Social authority stems from recognized expertise or formal positions, establishing trust and credibility in the social pet landscape. Social influence, on the other hand, arises through interactive engagement and peer recommendations, driving behavior change and community participation. Balancing social authority and social influence enhances brand loyalty and fosters authentic connections within pet owner networks.
Table of Comparison
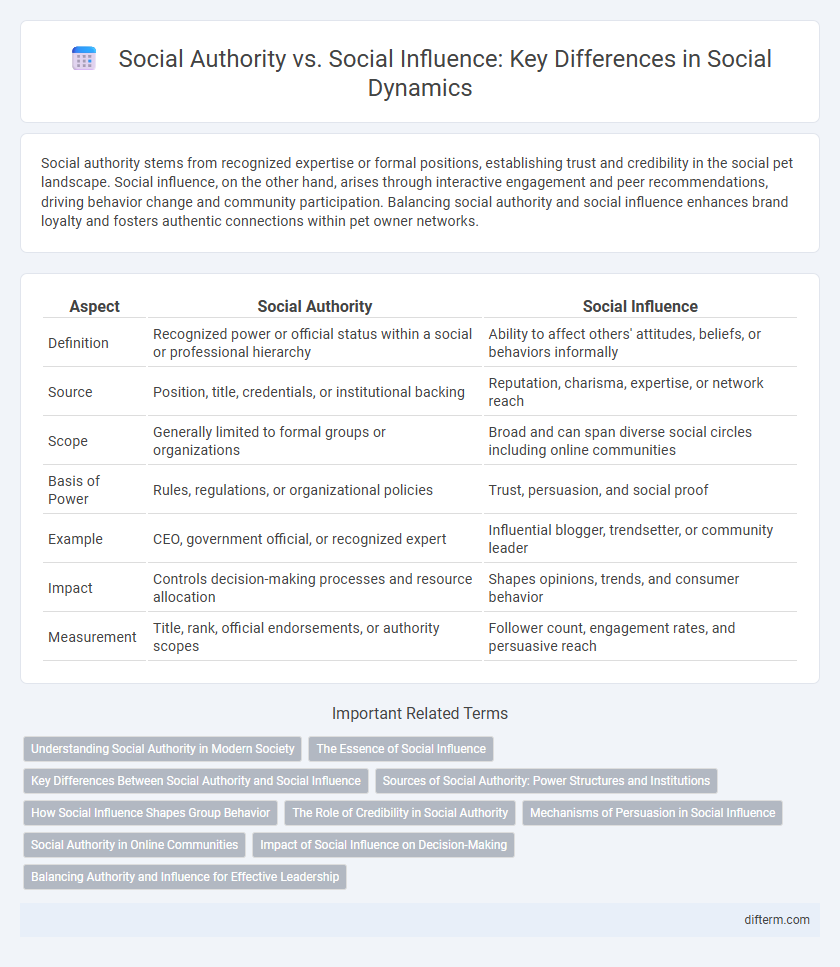
| Aspect | Social Authority | Social Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recognized power or official status within a social or professional hierarchy | Ability to affect others' attitudes, beliefs, or behaviors informally |
| Source | Position, title, credentials, or institutional backing | Reputation, charisma, expertise, or network reach |
| Scope | Generally limited to formal groups or organizations | Broad and can span diverse social circles including online communities |
| Basis of Power | Rules, regulations, or organizational policies | Trust, persuasion, and social proof |
| Example | CEO, government official, or recognized expert | Influential blogger, trendsetter, or community leader |
| Impact | Controls decision-making processes and resource allocation | Shapes opinions, trends, and consumer behavior |
| Measurement | Title, rank, official endorsements, or authority scopes | Follower count, engagement rates, and persuasive reach |
Understanding Social Authority in Modern Society
Social authority represents recognized power grounded in formal roles, expertise, or institutional legitimacy, driving compliance and shaping societal norms efficiently. Social influence, however, operates through interpersonal interactions, persuasion, and emotional appeal, affecting attitudes and behaviors on a more subtle, often informal level. Understanding social authority in modern society requires analyzing its evolving sources, such as digital platforms and expert networks, which coexist and sometimes compete with traditional authority structures.
The Essence of Social Influence
Social influence stems from an individual's ability to affect others' behaviors, attitudes, or beliefs through persuasion, emotional appeal, or social proof. Social authority, often derived from established roles or expertise, commands respect and compliance based on recognized status or knowledge. The essence of social influence lies in the dynamic interaction where trust, credibility, and relatability drive voluntary behavior change beyond mere authority.
Key Differences Between Social Authority and Social Influence
Social authority stems from established credibility and recognized expertise within a community, granting individuals formal power and trust. Social influence operates through subtle persuasion and behavioral impact, often without explicit authority, relying on charisma and relational dynamics. Key differences lie in legitimacy--authority is granted, influence is earned--and in application, where authority enforces norms, and influence shapes attitudes and decisions.
Sources of Social Authority: Power Structures and Institutions
Sources of social authority primarily derive from established power structures and institutions such as governments, religious organizations, and corporate entities, which enforce norms and regulate behavior through formal rules and laws. These institutions legitimize authority by maintaining hierarchical systems that confer decision-making power and social status. Understanding the role of institutional authority is crucial in analyzing how societal norms are upheld and how compliance is achieved within communities.
How Social Influence Shapes Group Behavior
Social influence shapes group behavior by altering individuals' attitudes, beliefs, and actions to align with group norms, often driven by the desire for acceptance and conformity. Unlike social authority, which relies on formal power and hierarchical position, social influence operates through subtle mechanisms such as persuasion, social proof, and peer pressure. This dynamic process fosters cohesion within groups, guiding decision-making and collective responses in social environments.
The Role of Credibility in Social Authority
Credibility serves as the cornerstone of social authority, establishing trust and legitimacy within social networks. Social authority derives from expertise, reliability, and consistency, which enhance an individual's or brand's ability to guide opinions and behaviors effectively. Without credibility, social influence lacks the foundation needed to generate genuine, sustained impact across communities.
Mechanisms of Persuasion in Social Influence
Social authority is based on recognized expertise, status, or formal position, compelling compliance through legitimacy, while social influence operates through persuasive mechanisms like social proof, reciprocity, and liking to shape attitudes and behaviors. The principle of social proof leverages the tendency to follow others' behaviors in uncertain situations, enhancing conformity and acceptance. Reciprocity triggers a sense of obligation to return favors, which, combined with likability, strengthens interpersonal persuasion and social influence dynamics.
Social Authority in Online Communities
Social authority in online communities is established through consistent expertise, trustworthiness, and active contributions that shape group norms and decisions. Members with high social authority often serve as moderators, thought leaders, or subject matter experts, whose opinions significantly impact community behavior and content quality. Building social authority requires sustained engagement, credibility, and the ability to foster meaningful interactions that enhance the community's collective knowledge.
Impact of Social Influence on Decision-Making
Social influence significantly shapes individual decision-making by altering perceptions, attitudes, and behaviors within group settings. This dynamic operates through mechanisms like conformity, compliance, and persuasion, which can override personal preferences to align with group norms or authoritative cues. Understanding the impact of social influence is crucial for analyzing behavioral changes in marketing, politics, and organizational contexts.
Balancing Authority and Influence for Effective Leadership
Balancing social authority and social influence is essential for effective leadership, as authority provides the formal power to make decisions while influence fosters trust and motivation among followers. Leaders who skillfully combine authoritative directives with genuine influence create an environment that drives collaboration and sustainable success. Research shows that leaders exhibiting both strong authority and high emotional intelligence achieve better team performance and engagement.
social authority vs social influence Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com