Functional foods provide essential nutrients and bioactive compounds that promote overall health and reduce disease risk through regular consumption. Nutraceuticals are concentrated forms of bioactive substances derived from foods, designed to offer therapeutic benefits beyond basic nutrition. Both play crucial roles in preventive healthcare by enhancing bodily functions and supporting immune health.
Table of Comparison
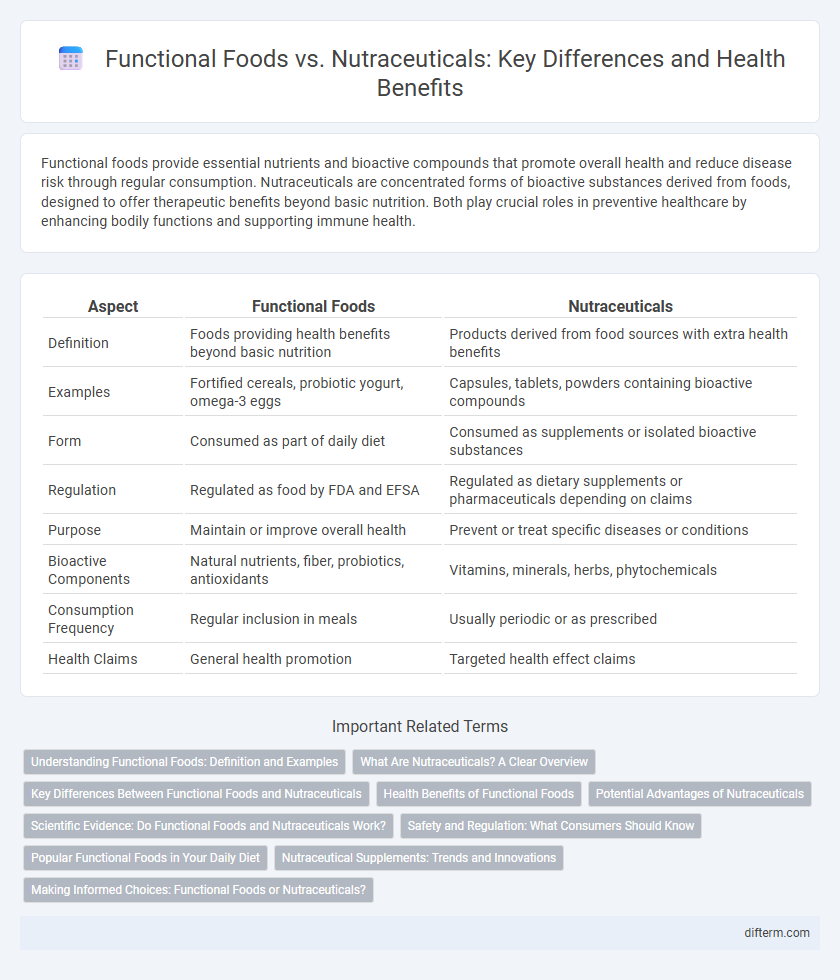
| Aspect | Functional Foods | Nutraceuticals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Foods providing health benefits beyond basic nutrition | Products derived from food sources with extra health benefits |
| Examples | Fortified cereals, probiotic yogurt, omega-3 eggs | Capsules, tablets, powders containing bioactive compounds |
| Form | Consumed as part of daily diet | Consumed as supplements or isolated bioactive substances |
| Regulation | Regulated as food by FDA and EFSA | Regulated as dietary supplements or pharmaceuticals depending on claims |
| Purpose | Maintain or improve overall health | Prevent or treat specific diseases or conditions |
| Bioactive Components | Natural nutrients, fiber, probiotics, antioxidants | Vitamins, minerals, herbs, phytochemicals |
| Consumption Frequency | Regular inclusion in meals | Usually periodic or as prescribed |
| Health Claims | General health promotion | Targeted health effect claims |
Understanding Functional Foods: Definition and Examples
Functional foods are natural or fortified foods that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition by promoting optimal body function and reducing disease risk. Examples include yogurt with probiotics, enriched with live bacteria to improve gut health, and omega-3 fortified eggs that support cardiovascular wellness. These foods contain bioactive compounds such as vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fibers that enhance physiological functions and contribute to overall well-being.
