Opinions on pets often reveal a spectrum between consensus and polarization, as many agree on the benefits of companionship and emotional support pets provide. However, debates arise over issues such as pet ownership responsibilities, animal rights, and cultural differences in pet treatment, leading to polarized views. Understanding this balance helps promote respectful dialogue and informed choices in pet care and policies.
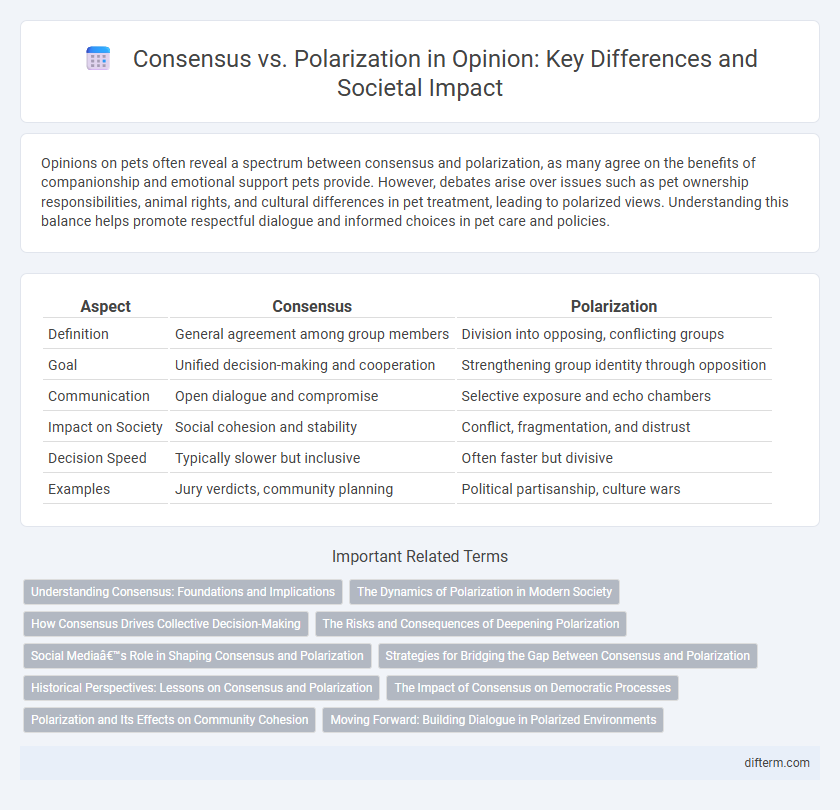
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Consensus | Polarization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | General agreement among group members | Division into opposing, conflicting groups |
| Goal | Unified decision-making and cooperation | Strengthening group identity through opposition |
| Communication | Open dialogue and compromise | Selective exposure and echo chambers |
| Impact on Society | Social cohesion and stability | Conflict, fragmentation, and distrust |
| Decision Speed | Typically slower but inclusive | Often faster but divisive |
| Examples | Jury verdicts, community planning | Political partisanship, culture wars |
Understanding Consensus: Foundations and Implications
Consensus emerges from shared values and mutual understanding, serving as a critical foundation for social cohesion and effective decision-making. It enables diverse groups to align interests, facilitating cooperative solutions that address complex challenges. Understanding the mechanisms and implications of consensus informs strategies to bridge divides and reduce polarization in political and organizational contexts.
The Dynamics of Polarization in Modern Society
Polarization in modern society intensifies as social media algorithms amplify echo chambers, reinforcing existing beliefs and reducing exposure to diverse perspectives. This dynamic fosters ideological segregation, where consensus becomes increasingly elusive due to heightened emotional engagement and group identity reinforcement. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing strategies to bridge divides and promote constructive dialogue.
How Consensus Drives Collective Decision-Making
Consensus fosters collective decision-making by aligning diverse perspectives toward a unified goal, enhancing collaboration and minimizing conflict. This process increases group cohesion and facilitates efficient implementation of decisions, as all members feel their viewpoints are acknowledged. Organizations and communities that prioritize consensus often achieve sustainable outcomes through shared commitment and mutual understanding.
The Risks and Consequences of Deepening Polarization
Deepening polarization exacerbates social fragmentation, undermining democratic processes and eroding public trust in institutions. Increasing ideological divides create echo chambers that stifle constructive dialogue and reinforce misinformation, leading to policy gridlocks and social unrest. The risk of entrenched polarization includes weakened social cohesion, heightened conflict, and reduced capacity for consensus-building essential for effective governance.
Social Media’s Role in Shaping Consensus and Polarization
Social media platforms amplify both consensus and polarization by shaping public discourse through algorithm-driven content curation that prioritizes engagement over accuracy. Echo chambers and filter bubbles intensify ideological divides, reinforcing users' existing beliefs and reducing exposure to diverse viewpoints. The interplay between viral misinformation and targeted communities further complicates efforts to build broad-based consensus in digital environments.
Strategies for Bridging the Gap Between Consensus and Polarization
Effective strategies for bridging the gap between consensus and polarization prioritize active listening and empathetic dialogue to foster mutual understanding across ideological divides. Implementing structured forums and deliberative democracy practices encourages collaboration, reducing misinformation and echo chambers that deepen polarization. Promoting inclusive policy-making and community engagement strengthens social cohesion by integrating diverse perspectives into shared decision-making processes.
Historical Perspectives: Lessons on Consensus and Polarization
Historical perspectives reveal that eras of strong consensus often coincide with social stability and effective governance, while periods marked by polarization frequently lead to social unrest and weakened institutions. Key examples include the post-World War II consensus fostering economic growth versus the polarization of the 1960s and its associated civil conflicts. Understanding these patterns highlights the importance of dialogue and compromise in maintaining cohesive societies and avoiding the detrimental impacts of deep divisions.
The Impact of Consensus on Democratic Processes
Consensus fosters cooperative decision-making in democratic processes by encouraging dialogue and mutual understanding among diverse groups. It enhances political stability and legitimacy by reducing conflicts and promoting policies that reflect collective interests. However, excessive consensus may suppress minority viewpoints, risking a democratic deficit through the marginalization of dissenting voices.
Polarization and Its Effects on Community Cohesion
Polarization intensifies social divisions by creating echo chambers where opposing groups rarely engage in constructive dialogue, leading to fragmented communities. This deepening divide erodes trust, reduces cooperation, and fuels conflict, impairing collective problem-solving efforts. The resulting social fragmentation threatens community cohesion, weakening the sense of shared identity and purpose essential for societal resilience.
Moving Forward: Building Dialogue in Polarized Environments
Building dialogue in polarized environments requires prioritizing active listening and creating spaces where diverse perspectives feel valued and understood. Emphasizing common goals and shared values fosters collaboration despite deep ideological divides. Strategies like facilitated discussions and community engagement break down barriers, enabling progress through mutual respect and empathy.
consensus vs polarization Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com