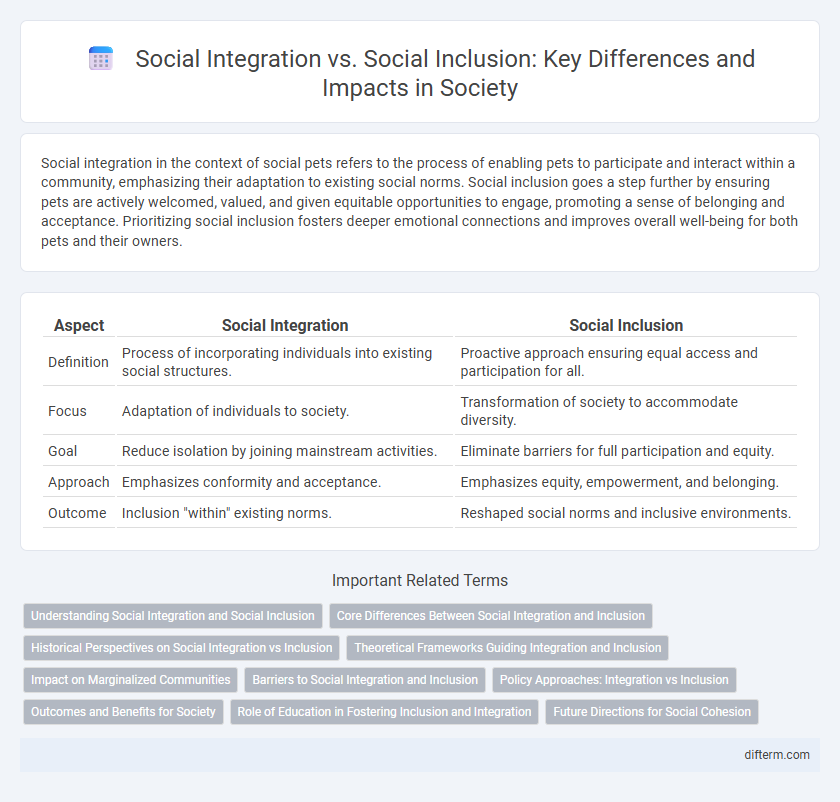
Social integration in the context of social pets refers to the process of enabling pets to participate and interact within a community, emphasizing their adaptation to existing social norms. Social inclusion goes a step further by ensuring pets are actively welcomed, valued, and given equitable opportunities to engage, promoting a sense of belonging and acceptance. Prioritizing social inclusion fosters deeper emotional connections and improves overall well-being for both pets and their owners.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Integration | Social Inclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of incorporating individuals into existing social structures. | Proactive approach ensuring equal access and participation for all. |
| Focus | Adaptation of individuals to society. | Transformation of society to accommodate diversity. |
| Goal | Reduce isolation by joining mainstream activities. | Eliminate barriers for full participation and equity. |
| Approach | Emphasizes conformity and acceptance. | Emphasizes equity, empowerment, and belonging. |
| Outcome | Inclusion "within" existing norms. | Reshaped social norms and inclusive environments. |
Understanding Social Integration and Social Inclusion
Social integration refers to the process through which individuals from diverse backgrounds become functional participants in mainstream society, emphasizing participation in social, economic, and cultural activities. Social inclusion focuses on ensuring equal access to opportunities and resources, reducing barriers related to discrimination, poverty, and marginalization. Understanding the distinction highlights that social integration is about active involvement, while social inclusion aims at creating equitable conditions for all individuals.
Core Differences Between Social Integration and Inclusion
Social integration emphasizes the process of incorporating individuals into existing social structures and systems, often requiring them to adapt to dominant cultural norms. Social inclusion, by contrast, prioritizes recognizing and valuing diverse identities and ensuring equitable participation and access to resources regardless of differences. Core differences lie in integration's focus on assimilation versus inclusion's commitment to embracing diversity and fostering belonging within all societal dimensions.
Historical Perspectives on Social Integration vs Inclusion
Historical perspectives on social integration emphasize the assimilation of minority groups into dominant cultural norms, often overlooking individual identities and systemic inequalities. Social inclusion, emerging as a more contemporary approach, prioritizes equal access to opportunities and active participation of marginalized communities within societal structures. This shift reflects evolving social policies aimed at addressing discrimination and promoting diversity in education, employment, and civic engagement.
Theoretical Frameworks Guiding Integration and Inclusion
Theoretical frameworks guiding social integration emphasize the process through which individuals become functioning members of society by adopting mainstream norms and values, often focusing on assimilation models. In contrast, social inclusion frameworks prioritize equitable access to resources and participation, grounded in rights-based and capability approaches that recognize diversity and aim to dismantle structural barriers. These differing paradigms influence policies by either promoting conformity or fostering pluralism and empowerment within social systems.
Impact on Marginalized Communities
Social integration emphasizes the assimilation of marginalized communities into dominant societal norms, often risking the loss of unique cultural identities and exacerbating feelings of exclusion. Social inclusion promotes equal access to opportunities and resources, fostering a sense of belonging and empowerment among marginalized groups. Research shows that social inclusion initiatives lead to improved mental health, increased civic participation, and reduced socio-economic disparities.
Barriers to Social Integration and Inclusion
Barriers to social integration and inclusion often stem from systemic discrimination, economic inequality, and cultural misunderstandings that hinder marginalized groups from fully participating in society. Language barriers, limited access to education, and social stigma create obstacles that prevent individuals from establishing meaningful connections and accessing essential resources. Addressing these challenges requires targeted policies that promote equal opportunities, foster intercultural dialogue, and remove institutional biases.
Policy Approaches: Integration vs Inclusion
Policy approaches to social integration often emphasize assimilating individuals into existing societal norms and structures, focusing on conformity and participation within dominant frameworks. In contrast, social inclusion policies prioritize equity by addressing systemic barriers and promoting diversity, ensuring marginalized groups have equal access and voice in social, economic, and political spheres. Effective social inclusion strategies foster environments where differences are valued and structural inequalities are actively dismantled.
Outcomes and Benefits for Society
Social integration fosters cohesion by enabling diverse groups to participate equally in societal activities, leading to reduced discrimination and enhanced mutual understanding. Social inclusion ensures marginalized communities access essential resources and opportunities, resulting in improved economic stability and social well-being. Both approaches contribute to stronger community resilience, lower inequality rates, and overall societal harmony.
Role of Education in Fostering Inclusion and Integration
Education serves as a fundamental platform for promoting social integration by equipping individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to participate fully in society. It fosters social inclusion by creating equitable learning environments where diverse cultural backgrounds and abilities are respected and valued. Schools and educational programs that emphasize multicultural understanding and collaborative learning help bridge social divides and cultivate a sense of belonging among all students.
Future Directions for Social Cohesion
Future directions for social cohesion emphasize transforming social integration models into comprehensive social inclusion strategies that recognize and embrace diversity in all its forms. Policymakers are increasingly focused on creating equitable access to resources, opportunities, and decision-making processes to dismantle systemic barriers that hinder marginalized groups. Innovative community-based programs leveraging digital platforms and participatory governance are being developed to strengthen social bonds and foster a more inclusive society.
social integration vs social inclusion Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com