Social dominance relies on coercion and control to assert authority within a group, often leading to compliance through fear or intimidation. In contrast, social prestige is achieved through respect, admiration, and positive influence, fostering voluntary support and cooperation among peers. Understanding the dynamics between social dominance and social prestige is crucial for managing social hierarchies and promoting harmonious interactions in social pet environments.
Table of Comparison
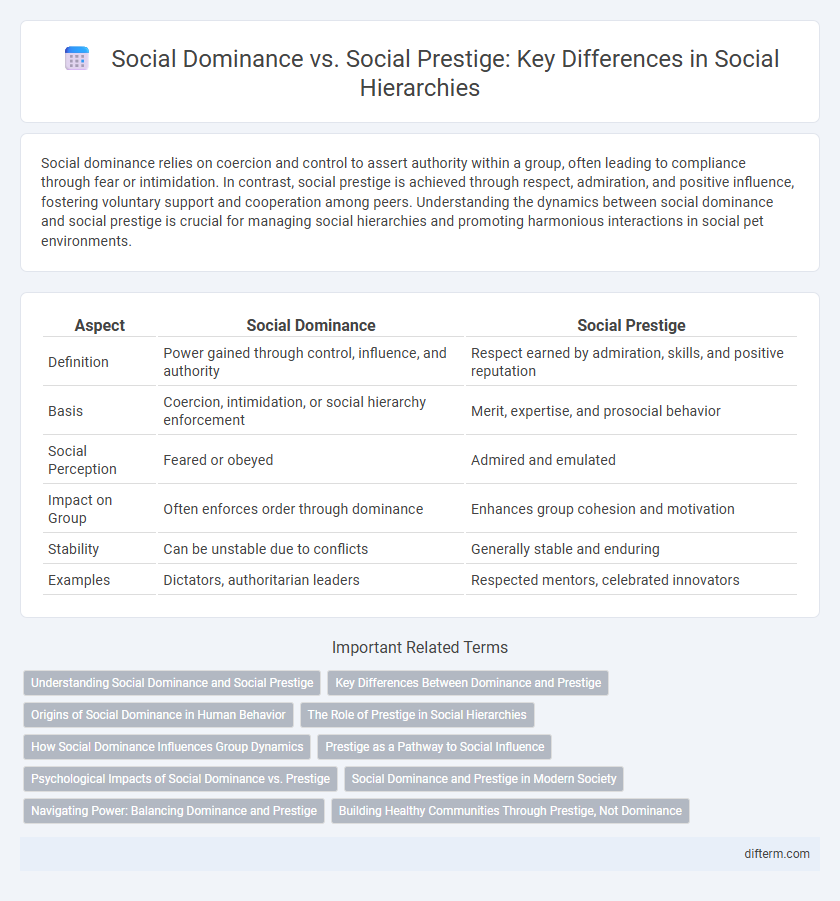
| Aspect | Social Dominance | Social Prestige |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Power gained through control, influence, and authority | Respect earned by admiration, skills, and positive reputation |
| Basis | Coercion, intimidation, or social hierarchy enforcement | Merit, expertise, and prosocial behavior |
| Social Perception | Feared or obeyed | Admired and emulated |
| Impact on Group | Often enforces order through dominance | Enhances group cohesion and motivation |
| Stability | Can be unstable due to conflicts | Generally stable and enduring |
| Examples | Dictators, authoritarian leaders | Respected mentors, celebrated innovators |
Understanding Social Dominance and Social Prestige
Social dominance refers to an individual's ability to assert control and influence over others through power, often linked to aggression or coercion, whereas social prestige arises from respect and admiration earned through competence, kindness, or status achievements. Understanding the differences between social dominance and social prestige helps clarify how individuals gain influence within groups--dominance through intimidation or hierarchy, prestige through skill and reputation. Research shows that social prestige tends to foster more stable and positive social bonds, while dominance may provoke conflict or submission.
Key Differences Between Dominance and Prestige
Social dominance relies on fear, coercion, and control to assert influence, often linked to aggression and competitiveness. Social prestige is earned through respect, expertise, and admiration, fostering voluntary followership and cooperation. Dominance creates hierarchy through power, while prestige builds hierarchy through valued skills and social approval.
Origins of Social Dominance in Human Behavior
Social dominance originates from evolutionary competition for resources, status, and mating opportunities, driving hierarchies based on force, intimidation, and control. In contrast, social prestige arises from skill, knowledge, and prosocial behavior, fostering voluntary deference and cooperation within groups. Human behavior reflects a balance between dominance strategies, rooted in primal survival mechanisms, and prestige strategies, shaped by cultural evolution and social learning.
The Role of Prestige in Social Hierarchies
Prestige plays a pivotal role in social hierarchies by fostering voluntary deference based on respect, expertise, and admiration rather than coercion. Unlike dominance, which relies on fear and control, prestige encourages cooperation and the sharing of resources, enhancing group cohesion and stability. This form of social influence is linked to increased access to social capital, higher status, and greater opportunities within both small communities and larger organizational structures.
How Social Dominance Influences Group Dynamics
Social dominance shapes group dynamics by establishing hierarchical structures that dictate power distribution and resource control within social networks. Dominant individuals often influence decision-making processes, access to opportunities, and the enforcement of social norms, thereby reinforcing their authority. This hierarchical influence contrasts with social prestige, which derives from respect and admiration rather than coercive power, affecting group cohesion and collaboration differently.
Prestige as a Pathway to Social Influence
Social prestige serves as a strategic pathway to social influence by fostering respect and admiration based on merit, competence, and prosocial behavior rather than coercion or dominance. Individuals who cultivate social prestige gain voluntary followers, enhancing their capacity to shape group norms and decisions sustainably. Research in social psychology highlights that prestige-based influence leads to more stable and cooperative group dynamics compared to dominance-based hierarchies.
Psychological Impacts of Social Dominance vs. Prestige
Social dominance often leads to increased stress, anxiety, and aggressive behavior due to constant efforts to maintain power and control, negatively impacting mental health. In contrast, social prestige fosters positive psychological outcomes such as higher self-esteem, intrinsic motivation, and stronger social bonds because it is associated with respect and admiration rather than fear. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for promoting healthier social environments and personal well-being.
Social Dominance and Prestige in Modern Society
Social dominance often relies on control, authority, and coercion to maintain power structures, while social prestige is earned through respect, competence, and positive reputation in modern society. Research indicates that prestige-based influence fosters cooperation and social cohesion more effectively than dominance-based power, which can provoke resistance and conflict. Contemporary social hierarchies increasingly favor prestige as digital platforms amplify skill recognition and social capital beyond traditional dominance mechanisms.
Navigating Power: Balancing Dominance and Prestige
Navigating social power requires balancing dominance, characterized by assertive control and influence, with social prestige, which stems from respect and admiration earned through competence and generosity. Individuals who effectively combine dominance and prestige strategies tend to build more sustainable influence and maintain positive relationships within social hierarchies. Emphasizing prestige can foster cooperation and long-term loyalty, while strategic displays of dominance may secure immediate authority and compliance.
Building Healthy Communities Through Prestige, Not Dominance
Building healthy communities thrives on social prestige, which fosters cooperation, trust, and mutual respect among members. Unlike social dominance, which relies on control and competition, prestige encourages sharing knowledge and collaborative problem-solving that strengthen social bonds. Emphasizing prestige-based leadership cultivates inclusive environments where individuals feel valued and motivated to contribute positively.
social dominance vs social prestige Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com