Social support involves the emotional, informational, and tangible assistance pets provide, enhancing owners' mental well-being and reducing feelings of loneliness. A social network, by contrast, refers to the broader web of relationships and social interactions that pets help facilitate among people. Understanding the distinction highlights how pets not only offer direct comfort but also act as catalysts for building and maintaining human social connections.
Table of Comparison
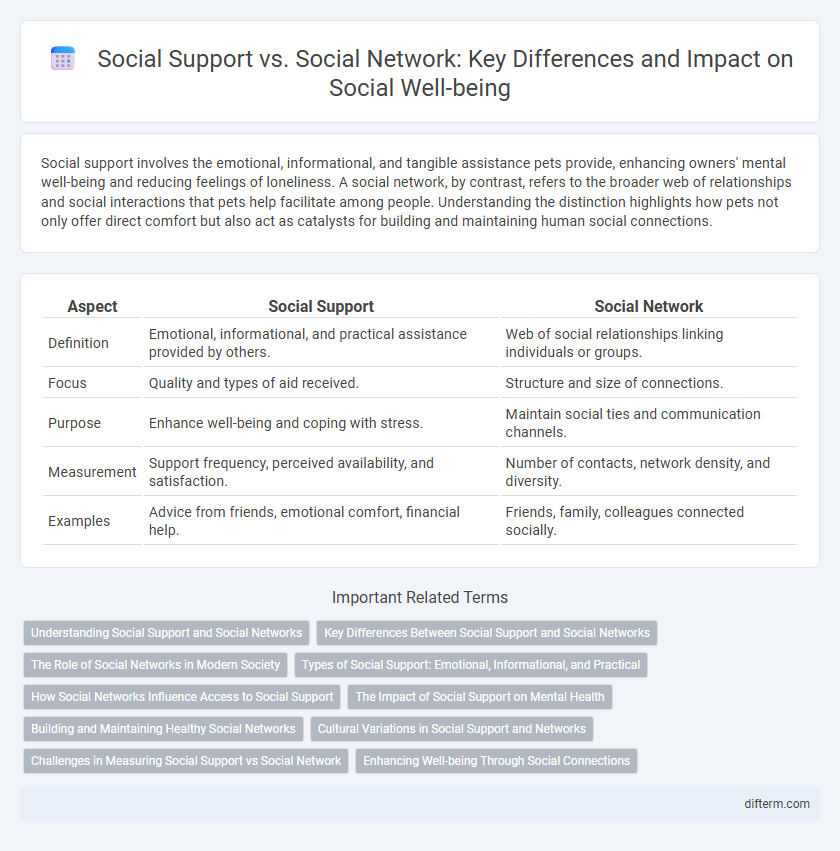
| Aspect | Social Support | Social Network |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional, informational, and practical assistance provided by others. | Web of social relationships linking individuals or groups. |
| Focus | Quality and types of aid received. | Structure and size of connections. |
| Purpose | Enhance well-being and coping with stress. | Maintain social ties and communication channels. |
| Measurement | Support frequency, perceived availability, and satisfaction. | Number of contacts, network density, and diversity. |
| Examples | Advice from friends, emotional comfort, financial help. | Friends, family, colleagues connected socially. |
Understanding Social Support and Social Networks
Social support refers to the emotional, informational, and practical assistance individuals receive from their social connections, enhancing mental health and resilience. Social networks consist of the web of relationships linking individuals, influencing access to resources and social support availability. Understanding the distinction helps in designing effective interventions that strengthen social ties and promote well-being.
Key Differences Between Social Support and Social Networks
Social support refers to the emotional, informational, and practical assistance individuals receive from others, while social networks are the structural web of relationships linking people. Social support emphasizes the quality and functionality of connections, providing resources like empathy and aid, whereas social networks focus on the quantity and patterns of social ties. Understanding the distinction highlights how strong, supportive interactions within a social network enhance well-being and resilience.
The Role of Social Networks in Modern Society
Social networks serve as vital platforms fostering connections, resource sharing, and emotional support among individuals. These interconnected systems enable the rapid dissemination of information and promote collective well-being in diverse communities. Access to robust social networks significantly enhances resilience and social integration within modern society.
Types of Social Support: Emotional, Informational, and Practical
Emotional support involves expressions of empathy, love, trust, and care that strengthen personal resilience and mental well-being. Informational support provides advice, guidance, and knowledge that help individuals navigate challenges and make informed decisions within their social networks. Practical support includes tangible assistance such as financial help, caregiving, or offering resources, directly addressing everyday needs in social relationships.
How Social Networks Influence Access to Social Support
Social networks shape access to social support by creating channels for emotional, informational, and instrumental assistance through strong and weak ties. Diverse networks enhance resource availability by bridging different social groups, facilitating timely help and advice. Network structure, size, and tie strength critically determine the quality and quantity of social support individuals receive in times of need.
The Impact of Social Support on Mental Health
Social support profoundly influences mental health by providing emotional, informational, and practical resources that help individuals cope with stress and adversity. Unlike broader social networks, which map general relationships, social support specifically involves quality interactions that foster a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation. Research consistently links strong social support to lower risks of depression, anxiety, and improved resilience against mental health disorders.
Building and Maintaining Healthy Social Networks
Building and maintaining healthy social networks involves cultivating genuine relationships that provide emotional support, practical assistance, and a sense of belonging. Effective social support stems from strong, trust-based connections within diverse networks, enhancing mental health and resilience. Regular communication, active listening, and mutual respect are essential practices for sustaining these valuable social ties.
Cultural Variations in Social Support and Networks
Cultural variations significantly impact the structure and function of social support and social networks, influencing how individuals seek and provide help within their communities. In collectivist cultures, social support often emphasizes family and close-knit networks, promoting emotional interdependence and shared resources. Conversely, individualistic cultures tend to prioritize broader, more diverse social networks that support autonomy and personal achievement.
Challenges in Measuring Social Support vs Social Network
Measuring social support presents challenges due to its subjective nature, often relying on individual perceptions of emotional, informational, or instrumental aid. In contrast, social network measurement focuses on quantifiable aspects like network size, density, and frequency of interactions, yet may overlook the quality and effectiveness of support provided. The disconnect between structural network analysis and functional support assessment complicates understanding their distinct impacts on well-being.
Enhancing Well-being Through Social Connections
Social support refers to the emotional, informational, and practical assistance received from close relationships, which directly contributes to enhanced mental health and stress reduction. A social network encompasses the broader web of social ties, including friends, family, colleagues, and community members, providing diverse resources and opportunities for social engagement. Strengthening both social support and social networks fosters resilience, promotes a sense of belonging, and significantly improves overall well-being.
social support vs social network Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com