Sentiment refers to the emotional response or feeling someone has toward a pet, often expressed through affection or joy. Attitude encompasses a broader evaluation, including beliefs, feelings, and behavioral tendencies toward animals. Understanding the difference between sentiment and attitude helps in accurately measuring pet owners' perspectives and their motivations for pet care.
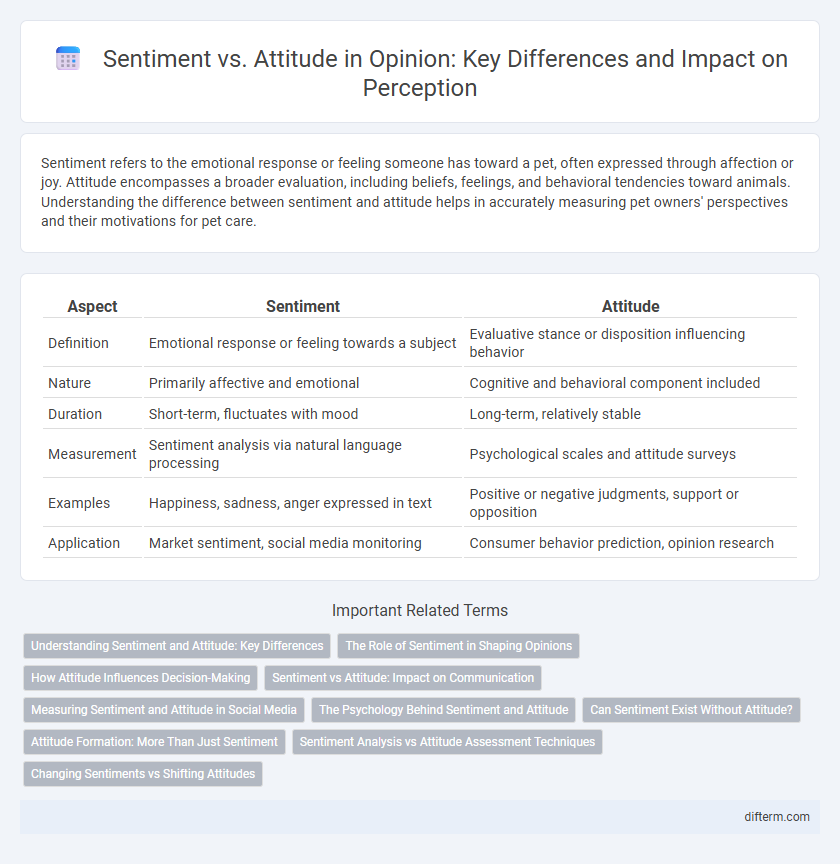
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sentiment | Attitude |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional response or feeling towards a subject | Evaluative stance or disposition influencing behavior |
| Nature | Primarily affective and emotional | Cognitive and behavioral component included |
| Duration | Short-term, fluctuates with mood | Long-term, relatively stable |
| Measurement | Sentiment analysis via natural language processing | Psychological scales and attitude surveys |
| Examples | Happiness, sadness, anger expressed in text | Positive or negative judgments, support or opposition |
| Application | Market sentiment, social media monitoring | Consumer behavior prediction, opinion research |
Understanding Sentiment and Attitude: Key Differences
Sentiment reflects an individual's immediate emotional response to a specific stimulus, often measured as positive, negative, or neutral feelings. Attitude encompasses a deeper, more enduring evaluation shaped by beliefs, experiences, and values, influencing consistent behavior over time. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate market analysis, customer feedback interpretation, and psychological assessments.
The Role of Sentiment in Shaping Opinions
Sentiment plays a crucial role in shaping opinions by influencing emotional reactions to information and experiences, which often guide individual preferences and judgments. Positive or negative sentiments can amplify or diminish the perceived value of an idea or event, making them central to opinion formation. Unlike attitudes, which are relatively stable predispositions, sentiments are more immediate emotional responses that directly impact how opinions are constructed and expressed.
How Attitude Influences Decision-Making
Attitude significantly influences decision-making by shaping individuals' perceptions and emotional responses to choices, often guiding behavior more reliably than transient sentiments. Unlike fleeting sentiments, attitudes represent enduring evaluations that predispose individuals to consistent decision patterns based on past experiences and beliefs. Understanding the role of attitude in decision-making provides critical insights into predicting consumer behavior and tailoring effective marketing strategies.
Sentiment vs Attitude: Impact on Communication
Sentiment shapes the emotional tone of communication, influencing how messages are perceived and received, while attitude reflects underlying beliefs that drive repetitive behavior in interactions. Effective communication relies on recognizing sentiment to manage immediate emotional responses and understanding attitudes to predict long-term conversational dynamics. Misalignment between expressed sentiment and true attitude can lead to misinterpretations, reducing message clarity and relational trust.
Measuring Sentiment and Attitude in Social Media
Measuring sentiment in social media involves analyzing emotional tones through natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to classify posts as positive, negative, or neutral. Attitude measurement extends beyond surface emotions by capturing underlying opinions and behavioral intentions using sentiment analysis combined with contextual and interaction data. Accurate sentiment and attitude assessment enables brands and researchers to gauge public opinion trends, identify influencers, and tailor communication strategies effectively.
The Psychology Behind Sentiment and Attitude
Sentiment reflects the emotional response toward an entity, rooted in affective psychology, while attitude encompasses cognitive beliefs, feelings, and behavioral intentions, demonstrating a complex psychological framework. Understanding the interplay between sentiment and attitude reveals how emotions influence perceptions and decision-making processes. Research in social psychology highlights that attitudes often guide behavior more reliably than transient sentiments, emphasizing the importance of cognitive evaluation in shaping human responses.
Can Sentiment Exist Without Attitude?
Sentiment and attitude are closely related, yet distinct psychological constructs; sentiment refers to the emotional response or feeling toward an object, while attitude encompasses a broader evaluative stance that includes beliefs, feelings, and behavioral intentions. Sentiment can exist without a fully formed attitude when an individual experiences an immediate emotional reaction lacking comprehensive cognitive evaluation or judgment. This distinction is critical for fields like marketing and social psychology, where understanding the interplay between raw emotions and structured attitudes informs strategies for influencing consumer behavior and public opinion.
Attitude Formation: More Than Just Sentiment
Attitude formation extends beyond mere sentiment by incorporating cognitive evaluations, beliefs, and experiences that shape an individual's response to an object or idea. Unlike sentiment, which primarily reflects emotional reactions, attitudes integrate deeper reasoning and knowledge, influencing long-term behaviors and decisions. This complex interplay of affective and cognitive components highlights the multifaceted nature of how attitudes develop and persist over time.
Sentiment Analysis vs Attitude Assessment Techniques
Sentiment analysis primarily quantifies emotions expressed in text, categorizing content as positive, negative, or neutral to gauge public opinion effectively. Attitude assessment techniques delve deeper by evaluating underlying beliefs, preferences, and behavioral intentions, providing nuanced insights beyond mere emotional polarity. Combining both approaches enhances the understanding of user perspectives, offering comprehensive data for informed decision-making in marketing and social research.
Changing Sentiments vs Shifting Attitudes
Changing sentiments often reflect temporary emotional reactions influenced by current events or immediate experiences. Shifting attitudes represent deeper, more stable transformations in beliefs and values that develop over time through reflection and social learning. Understanding the difference between these two is crucial for assessing long-term behavior changes in consumers or social groups.
Sentiment vs Attitude Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com