Speculating about a pet's behavior often leads to misunderstanding their true needs and emotions. Focusing on observable actions and consistent patterns provides certainty and builds a stronger bond between owner and pet. Clear communication based on evidence enhances the pet's well-being and owner's confidence.
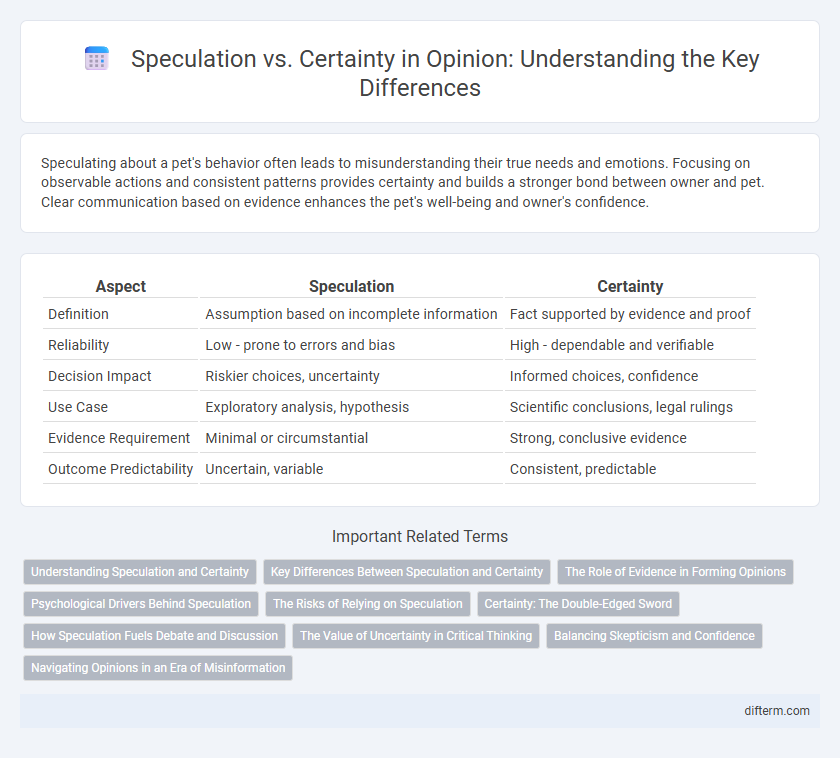
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Speculation | Certainty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assumption based on incomplete information | Fact supported by evidence and proof |
| Reliability | Low - prone to errors and bias | High - dependable and verifiable |
| Decision Impact | Riskier choices, uncertainty | Informed choices, confidence |
| Use Case | Exploratory analysis, hypothesis | Scientific conclusions, legal rulings |
| Evidence Requirement | Minimal or circumstantial | Strong, conclusive evidence |
| Outcome Predictability | Uncertain, variable | Consistent, predictable |
Understanding Speculation and Certainty
Speculation involves forming opinions or conclusions based on incomplete or uncertain information, often leading to diverse interpretations that lack definitive proof. Certainty, in contrast, is achieved through verified facts and clear evidence, providing a solid foundation for decision-making and belief. Understanding the difference between speculation and certainty is crucial for evaluating information critically and making informed judgments.
Key Differences Between Speculation and Certainty
Speculation involves forming opinions or hypotheses based on incomplete information, relying heavily on assumptions and potential outcomes that lack verification. Certainty is characterized by concrete evidence and irrefutable facts that support a definitive conclusion, minimizing doubt or ambiguity. The key difference lies in the level of evidence and assurance, with speculation embracing possibility and uncertainty while certainty demands proof and logical validation.
The Role of Evidence in Forming Opinions
Opinions grounded in evidence are more reliable and persuasive, as concrete data provides a foundation for informed judgment. Speculation often leads to bias and misinterpretation, whereas evidence-based opinions facilitate critical thinking and objective analysis. The integration of verified facts strengthens the credibility and validity of personal and public viewpoints.
Psychological Drivers Behind Speculation
Speculation thrives on uncertainty and the human brain's innate attraction to risk and reward, activating neural circuits associated with dopamine release. Psychological drivers such as overconfidence, fear of missing out (FOMO), and cognitive biases amplify speculative behaviors despite the availability of more certain investment options. These emotional and cognitive factors often override rational decision-making, leading investors to prioritize potential high returns over stable outcomes.
The Risks of Relying on Speculation
Relying on speculation introduces significant risks that can lead to financial instability and poor decision-making due to its inherent uncertainty and lack of concrete evidence. Market speculation often fuels volatility, increasing the likelihood of substantial losses when predictions fail to materialize. Emphasizing certainty through thorough research and verified data reduces exposure to these risks and promotes more reliable outcomes.
Certainty: The Double-Edged Sword
Certainty offers a strong foundation for decision-making, yet its rigid nature can blind individuals to alternative perspectives and emerging evidence. Excessive reliance on certainty may foster intellectual stagnation, limiting adaptability in complex, evolving situations. Balancing confidence with openness to uncertainty enhances critical thinking and promotes more nuanced, informed conclusions.
How Speculation Fuels Debate and Discussion
Speculation ignites robust debate by encouraging exploration of multiple perspectives and possibilities beyond established facts. It stimulates critical thinking and creativity, prompting participants to analyze underlying assumptions and potential outcomes. This dynamic exchange of ideas fosters a deeper understanding of complex issues, fueling ongoing dialogue and intellectual growth.
The Value of Uncertainty in Critical Thinking
Uncertainty plays a crucial role in critical thinking by encouraging open-mindedness and the continuous evaluation of evidence. Speculation allows for the exploration of multiple perspectives, fostering intellectual flexibility and preventing cognitive biases. Embracing uncertainty enhances decision-making by promoting adaptive reasoning and the willingness to revise conclusions as new information emerges.
Balancing Skepticism and Confidence
Balancing skepticism and confidence requires evaluating evidence critically while maintaining an open mind to possibilities beyond current knowledge. Embracing a healthy level of doubt prevents misconceptions driven by speculation, yet unwavering certainty can hinder growth and discovery. Optimal decision-making emerges from integrating cautious inquiry with measured conviction based on reliable data and rational analysis.
Navigating Opinions in an Era of Misinformation
Navigating opinions in an era of misinformation requires a critical evaluation of sources and recognition of biases that influence speculative claims. Distinguishing between speculation and certainty involves prioritizing evidence-based information and understanding the impact of echo chambers on public perception. Developing media literacy skills enhances the ability to discern factual accuracy amidst the proliferation of misleading content.
speculation vs certainty Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com