Bias in opinions about pets often stems from personal experiences and emotional attachments, which can cloud objective judgment. Impartiality requires setting aside these preferences to evaluate pets based on factual information and individual needs. Achieving impartiality ensures fair and balanced perspectives when choosing or caring for pets.
Table of Comparison
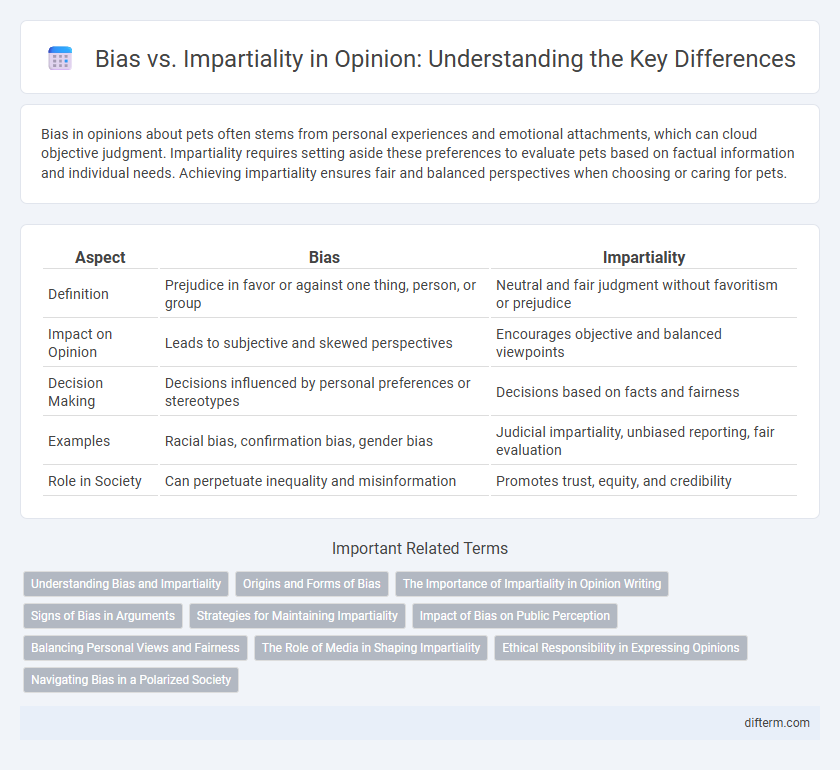
| Aspect | Bias | Impartiality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prejudice in favor or against one thing, person, or group | Neutral and fair judgment without favoritism or prejudice |
| Impact on Opinion | Leads to subjective and skewed perspectives | Encourages objective and balanced viewpoints |
| Decision Making | Decisions influenced by personal preferences or stereotypes | Decisions based on facts and fairness |
| Examples | Racial bias, confirmation bias, gender bias | Judicial impartiality, unbiased reporting, fair evaluation |
| Role in Society | Can perpetuate inequality and misinformation | Promotes trust, equity, and credibility |
Understanding Bias and Impartiality
Bias often stems from unconscious tendencies shaped by personal experiences, cultural background, and institutional influences, leading to subjective judgments that distort objectivity. Impartiality requires deliberate awareness and critical analysis to recognize these biases and ensure decisions are based on facts rather than emotions or preconceived notions. Understanding the roots and manifestations of bias is essential to fostering impartiality and maintaining fairness in evaluations and decision-making processes.
Origins and Forms of Bias
Bias originates from cognitive shortcuts, social influences, and cultural norms, shaping perceptions and judgments subconsciously. Forms of bias range from confirmation bias and stereotyping to implicit bias, each distorting impartial decision-making processes. Understanding these origins and manifestations is crucial for fostering genuine impartiality in analysis and discourse.
The Importance of Impartiality in Opinion Writing
Impartiality in opinion writing preserves credibility by presenting balanced perspectives and fostering trust among readers. Avoiding bias ensures arguments are grounded in facts and reason, allowing audiences to evaluate viewpoints without manipulation. Maintaining neutrality promotes a fair discourse, encouraging informed decision-making and respectful dialogue.
Signs of Bias in Arguments
Signs of bias in arguments often include selective use of evidence that supports only one perspective while ignoring contradictory data. Emotional language and sweeping generalizations also indicate partiality rather than objective reasoning. Recognizing these markers helps distinguish biased arguments from impartial, logically sound discourse.
Strategies for Maintaining Impartiality
Maintaining impartiality requires implementing structured decision-making frameworks that minimize cognitive biases by promoting evidence-based evaluations and diverse viewpoints. Regular training on recognizing personal biases and fostering a culture of accountability strengthens objectivity in judgments. Utilizing blind review processes and standardized criteria further ensures fair and unbiased outcomes across various contexts.
Impact of Bias on Public Perception
Bias significantly distorts public perception by framing information through a subjective lens, which can manipulate opinions and undermine trust in media sources. Impartiality ensures balanced coverage, fostering informed decisions and promoting social cohesion by presenting multiple perspectives fairly. Persistent bias not only polarizes communities but also erodes the credibility of institutions responsible for disseminating knowledge.
Balancing Personal Views and Fairness
Balancing personal views with fairness requires recognizing inherent biases while striving for impartial judgment grounded in facts. Awareness of one's cognitive shortcuts enables more objective analysis and equitable treatment of differing perspectives. This equilibrium is essential for credible decision-making in diverse social and professional contexts.
The Role of Media in Shaping Impartiality
Media plays a crucial role in shaping impartiality by influencing public perception through the framing of news stories and the selection of sources. Bias can emerge when media outlets prioritize particular narratives or viewpoints, impacting the audience's understanding of complex issues. Ensuring balanced reporting and diverse perspectives is essential to maintain credibility and foster an informed and impartial public discourse.
Ethical Responsibility in Expressing Opinions
Ethical responsibility in expressing opinions demands a commitment to impartiality, ensuring that personal biases do not distort facts or mislead audiences. Recognizing the influence of cognitive biases enables individuals to critically assess their own viewpoints and present balanced perspectives. Upholding transparency and fairness fosters trust and supports informed decision-making within public discourse.
Navigating Bias in a Polarized Society
Navigating bias in a polarized society requires a conscious effort to recognize personal and systemic prejudices that influence our viewpoints. Employing critical thinking and seeking diverse perspectives helps mitigate the impact of confirmation bias and echo chambers. Achieving impartiality involves balancing empathy with skepticism, fostering open dialogue while questioning entrenched beliefs.
bias vs impartiality Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com