Social pet experiences enhance social interaction by encouraging engagement and communication within community settings, fostering a sense of belonging and shared interests. Interpersonal interaction, on the other hand, focuses on one-on-one connections that build deeper emotional bonds and trust between individuals and their pets. Balancing both forms of interaction supports well-rounded social development and emotional well-being for pet owners and their animals.
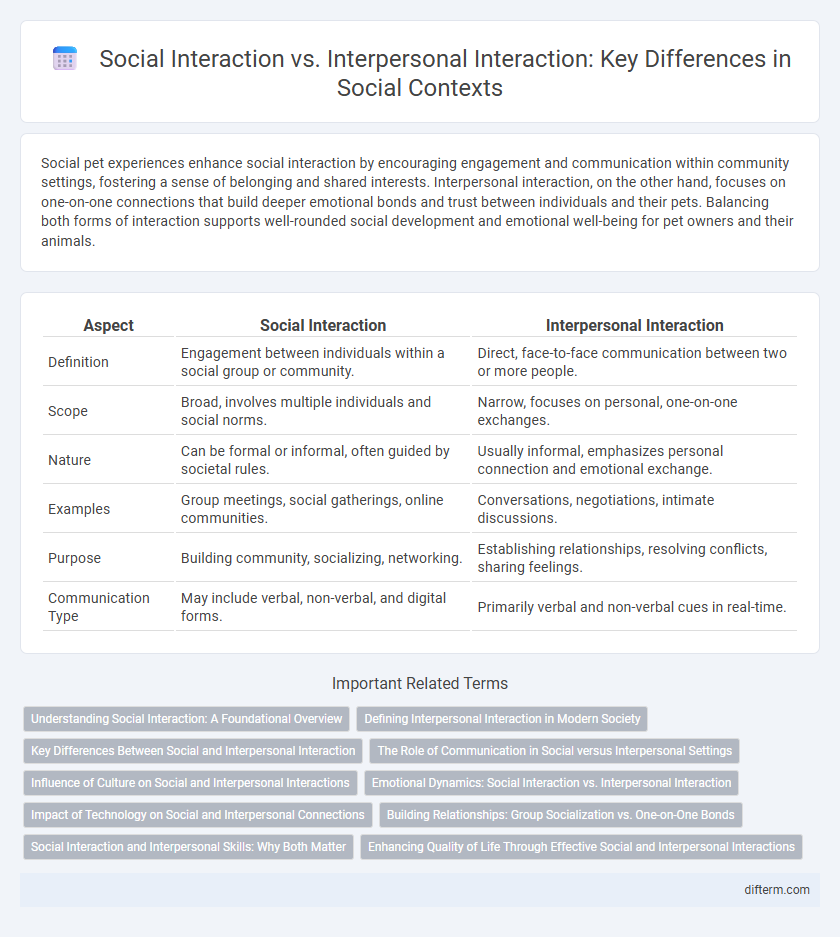
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Interaction | Interpersonal Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Engagement between individuals within a social group or community. | Direct, face-to-face communication between two or more people. |
| Scope | Broad, involves multiple individuals and social norms. | Narrow, focuses on personal, one-on-one exchanges. |
| Nature | Can be formal or informal, often guided by societal rules. | Usually informal, emphasizes personal connection and emotional exchange. |
| Examples | Group meetings, social gatherings, online communities. | Conversations, negotiations, intimate discussions. |
| Purpose | Building community, socializing, networking. | Establishing relationships, resolving conflicts, sharing feelings. |
| Communication Type | May include verbal, non-verbal, and digital forms. | Primarily verbal and non-verbal cues in real-time. |
Understanding Social Interaction: A Foundational Overview
Social interaction involves the exchange of communication and behavior between individuals within a group, encompassing broader societal norms and contexts. Interpersonal interaction specifically focuses on direct, face-to-face communication between two or more people, emphasizing personal relationships and emotional connections. Understanding these distinctions is essential for analyzing human behavior in both social networks and intimate relationships.
