Fermented foods contain beneficial probiotics that support gut health and boost the immune system, while pickled foods are preserved in vinegar and often lack live cultures but offer antioxidants and can aid digestion. Fermentation enhances nutrient availability and promotes a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which is crucial for pets' overall well-being. Choosing fermented over pickled foods can provide more comprehensive health benefits for pets by improving digestion and strengthening their natural defenses.
Table of Comparison
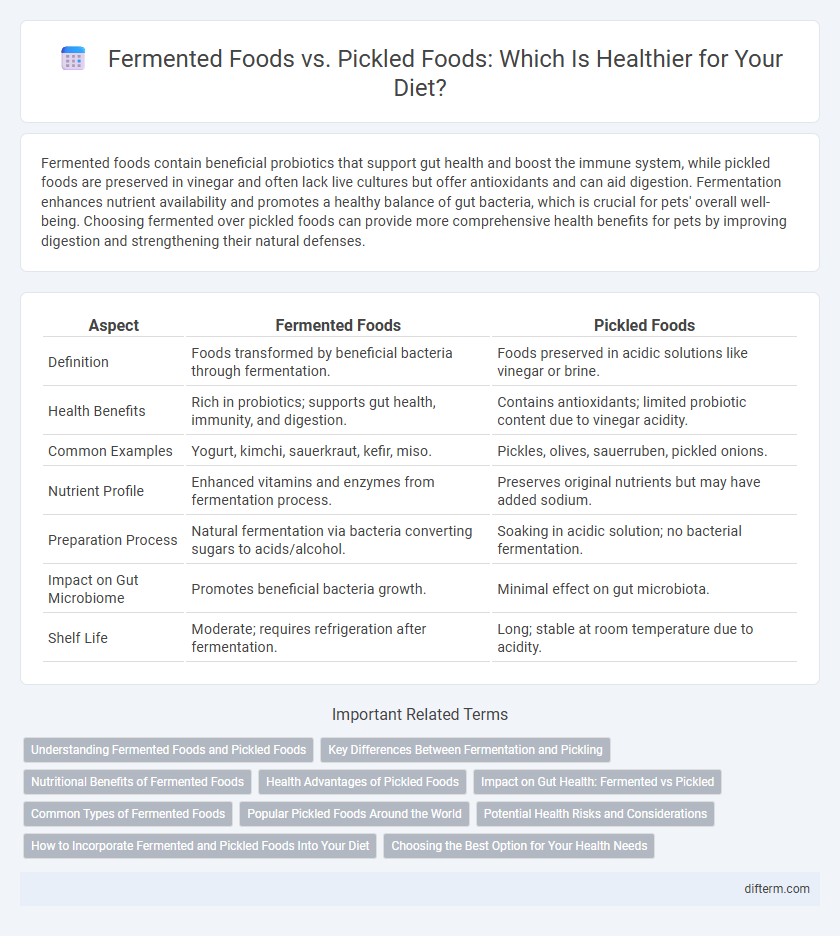
| Aspect | Fermented Foods | Pickled Foods |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Foods transformed by beneficial bacteria through fermentation. | Foods preserved in acidic solutions like vinegar or brine. |
| Health Benefits | Rich in probiotics; supports gut health, immunity, and digestion. | Contains antioxidants; limited probiotic content due to vinegar acidity. |
| Common Examples | Yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, kefir, miso. | Pickles, olives, sauerruben, pickled onions. |
| Nutrient Profile | Enhanced vitamins and enzymes from fermentation process. | Preserves original nutrients but may have added sodium. |
| Preparation Process | Natural fermentation via bacteria converting sugars to acids/alcohol. | Soaking in acidic solution; no bacterial fermentation. |
| Impact on Gut Microbiome | Promotes beneficial bacteria growth. | Minimal effect on gut microbiota. |
| Shelf Life | Moderate; requires refrigeration after fermentation. | Long; stable at room temperature due to acidity. |
Understanding Fermented Foods and Pickled Foods
Fermented foods, such as yogurt and kimchi, undergo a controlled microbial process that enhances beneficial probiotics, improving gut health and digestion. Pickled foods are typically preserved in an acidic solution like vinegar, which extends shelf-life without necessarily promoting probiotic growth. Understanding the distinction between fermentation and pickling helps optimize dietary choices for microbiome support and nutrient absorption.
