Social hierarchies in pets establish a ranking system that determines access to resources and mating opportunities, often leading to dominance and submission behaviors. Social roles, however, emphasize the specific functions or responsibilities an individual pet holds within a group, such as protector, nurturer, or scout. Understanding the distinction between hierarchy and role helps pet owners better manage group dynamics and promote harmonious interactions.
Table of Comparison
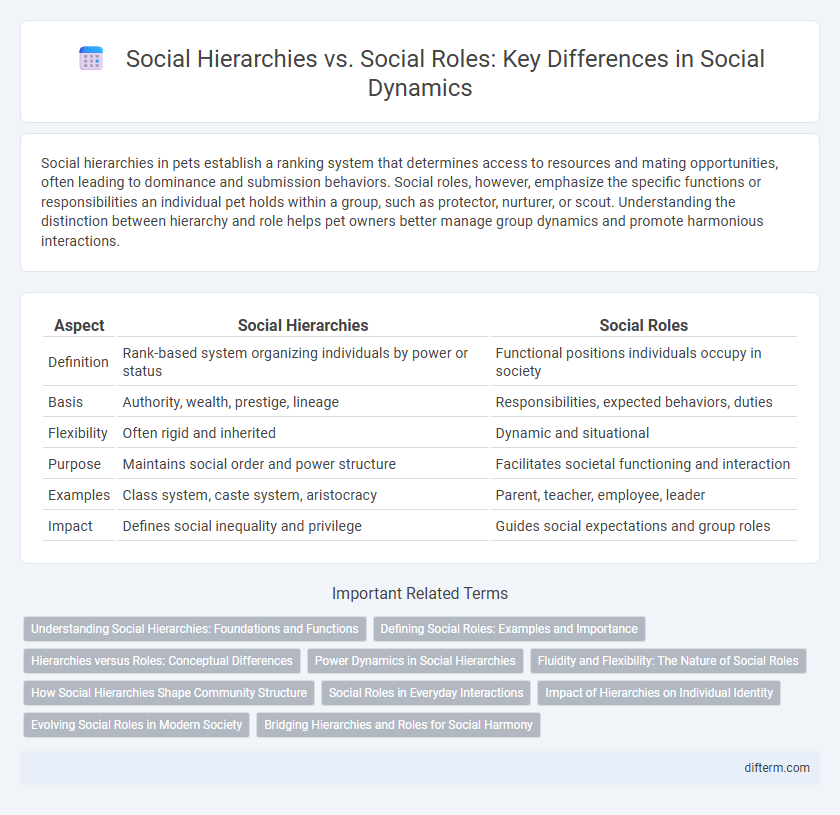
| Aspect | Social Hierarchies | Social Roles |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rank-based system organizing individuals by power or status | Functional positions individuals occupy in society |
| Basis | Authority, wealth, prestige, lineage | Responsibilities, expected behaviors, duties |
| Flexibility | Often rigid and inherited | Dynamic and situational |
| Purpose | Maintains social order and power structure | Facilitates societal functioning and interaction |
| Examples | Class system, caste system, aristocracy | Parent, teacher, employee, leader |
| Impact | Defines social inequality and privilege | Guides social expectations and group roles |
Understanding Social Hierarchies: Foundations and Functions
Social hierarchies establish structured layers of power and status within groups, influencing access to resources and decision-making authority. Social roles, by contrast, define expected behaviors and responsibilities tied to specific positions within these hierarchies, shaping individual interactions and group dynamics. Understanding these foundations clarifies how hierarchy stabilizes societies by organizing roles that promote cooperation and social order.
Defining Social Roles: Examples and Importance
Social roles represent the expected behaviors and responsibilities associated with a particular position within a community, such as teacher, parent, or leader, providing structure to social interactions. Unlike social hierarchies that emphasize rankings or power dynamics, social roles focus on functional contributions to group cohesion and individual identity. Understanding social roles is crucial for analyzing social organization and the ways people navigate societal expectations in various contexts.
Hierarchies versus Roles: Conceptual Differences
Social hierarchies organize individuals into ranked levels based on power, status, or authority, establishing a structured order within a community. In contrast, social roles define expected behaviors and responsibilities assigned to individuals regardless of their hierarchical position, guiding interactions within various contexts. Understanding the conceptual differences between hierarchies and roles clarifies how societal order and individual functions coexist and influence social dynamics.
Power Dynamics in Social Hierarchies
Power dynamics in social hierarchies are characterized by unequal access to resources, authority, and influence, which reinforces systemic dominance and subordination among groups. Social roles, while defined by expected behaviors within a community, interact with hierarchies by shaping individuals' status and control within the social structure. Understanding these dynamics is essential for analyzing how privilege and inequality persist across different societal levels.
Fluidity and Flexibility: The Nature of Social Roles
Social roles demonstrate significant fluidity and flexibility, allowing individuals to adapt their behaviors based on context, relationships, and expectations. Unlike rigid social hierarchies, roles facilitate dynamic interactions and empower adaptability across varying social settings. This inherent versatility enhances social cohesion and personal agency within diverse communities.
How Social Hierarchies Shape Community Structure
Social hierarchies establish a ranked framework within communities that influences access to resources, decision-making power, and social status, creating distinct layers of influence. These hierarchies affect social cohesion by determining roles tied to prestige and authority, which often guide behavioral expectations and intergroup interactions. Consequently, community structure reflects the complex dynamics of power distribution shaped by hierarchical positions rather than just functional social roles.
Social Roles in Everyday Interactions
Social roles in everyday interactions define expected behaviors and responsibilities tied to an individual's position within a group, guiding communication and cooperation. Unlike social hierarchies, which emphasize status and ranking, social roles focus on functional contributions and relational dynamics in social settings. Understanding social roles helps explain how individuals navigate complex social environments by fulfilling culturally prescribed expectations.
Impact of Hierarchies on Individual Identity
Social hierarchies shape individual identity by influencing access to resources, status, and power, often reinforcing societal norms and expectations. Individuals positioned within higher ranks gain privileges that enhance self-perception and social recognition, while those in lower tiers may experience marginalization and identity limitations. This stratification deeply affects personal behavior, opportunities, and interactions within communities, embedding hierarchy as a critical factor in identity formation.
Evolving Social Roles in Modern Society
Evolving social roles in modern society reflect shifts from rigid social hierarchies to more fluid and dynamic frameworks, emphasizing individual agency and diverse identities. Technological advancements and globalization continuously reshape these roles, fostering inclusivity and challenging traditional status boundaries. This transformation highlights the importance of adaptability in navigating contemporary social structures and cultural expectations.
Bridging Hierarchies and Roles for Social Harmony
Bridging social hierarchies and social roles fosters inclusive communities by balancing structured authority with individual responsibilities. Social harmony emerges when hierarchical positions are respected while roles encourage collaboration, reducing conflicts and enhancing group cohesion. Effective communication and mutual recognition between different social strata promote trust and equitable participation in collective decision-making.
social hierarchies vs social roles Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com