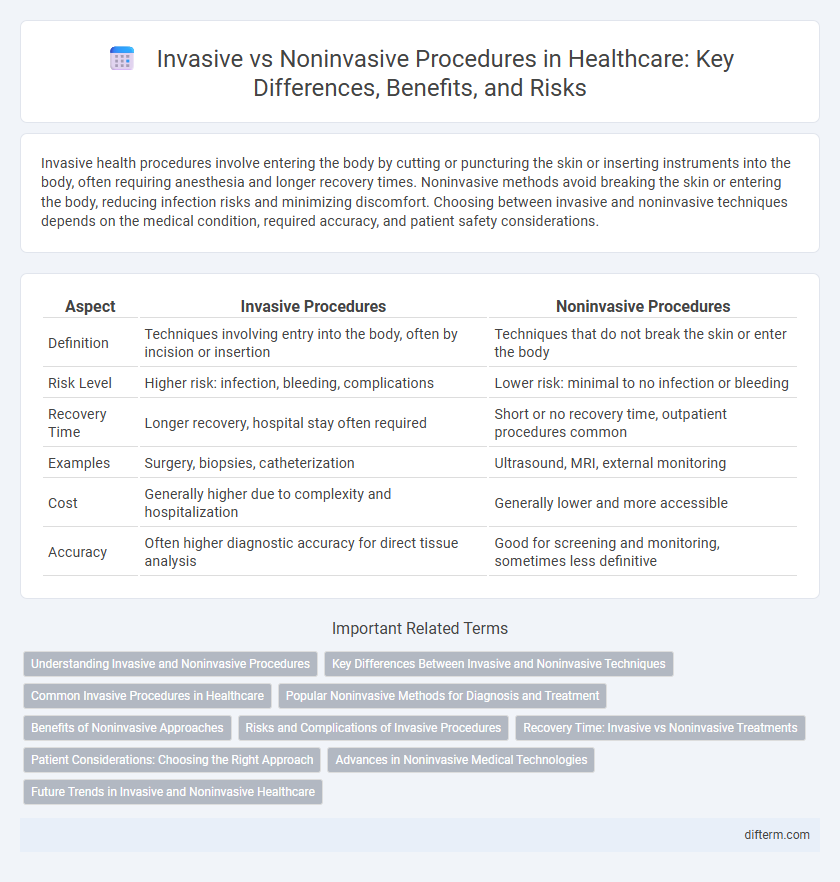
Invasive health procedures involve entering the body by cutting or puncturing the skin or inserting instruments into the body, often requiring anesthesia and longer recovery times. Noninvasive methods avoid breaking the skin or entering the body, reducing infection risks and minimizing discomfort. Choosing between invasive and noninvasive techniques depends on the medical condition, required accuracy, and patient safety considerations.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Invasive Procedures | Noninvasive Procedures |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Techniques involving entry into the body, often by incision or insertion | Techniques that do not break the skin or enter the body |
| Risk Level | Higher risk: infection, bleeding, complications | Lower risk: minimal to no infection or bleeding |
| Recovery Time | Longer recovery, hospital stay often required | Short or no recovery time, outpatient procedures common |
| Examples | Surgery, biopsies, catheterization | Ultrasound, MRI, external monitoring |
| Cost | Generally higher due to complexity and hospitalization | Generally lower and more accessible |
| Accuracy | Often higher diagnostic accuracy for direct tissue analysis | Good for screening and monitoring, sometimes less definitive |
Understanding Invasive and Noninvasive Procedures
Invasive procedures involve entering the body through incisions or punctures to diagnose or treat conditions, often requiring anesthesia and longer recovery times. Noninvasive procedures use external methods like imaging or surface treatments, minimizing risk and discomfort while allowing quicker patient recovery. Understanding the differences helps in selecting appropriate medical interventions based on condition severity, patient health status, and desired outcomes.