Defining Interpersonal Interaction in Modern Society
Interpersonal interaction in modern society refers to direct, face-to-face communication between individuals that fosters emotional connections and mutual understanding. It encompasses verbal and nonverbal exchanges essential for relationship building and conflict resolution. Unlike broader social interaction, which includes group dynamics and societal norms, interpersonal interaction centers on personalized, dyadic exchanges critical for social cohesion and personal well-being.
Key Differences Between Social and Interpersonal Interaction
Social interaction involves communication within larger groups and networks, emphasizing societal norms and collective behavior, while interpersonal interaction occurs between individuals focusing on personal relationships and emotional exchange. Social interaction often shapes cultural trends and grup dynamics, whereas interpersonal interaction builds trust and intimacy through direct, face-to-face engagement. Understanding these distinctions highlights how social contexts influence broader social structures, while interpersonal connections drive individual experiences and emotional bonds.
The Role of Communication in Social versus Interpersonal Settings
Communication in social settings often involves broader, more formal exchanges aimed at maintaining group harmony and conveying information to diverse audiences. In interpersonal interactions, communication is more personalized, allowing for deeper emotional connection and understanding between individuals. Effective communication adapts to these contexts by balancing clarity, empathy, and responsiveness to meet social expectations and strengthen personal bonds.
Influence of Culture on Social and Interpersonal Interactions
Cultural norms and values profoundly shape both social and interpersonal interactions, influencing communication styles, conflict resolution, and relationship dynamics. High-context cultures prioritize indirect communication and group harmony, while low-context cultures emphasize directness and individual expression in social exchanges. Understanding these cultural differences enhances cross-cultural competence and fosters more effective, respectful interactions in diverse social settings.
Emotional Dynamics: Social Interaction vs. Interpersonal Interaction
Social interaction involves dynamic emotional exchanges within larger groups or communities, often guided by societal norms and roles, influencing mood and collective behavior. Interpersonal interaction centers on deep emotional connections between individuals, where empathy, trust, and non-verbal cues play critical roles in shaping personal relationships. Understanding emotional dynamics in both contexts reveals how group emotions differ from individual emotional bonds in complexity and intensity.
Impact of Technology on Social and Interpersonal Connections
Technology reshapes social and interpersonal connections by facilitating instant communication across global networks while potentially reducing face-to-face interactions and emotional depth. Social interaction often spans broader, less personal networks via digital platforms, whereas interpersonal interaction involves more intimate, direct exchanges that technology can both enhance and hinder. The impact of technological tools like social media, video calls, and messaging apps redefines relational dynamics, influencing empathy, trust, and community engagement in modern societies.
Building Relationships: Group Socialization vs. One-on-One Bonds
Group socialization fosters a dynamic environment where individuals build relationships through shared experiences and collective activities, enhancing social skills and a sense of belonging. One-on-one interpersonal interactions create deeper emotional connections by allowing focused communication and personalized understanding between individuals. Balancing group settings and one-on-one bonds is essential for holistic relationship development and effective social integration.
Social Interaction and Interpersonal Skills: Why Both Matter
Social interaction forms the foundation of building relationships by enabling individuals to communicate and connect within a community, while interpersonal skills enhance the quality and effectiveness of these exchanges through empathy, active listening, and emotional intelligence. Mastery of social interaction facilitates networking and group dynamics, whereas strong interpersonal skills foster trust and cooperation in one-on-one or small group settings. Together, social interaction and interpersonal skills drive personal and professional success by promoting meaningful connections and collaboration.
Enhancing Quality of Life Through Effective Social and Interpersonal Interactions
Effective social and interpersonal interactions significantly enhance quality of life by fostering emotional support, trust, and mutual understanding. Engaging in meaningful conversations and active listening improves mental health, reduces stress, and strengthens relationships. Prioritizing empathy and communication skills cultivates a positive environment that promotes well-being and social fulfillment.
social interaction vs interpersonal interaction Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com