Opinion reflects personal beliefs or feelings about a subject, often influenced by individual experiences and emotions. Interpretation involves analyzing information to derive meaning or understanding, which can be more objective and based on evidence. While opinions are subjective and vary widely, interpretations aim for coherent explanations grounded in context.
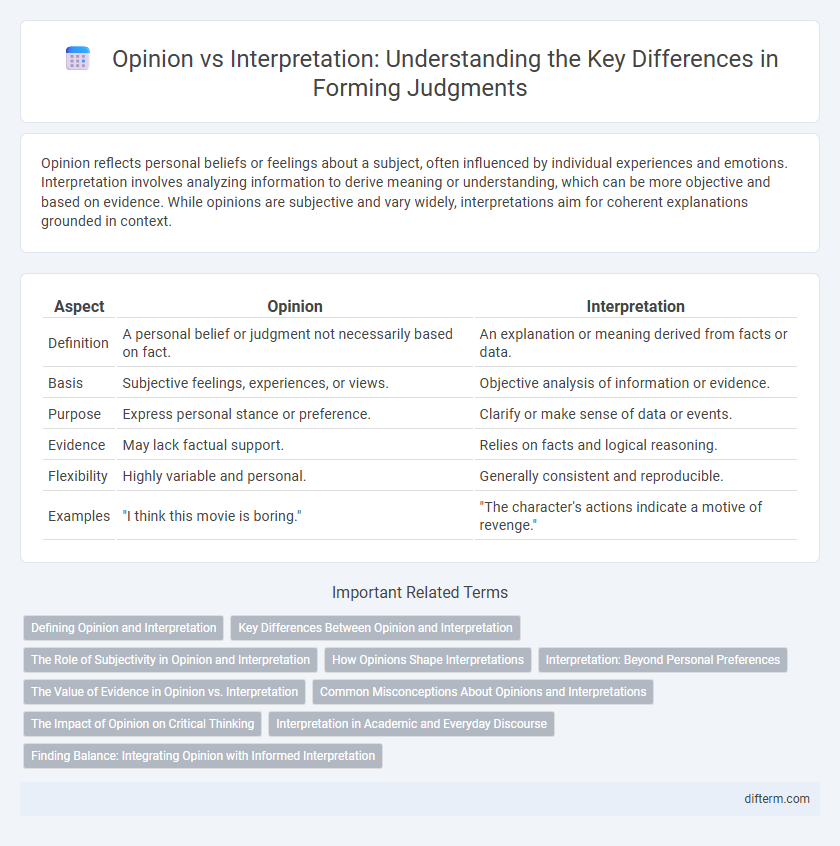
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Opinion | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A personal belief or judgment not necessarily based on fact. | An explanation or meaning derived from facts or data. |
| Basis | Subjective feelings, experiences, or views. | Objective analysis of information or evidence. |
| Purpose | Express personal stance or preference. | Clarify or make sense of data or events. |
| Evidence | May lack factual support. | Relies on facts and logical reasoning. |
| Flexibility | Highly variable and personal. | Generally consistent and reproducible. |
| Examples | "I think this movie is boring." | "The character's actions indicate a motive of revenge." |
Defining Opinion and Interpretation
Opinion is a personal belief or judgment that reflects an individual's feelings, attitudes, or preferences, often subjective and influenced by experience. Interpretation involves analyzing and explaining the meaning or significance of information, texts, or events based on evidence and reasoning. While opinion expresses personal viewpoints, interpretation seeks to provide an informed understanding grounded in context and analysis.
Key Differences Between Opinion and Interpretation
Opinion reflects a personal belief or judgment influenced by individual feelings and experiences, while interpretation involves analyzing information to derive meaning based on objective evidence or context. Opinions are subjective and vary widely among individuals, whereas interpretations aim for a reasoned understanding grounded in facts. The key difference lies in the basis of formation: opinions stem from personal perspectives, interpretations from analytical reasoning.
The Role of Subjectivity in Opinion and Interpretation
Subjectivity fundamentally shapes both opinion and interpretation, as personal experiences, emotions, and biases influence how individuals perceive information. Opinions reflect subjective judgments and preferences, often without requiring objective evidence, while interpretations involve analyzing meaning but remain colored by individual perspectives. Recognizing the role of subjectivity allows deeper insight into how knowledge and beliefs are formed and communicated.
How Opinions Shape Interpretations
Opinions act as the lens through which interpretations are formed, influencing the perception and meaning assigned to information or events. Personal beliefs, cultural background, and emotions shape opinions, which subsequently guide how individuals interpret facts and narratives. This dynamic underscores that interpretations are rarely objective, as they are inherently colored by the subjective nature of opinions.
Interpretation: Beyond Personal Preferences
Interpretation transcends personal preferences by analyzing context, intentions, and evidence to derive meaning, whereas opinions mainly reflect individual beliefs and emotions. It requires critical thinking and a comprehensive understanding of different perspectives, making it more objective and nuanced. This approach enables deeper appreciation and informed discussions beyond subjective viewpoints.
The Value of Evidence in Opinion vs. Interpretation
The value of evidence in opinion versus interpretation lies primarily in its ability to anchor subjective viewpoints with objective data, enhancing credibility and reducing bias. While opinions often reflect personal beliefs or preferences, interpretations depend heavily on evidence to construct meaning and provide context, making them more analytically robust. Critical evaluation of evidence ensures interpretations remain flexible and responsive to new information, whereas opinions may remain static regardless of empirical support.
Common Misconceptions About Opinions and Interpretations
Opinions are often mistaken for facts, leading to misunderstandings in communication, whereas interpretations involve analyzing available information to derive meaning. Common misconceptions include treating opinions as objective truths and assuming interpretations are purely subjective, when in reality, interpretations require a critical evaluation of evidence. Clarifying these distinctions enhances critical thinking and improves dialogue by recognizing the validity and limits of both opinions and interpretations.
The Impact of Opinion on Critical Thinking
Opinion influences critical thinking by shaping how individuals process information through personal biases and beliefs, potentially limiting objective analysis. Interpretation requires a more analytical approach, emphasizing evidence and context to understand meaning beyond personal perspective. Balancing opinion with interpretation enhances critical thinking by fostering open-minded evaluation and comprehensive understanding.
Interpretation in Academic and Everyday Discourse
Interpretation in academic discourse involves analyzing texts, data, or phenomena with evidence-based reasoning, aiming to uncover deeper meanings or contextual significance. Everyday discourse relies on personal experiences and cultural backgrounds, making interpretations subjective and fluid. Recognizing the distinction between opinion as a personal belief and interpretation as an analytical process enhances critical thinking and communication across diverse settings.
Finding Balance: Integrating Opinion with Informed Interpretation
Balancing opinion with informed interpretation requires grounding personal views in credible evidence and thoughtful analysis to enhance understanding. Opinions gain depth and reliability when supported by factual data and logical reasoning, creating a more nuanced perspective. Integrating these elements promotes critical thinking and prevents bias, fostering well-rounded conclusions.
opinion vs interpretation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com