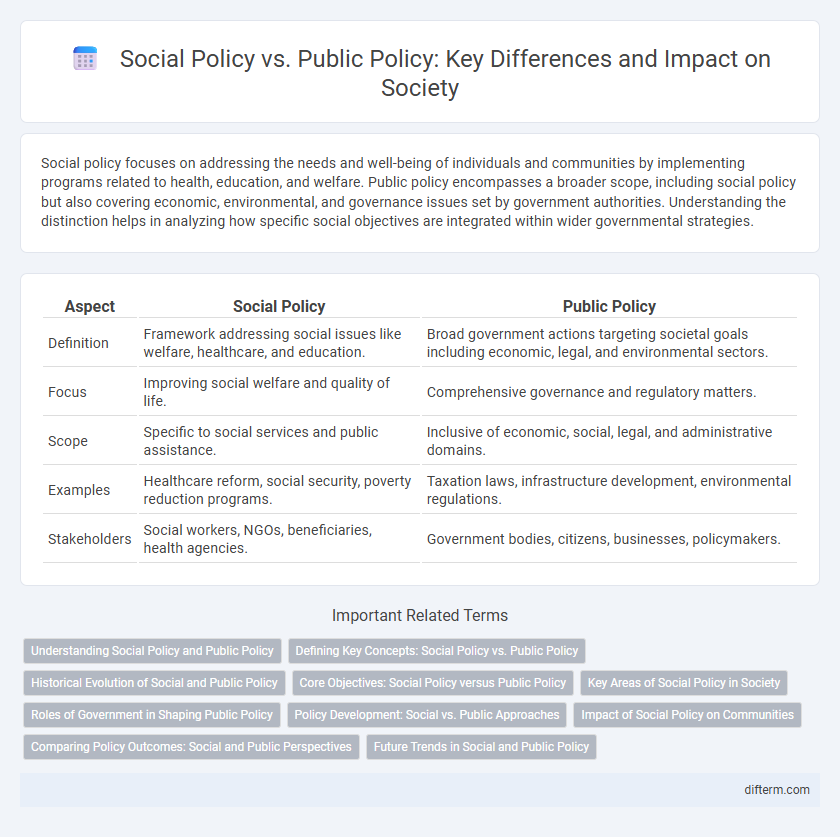
| Aspect | Social Policy | Public Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Framework addressing social issues like welfare, healthcare, and education. | Broad government actions targeting societal goals including economic, legal, and environmental sectors. |
| Focus | Improving social welfare and quality of life. | Comprehensive governance and regulatory matters. |
| Scope | Specific to social services and public assistance. | Inclusive of economic, social, legal, and administrative domains. |
| Examples | Healthcare reform, social security, poverty reduction programs. | Taxation laws, infrastructure development, environmental regulations. |
| Stakeholders | Social workers, NGOs, beneficiaries, health agencies. | Government bodies, citizens, businesses, policymakers. |
Understanding Social Policy and Public Policy
Social policy focuses on welfare, equity, and the provision of services to improve societal well-being, addressing issues like healthcare, education, and housing. Public policy encompasses a broader spectrum, including economic, environmental, and regulatory frameworks designed by governments to manage public resources and societal behavior. Understanding the distinctions and interactions between social policy and public policy is essential for developing comprehensive strategies that promote social justice and effective governance.
Defining Key Concepts: Social Policy vs. Public Policy
Social policy specifically addresses issues related to welfare, health, education, and social services aimed at improving individual and community well-being. Public policy encompasses a broader range of governmental decisions and actions, including economic, environmental, and regulatory measures beyond social welfare. Understanding the distinction is crucial for targeted policy-making and effective allocation of resources within social and governmental sectors.
Historical Evolution of Social and Public Policy
Social policy emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as a response to industrialization's impact on labor and welfare, focusing on issues such as poverty, health, and education. Public policy developed alongside, encompassing a broader range of governmental actions beyond social welfare, including economic regulation, defense, and infrastructure. The historical evolution shows social policy gradually becoming a specialized subset within the larger framework of public policy, reflecting changing societal priorities and governance structures.
Core Objectives: Social Policy versus Public Policy
Social policy primarily focuses on improving individual well-being and promoting social equity through programs like healthcare, education, and welfare support. Public policy encompasses broader governmental strategies aimed at regulating economic activities, infrastructure, and national security alongside social interventions. Core objectives of social policy are human-centric, targeting poverty alleviation and social justice, whereas public policy emphasizes systemic governance and public resource management.
Key Areas of Social Policy in Society
Key areas of social policy in society include healthcare, education, social welfare, and housing, targeting improvements in quality of life and social equity. Social policy focuses on addressing societal needs such as poverty alleviation, unemployment support, and social inclusion, differing from public policy's broader scope that encompasses economic and environmental regulations. Effective social policy design involves coordination between government agencies and non-profit organizations to implement programs that promote social justice and protect vulnerable populations.
Roles of Government in Shaping Public Policy
Government plays a critical role in shaping public policy by establishing regulatory frameworks that address economic, social, and environmental issues. In social policy, the government targets specific societal needs such as healthcare, education, and welfare programs to promote social equity and improve quality of life. Public policy encompasses a broader scope, integrating multiple sectors and stakeholder interests to ensure sustainable development and national security.
Policy Development: Social vs. Public Approaches
Social policy development primarily addresses welfare, health, education, and income distribution to improve individual and community well-being. Public policy development encompasses a broader scope, including economic regulation, national security, and environmental protection, balancing diverse societal needs and governmental objectives. Both approaches rely on evidence-based research and stakeholder engagement to formulate effective, sustainable solutions for social challenges.
Impact of Social Policy on Communities
Social policy directly targets the welfare and development of communities by addressing issues such as education, healthcare, housing, and social justice. Its impact manifests in reduced poverty rates, improved quality of life, and enhanced social cohesion among diverse populations. Effective social policies foster inclusive growth and empower marginalized groups, leading to stronger, more resilient communities.
Comparing Policy Outcomes: Social and Public Perspectives
Social policy primarily targets improving individual and community welfare through programs addressing health, education, and social security, while public policy encompasses broader government actions influencing economic, environmental, and regulatory frameworks. Outcome comparisons reveal that social policy often yields direct, measurable benefits in quality of life and social equity, whereas public policy outcomes may affect systemic change and long-term societal stability. Evaluating both perspectives highlights the importance of integrating targeted social interventions within comprehensive public governance to optimize overall policy effectiveness.
Future Trends in Social and Public Policy
Future trends in social and public policy emphasize integrating technology and data analytics to enhance decision-making and service delivery. Increasing focus on equity and inclusivity drives the development of policies that address systemic inequalities and promote social justice. Collaborative governance models involving multiple stakeholders are expected to shape more adaptive and responsive policy frameworks.
social policy vs public policy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com