Key Differences Between Fermentation and Pickling
Fermentation involves natural bacterial growth that converts sugars into beneficial probiotics, enhancing gut health and nutrient absorption, while pickling is a preservation method using acidic solutions like vinegar to inhibit microbial growth without producing probiotics. Fermented foods such as yogurt, sauerkraut, and kimchi contain live microorganisms that promote digestive health, whereas pickled foods like cucumbers or beets are preserved for flavor and shelf life but typically lack live cultures. Understanding these differences helps in choosing foods that contribute either to gut microbiome support or long-term preservation.
Nutritional Benefits of Fermented Foods
Fermented foods are rich in probiotics, which enhance gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and improving digestion. These foods also increase the bioavailability of nutrients like vitamins B and K, essential for energy metabolism and blood clotting. Unlike pickled foods, which are preserved primarily with vinegar and often lack live cultures, fermented foods provide live enzymes and organic acids that support immune function and overall wellness.
Health Advantages of Pickled Foods
Pickled foods contain beneficial probiotics that support gut health by promoting a diverse microbiome and enhancing digestion. The vinegar used in pickling provides antioxidants and helps regulate blood sugar levels, contributing to improved metabolic health. Rich in essential vitamins and minerals, pickled foods also aid in boosting the immune system and reducing inflammation.
Impact on Gut Health: Fermented vs Pickled
Fermented foods like yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut contain live probiotics that enhance gut microbiota diversity and improve digestion. Pickled foods, typically preserved in vinegar, lack live beneficial bacteria but still provide antioxidants and can aid in digestion. Consuming fermented foods regularly supports a balanced gut ecosystem, while pickled foods offer limited gut health benefits without live microbial action.
Common Types of Fermented Foods
Common types of fermented foods include yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, miso, tempeh, and kefir, each rich in probiotics that support gut health. These foods undergo natural microbial fermentation, which enhances nutrient absorption and promotes beneficial bacteria growth. Unlike pickled foods that are preserved mainly in vinegar, fermented foods rely on live cultures to transform their ingredients.
Popular Pickled Foods Around the World
Popular pickled foods around the world include kimchi from Korea, sauerkraut from Germany, and dill pickles from the United States, each offering unique health benefits due to their fermentation or pickling processes. Kimchi contains probiotics that support gut health, while sauerkraut provides fiber and vitamins, and dill pickles offer antioxidants and low-calorie hydration. Understanding the differences between fermented and pickled foods helps consumers choose options that best support digestion and overall wellness.
Potential Health Risks and Considerations
Fermented foods contain beneficial probiotics that can improve gut health, but improper fermentation can lead to harmful bacteria growth and foodborne illness. Pickled foods are preserved in vinegar or brine, reducing harmful microbes but often containing high levels of sodium, which may increase blood pressure and cardiovascular risk. Both fermented and pickled products should be consumed in moderation and prepared hygienically to minimize potential health risks.
How to Incorporate Fermented and Pickled Foods Into Your Diet
Incorporating fermented and pickled foods into your diet can enhance gut health and diversify your nutrient intake. Start by adding small servings of kimchi, sauerkraut, or yogurt to meals, gradually increasing portions to allow your digestive system to adjust. Use pickled vegetables like cucumbers or beets as flavorful side dishes or salad toppings to benefit from their probiotic and antioxidant properties.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Health Needs
Fermented foods like yogurt and kimchi contain beneficial probiotics that support gut health and improve digestion, while pickled foods, typically preserved in vinegar, offer antioxidants but may lack live cultures. Choosing the best option depends on your health goals; for enhancing microbiome diversity and immune function, fermented foods are preferable, whereas pickled foods provide flavor and some nutrients with lower probiotic benefits. Monitoring sodium intake is crucial with both options, as excessive salt in pickled products can impact cardiovascular health.
Fermented Foods vs Pickled Foods Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com