Antioxidants neutralize free radicals, protecting cells from oxidative stress and damage, which helps prevent chronic diseases. Anti-inflammatory agents reduce inflammation by inhibiting pathways that trigger immune responses, alleviating pain and swelling. Both antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds work synergistically to promote overall health and reduce the risk of disease progression.
Table of Comparison
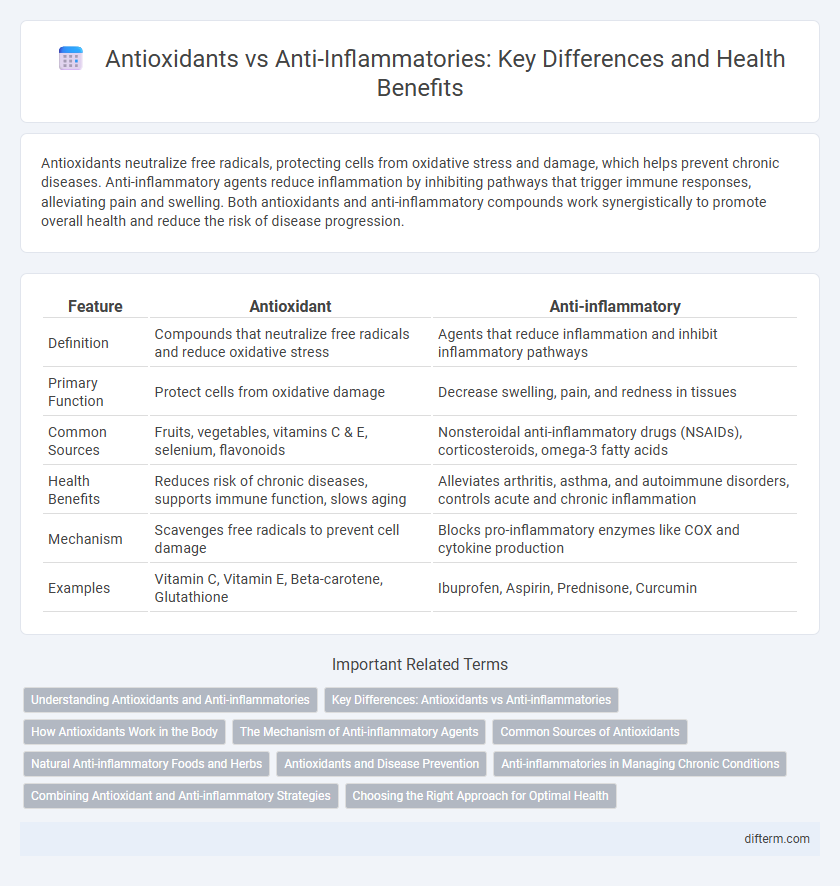
| Feature | Antioxidant | Anti-inflammatory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compounds that neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress | Agents that reduce inflammation and inhibit inflammatory pathways |
| Primary Function | Protect cells from oxidative damage | Decrease swelling, pain, and redness in tissues |
| Common Sources | Fruits, vegetables, vitamins C & E, selenium, flavonoids | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, omega-3 fatty acids |
| Health Benefits | Reduces risk of chronic diseases, supports immune function, slows aging | Alleviates arthritis, asthma, and autoimmune disorders, controls acute and chronic inflammation |
| Mechanism | Scavenges free radicals to prevent cell damage | Blocks pro-inflammatory enzymes like COX and cytokine production |
| Examples | Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Beta-carotene, Glutathione | Ibuprofen, Aspirin, Prednisone, Curcumin |
Understanding Antioxidants and Anti-inflammatories
Antioxidants neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress linked to chronic diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular conditions. Anti-inflammatories target inflammation pathways to alleviate symptoms in conditions like arthritis and autoimmune disorders. Both compounds support cellular health by preventing damage and modulating immune responses, playing crucial roles in disease prevention and management.
Key Differences: Antioxidants vs Anti-inflammatories
Antioxidants neutralize free radicals to prevent oxidative stress and cellular damage, while anti-inflammatories reduce inflammation by inhibiting inflammatory pathways in the body. Antioxidants are found in foods rich in vitamins C and E, selenium, and flavonoids, whereas anti-inflammatory agents include medications like NSAIDs and natural compounds such as curcumin and omega-3 fatty acids. Both play crucial roles in chronic disease prevention, but antioxidants primarily target oxidative damage, while anti-inflammatories focus on controlling inflammatory responses.
How Antioxidants Work in the Body
Antioxidants neutralize free radicals by donating electrons, preventing oxidative damage to cells and tissues. This reduction in oxidative stress supports cellular health and lowers the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disorders and cancer. Their mechanism complements anti-inflammatory processes by protecting cellular components from damage that triggers inflammation.
The Mechanism of Anti-inflammatory Agents
Anti-inflammatory agents work by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enzymes such as cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase (LOX), reducing oxidative stress and cellular signaling pathways that trigger inflammation. These agents target molecular pathways including nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), which regulate the expression of inflammatory mediators. By modulating immune cell activity and suppressing inflammatory gene expression, anti-inflammatory compounds alleviate tissue damage and chronic inflammation linked to diseases.
Common Sources of Antioxidants
Common sources of antioxidants include berries, dark chocolate, nuts, and leafy green vegetables, which contain high levels of vitamins C and E, flavonoids, and polyphenols. These antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and cellular damage. Incorporating foods like blueberries, spinach, and almonds into the diet supports overall health and complements anti-inflammatory strategies.
Natural Anti-inflammatory Foods and Herbs
Natural anti-inflammatory foods and herbs such as turmeric, ginger, berries, and leafy greens contain potent antioxidants that help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. These compounds inhibit pro-inflammatory pathways and neutralize free radicals, promoting cellular health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Incorporating foods rich in antioxidants like polyphenols, flavonoids, and vitamin C supports the body's natural defenses against inflammation and oxidative damage.
Antioxidants and Disease Prevention
Antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals, which can cause oxidative stress and damage cells, leading to chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. By reducing oxidative damage, antioxidants support the body's natural defense systems and help maintain cellular health. Foods rich in antioxidants, including berries, nuts, and green leafy vegetables, are essential for disease prevention and overall well-being.
Anti-inflammatories in Managing Chronic Conditions
Anti-inflammatory agents play a crucial role in managing chronic conditions by reducing inflammation that contributes to disease progression in ailments such as arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes. Unlike antioxidants that primarily neutralize free radicals, anti-inflammatories target the molecular pathways involved in inflammatory responses, thereby alleviating pain and preventing tissue damage. Effective use of anti-inflammatory medications or natural compounds can improve patient outcomes and quality of life by controlling chronic inflammation at its source.
Combining Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Strategies
Combining antioxidant and anti-inflammatory strategies enhances cellular protection by reducing oxidative stress and modulating immune response, which helps prevent chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. Nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin E, and polyphenols work synergistically with anti-inflammatory agents such as omega-3 fatty acids and curcumin to decrease inflammation and neutralize free radicals. This integrative approach supports overall health by improving immune function and reducing tissue damage.
Choosing the Right Approach for Optimal Health
Selecting the right approach between antioxidant and anti-inflammatory strategies depends on individual health goals and underlying conditions. Antioxidants neutralize free radicals to prevent cellular damage, while anti-inflammatory measures reduce chronic inflammation associated with diseases like arthritis and heart disease. Integrating both approaches through diet rich in fruits, vegetables, omega-3 fatty acids, and polyphenols supports comprehensive health optimization.
Antioxidant vs Anti-inflammatory Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com