What Are Nutraceuticals? A Clear Overview
Nutraceuticals are products derived from food sources that provide extra health benefits beyond basic nutrition, often used to prevent or treat chronic diseases. They include dietary supplements, herbal products, vitamins, minerals, and fortified foods rich in bioactive compounds such as antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids. Distinct from functional foods, nutraceuticals are typically consumed in concentrated forms to deliver targeted therapeutic effects.
Key Differences Between Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals
Functional foods are whole or fortified foods that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition, such as fortified cereals rich in vitamins or probiotics in yogurt, while nutraceuticals are concentrated bioactive compounds extracted or isolated from foods, like omega-3 capsules or herbal supplements. Functional foods are consumed as part of the daily diet and offer a synergistic effect of various nutrients, whereas nutraceuticals are often taken in dosage forms like pills or powders targeting specific health conditions. The key difference lies in their form, regulatory status, and mode of consumption, with functional foods integrated into meals and nutraceuticals marketed as supplements or therapeutic agents.
Health Benefits of Functional Foods
Functional foods provide a wide range of health benefits, including improved digestion, enhanced immune function, and reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. Rich in bioactive compounds like antioxidants, vitamins, and probiotics, these foods support overall well-being by promoting cellular health and reducing inflammation. Consuming functional foods regularly can lead to better nutrient absorption and aid in maintaining healthy body weight and metabolic balance.
Potential Advantages of Nutraceuticals
Nutraceuticals offer targeted health benefits by providing concentrated bioactive compounds that support disease prevention and overall wellness. They often contain specific vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and herbal extracts that enhance immune function, reduce inflammation, and improve metabolic health. Compared to general functional foods, nutraceuticals deliver higher potency and scientific precision, making them valuable for therapeutic support and personalized nutrition strategies.
Scientific Evidence: Do Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals Work?
Functional foods contain bioactive compounds that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition, supported by numerous clinical studies demonstrating reduced risk of chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Nutraceuticals, often concentrated forms of bioactive ingredients, have shown efficacy in improving specific health conditions, such as omega-3 fatty acids reducing inflammation and certain probiotics enhancing gut health. Scientific evidence underscores the importance of dosage, bioavailability, and individual variability in determining the effectiveness of both functional foods and nutraceuticals.
Safety and Regulation: What Consumers Should Know
Functional foods and nutraceuticals undergo distinct regulatory scrutiny to ensure consumer safety; functional foods are typically regulated as conventional foods, requiring proof of safety and accurate labeling, while nutraceuticals often fall under dietary supplement regulations with less stringent pre-market approval. Consumers should verify product claims against regulatory standards set by agencies such as the FDA or EFSA, which monitor adverse effects and validate health benefits. Awareness of these regulatory differences is essential to avoid misleading claims and ensure safe consumption.
Popular Functional Foods in Your Daily Diet
Popular functional foods in your daily diet include yogurt enriched with probiotics, fortified cereals packed with vitamins and minerals, and fatty fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These foods provide essential nutrients that support digestion, boost immune function, and promote heart health. Incorporating functional foods consistently helps optimize overall well-being by delivering bioactive compounds beyond basic nutrition.
Nutraceutical Supplements: Trends and Innovations
Nutraceutical supplements are rapidly evolving with innovations such as enhanced bioavailability, personalized formulations, and incorporation of probiotics and adaptogens to support immune and cognitive health. Market trends indicate a significant rise in consumer demand for plant-based, clinically validated ingredients that offer preventive health benefits beyond basic nutrition. Advances in delivery systems like nanoencapsulation and sustained-release technologies are optimizing nutrient absorption and efficacy in nutraceutical products.
Making Informed Choices: Functional Foods or Nutraceuticals?
Functional foods contain natural or fortified ingredients that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition, supporting immune function and reducing disease risk. Nutraceuticals are concentrated bioactive compounds, often in supplement form, designed for targeted therapeutic effects and enhanced bioavailability. Evaluating scientific evidence, individual health needs, and regulatory standards helps make informed choices between these options for optimal wellness.
Functional Foods vs Nutraceuticals Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com