Social pets play a significant role in cultural diffusion by fostering shared experiences and mutual respect across diverse communities. They can bridge cultural gaps through interactions that celebrate traditions without exploiting or misrepresenting them. Careful attention ensures these exchanges honor the origins of cultural practices while promoting inclusivity and understanding.
Table of Comparison
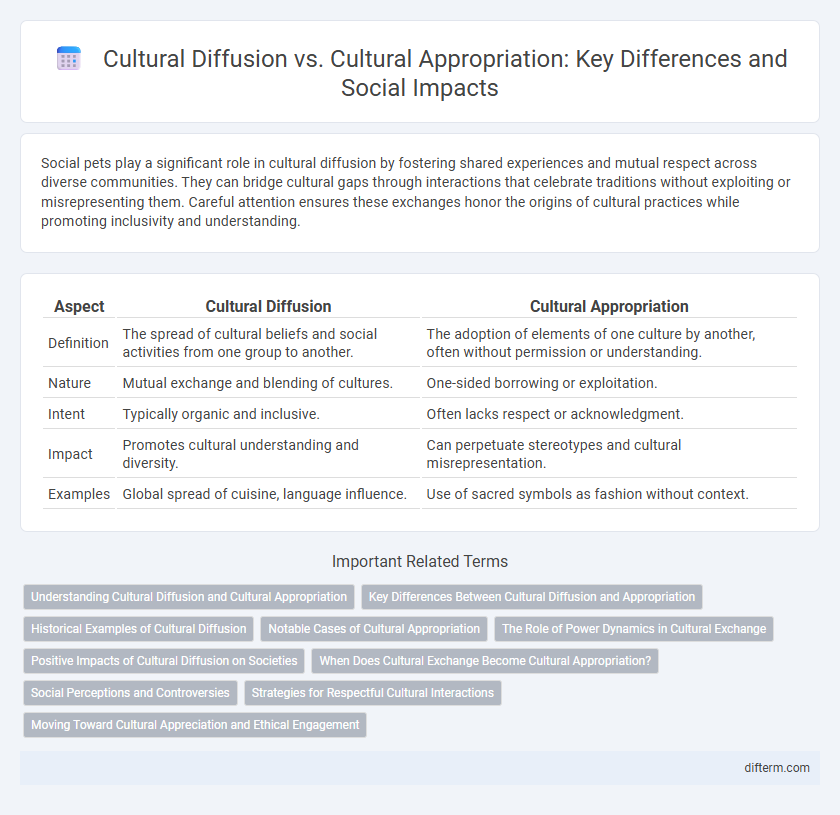
| Aspect | Cultural Diffusion | Cultural Appropriation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The spread of cultural beliefs and social activities from one group to another. | The adoption of elements of one culture by another, often without permission or understanding. |
| Nature | Mutual exchange and blending of cultures. | One-sided borrowing or exploitation. |
| Intent | Typically organic and inclusive. | Often lacks respect or acknowledgment. |
| Impact | Promotes cultural understanding and diversity. | Can perpetuate stereotypes and cultural misrepresentation. |
| Examples | Global spread of cuisine, language influence. | Use of sacred symbols as fashion without context. |
Understanding Cultural Diffusion and Cultural Appropriation
Cultural diffusion refers to the natural spread of cultural elements such as language, customs, and technology between societies through trade, migration, or communication, fostering mutual enrichment and innovation. Cultural appropriation involves adopting elements of a marginalized culture without understanding or respecting its significance, often leading to misrepresentation and perpetuation of stereotypes. Understanding the distinction is crucial for promoting cultural exchange that honors origins while preventing exploitation or disrespect.
Key Differences Between Cultural Diffusion and Appropriation
Cultural diffusion involves the natural sharing and blending of cultural elements such as language, art, and customs through trade, migration, or communication, promoting mutual respect and understanding. Cultural appropriation occurs when dominant groups adopt elements of marginalized cultures without permission, often stripping the original meaning and causing harm or disrespect. The key difference lies in intention and power dynamics: diffusion fosters exchange and enrichment, while appropriation exploits and diminishes cultural significance.
Historical Examples of Cultural Diffusion
Cultural diffusion, the spread of cultural beliefs and social activities from one group to another, can be observed in historical examples such as the Silk Road facilitating the exchange of goods, technology, and religion between East Asia and the Mediterranean. The Roman Empire's adoption and adaptation of Greek art, architecture, and philosophy exemplify cultural diffusion rather than appropriation. These instances highlight the blending and sharing of cultural elements through trade, conquest, and migration, fostering multicultural development over time.
Notable Cases of Cultural Appropriation
Notable cases of cultural appropriation include the fashion industry's use of Indigenous patterns without permission and the commercialization of sacred Native American symbols in mainstream clothing lines. Examples also involve popular music artists adopting traditional African or Asian styles, often stripping the cultural significance and profiting from those stylistic elements. These instances highlight ongoing tension between cultural diffusion, where exchange enriches societies, and appropriation, which can perpetuate disrespect and inequality.
The Role of Power Dynamics in Cultural Exchange
Power dynamics profoundly shape cultural diffusion and appropriation by influencing who controls the narrative and benefits from cultural exchange. Dominant groups often appropriate elements from marginalized cultures without proper recognition or respect, leading to exploitation and misrepresentation. Equitable cultural exchange requires acknowledging historical inequalities and fostering mutual respect to ensure authentic and respectful sharing.
Positive Impacts of Cultural Diffusion on Societies
Cultural diffusion fosters innovation and creativity by blending diverse traditions, languages, and customs, enriching societies with new perspectives and practices. It promotes social cohesion and mutual understanding by encouraging cross-cultural interactions that reduce prejudice and intolerance. The exchange of ideas and technologies through cultural diffusion accelerates economic growth and enhances global cooperation, contributing to more dynamic and resilient communities.
When Does Cultural Exchange Become Cultural Appropriation?
Cultural exchange occurs when individuals or groups share traditions, languages, or customs respectfully, fostering understanding and appreciation. Cultural appropriation happens when elements of a marginalized culture are taken out of context, used without permission, or commodified, often perpetuating stereotypes and power imbalances. The key distinction lies in intent, respect, and awareness of historical and social dynamics influencing the relationship between cultures.
Social Perceptions and Controversies
Social perceptions of cultural diffusion often emphasize appreciation and mutual exchange, fostering understanding across diverse communities. In contrast, cultural appropriation is frequently viewed as exploitation, sparking controversies rooted in power imbalances and historical context. Debates surrounding these concepts highlight tensions between cultural respect and identity, influencing social discourse and policies on inclusivity.
Strategies for Respectful Cultural Interactions
Effective strategies for respectful cultural interactions emphasize active listening, genuine engagement, and education about the origins and meanings behind cultural practices. Encouraging collaboration and mutual exchange fosters cultural diffusion without exploitation or misrepresentation, allowing communities to share traditions while honoring their significance. Implementing consent and crediting original creators in cultural expressions ensures respect and minimizes the risks of cultural appropriation.
Moving Toward Cultural Appreciation and Ethical Engagement
Cultural appreciation involves respectful engagement and acknowledgment of the origins and significance of cultural elements, promoting mutual understanding and inclusion. Ethical engagement requires active learning, consent, and sensitivity to historical context to avoid reinforcing stereotypes or causing harm. Emphasizing education and dialogue fosters meaningful connections and supports authentic cultural exchange without exploitation.
cultural diffusion vs cultural appropriation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com