Key Differences Between Invasive and Noninvasive Techniques
Invasive techniques involve entering the body through incisions or injections, enabling direct access to organs or tissues for diagnosis or treatment, whereas noninvasive methods assess the body externally without breaching skin or membranes. Key differences include the risk of infection, recovery time, and the precision of results, with invasive procedures often providing more detailed information but requiring longer healing periods. Noninvasive techniques, such as ultrasound or MRI, offer safer, less painful options with quicker recovery while sometimes offering less detailed data compared to invasive alternatives like biopsies or endoscopies.
Common Invasive Procedures in Healthcare
Common invasive procedures in healthcare include surgeries such as laparotomy, biopsies involving needle or surgical tissue extraction, and catheter insertions for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. These procedures require penetration of the skin or body cavities, increasing the risk of infection and necessitating sterile techniques and often anesthesia. Invasive methods contrast with noninvasive techniques by providing direct access to internal organs or tissues, essential for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of various medical conditions.
Popular Noninvasive Methods for Diagnosis and Treatment
Popular noninvasive methods for diagnosis and treatment in health include imaging techniques such as ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans that provide detailed internal views without surgery. Noninvasive treatments like laser therapy, physical therapy, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) offer effective pain relief and tissue healing without incisions. These approaches reduce patient risk, recovery time, and healthcare costs compared to invasive procedures.
Benefits of Noninvasive Approaches
Noninvasive approaches in healthcare minimize patient discomfort and reduce the risk of infections compared to invasive procedures. Techniques such as imaging, external monitoring, and topical treatments offer faster recovery times and lower healthcare costs. These methods enhance patient safety while providing accurate diagnostic and therapeutic outcomes.
Risks and Complications of Invasive Procedures
Invasive procedures carry higher risks and complications compared to noninvasive methods due to the breach of skin or body cavities, increasing chances of infection, bleeding, and organ damage. Common complications include adverse reactions to anesthesia, post-operative pain, and prolonged recovery time, which can lead to hospital-acquired infections or sepsis. Understanding these risks is crucial for informed consent and choosing appropriate interventions in medical practice.
Recovery Time: Invasive vs Noninvasive Treatments
Invasive treatments typically involve longer recovery times due to tissue disruption and the risk of complications, often requiring weeks to months for full healing. Noninvasive treatments generally allow for faster recovery, minimizing hospital stays and enabling quicker return to daily activities. Choosing noninvasive procedures reduces post-treatment pain and accelerates rehabilitation, which is critical for patient quality of life and healthcare resource optimization.
Patient Considerations: Choosing the Right Approach
Patient considerations for choosing between invasive and noninvasive health procedures revolve around risk assessment, recovery time, and overall effectiveness. Invasive methods often involve higher risks of infection and longer recovery but may be necessary for accurate diagnosis or treatment, while noninvasive approaches minimize physical trauma and typically allow quicker return to daily activities. Evaluating individual health conditions, patient preferences, and potential outcomes guides healthcare providers in recommending the optimal approach.
Advances in Noninvasive Medical Technologies
Recent advances in noninvasive medical technologies have revolutionized diagnostic and therapeutic procedures by minimizing patient risk and recovery time. Innovations such as wearable biosensors, high-resolution imaging techniques like MRI and ultrasound, and noninvasive blood glucose monitoring devices have enhanced early disease detection and personalized treatment plans. These technologies contribute to improved patient outcomes while reducing the need for invasive surgeries and biopsies.
Future Trends in Invasive and Noninvasive Healthcare
Advancements in wearable technology and AI-driven diagnostics are poised to revolutionize noninvasive healthcare by enabling continuous monitoring and early disease detection without discomfort. Minimally invasive techniques, such as robotic-assisted surgeries and precision-targeted drug delivery, are expected to reduce recovery time and improve patient outcomes significantly. Integration of big data analytics with noninvasive imaging and biosensing will pave the way for personalized treatment plans and proactive health management in the near future.
Invasive vs Noninvasive Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com