Centralization in government pet policies streamlines decision-making and enforces uniform standards across regions, enhancing control and consistency. Decentralization allows local authorities to tailor pet regulations to community needs, promoting flexibility and responsiveness. Balancing these approaches can optimize governance efficiency while addressing diverse local concerns effectively.
Table of Comparison
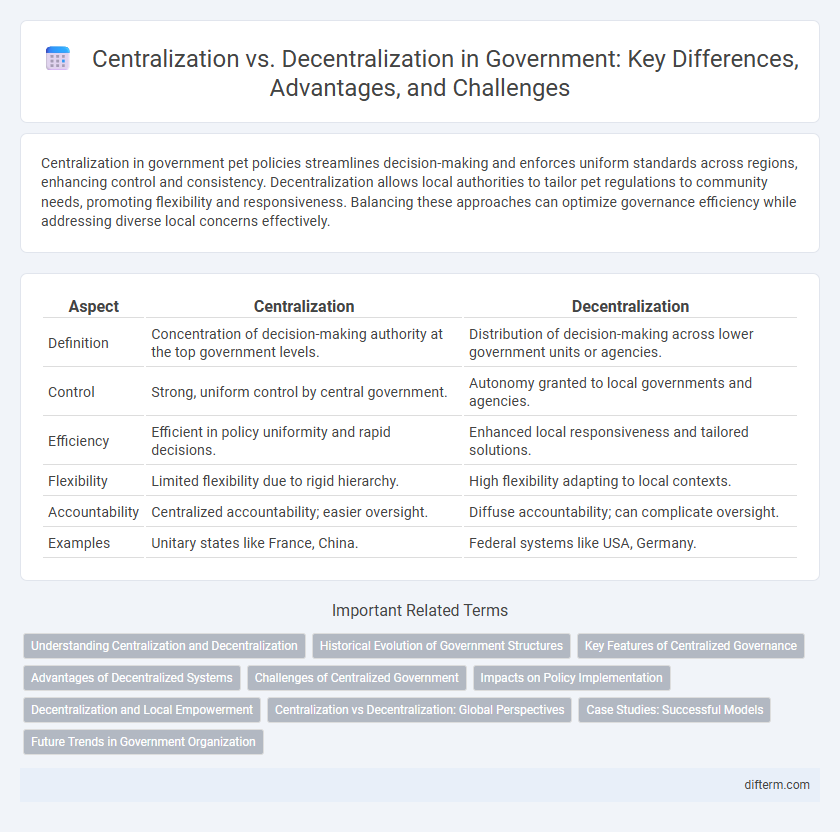
| Aspect | Centralization | Decentralization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concentration of decision-making authority at the top government levels. | Distribution of decision-making across lower government units or agencies. |
| Control | Strong, uniform control by central government. | Autonomy granted to local governments and agencies. |
| Efficiency | Efficient in policy uniformity and rapid decisions. | Enhanced local responsiveness and tailored solutions. |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility due to rigid hierarchy. | High flexibility adapting to local contexts. |
| Accountability | Centralized accountability; easier oversight. | Diffuse accountability; can complicate oversight. |
| Examples | Unitary states like France, China. | Federal systems like USA, Germany. |
Understanding Centralization and Decentralization
Centralization consolidates decision-making authority within a single central government body, enhancing uniform policy implementation and control. Decentralization distributes power across various regional or local governments, promoting responsiveness and adaptability to diverse community needs. Understanding the balance between centralization and decentralization is crucial for designing efficient governance structures that optimize resource allocation and public service delivery.
Historical Evolution of Government Structures
Government structures evolved from highly centralized monarchies in ancient civilizations to more decentralized forms seen in federal systems like the United States. The shift towards decentralization emerged during the Enlightenment, promoting local governance and citizen participation as seen in the development of democratic institutions. Modern governments balance central authority with decentralized autonomy to enhance efficiency, accountability, and responsiveness.
Key Features of Centralized Governance
Centralized governance concentrates decision-making authority within a single, central government body, enabling uniform policy implementation and streamlined administrative processes. Key features include strict hierarchical control, reduced regional autonomy, and enhanced coordination across different sectors and agencies. This system facilitates efficient resource allocation and consistent enforcement of laws nationwide.
Advantages of Decentralized Systems
Decentralized government systems enhance local autonomy, allowing communities to tailor policies and services to their specific needs, which increases responsiveness and citizen satisfaction. These systems promote greater accountability and transparency by distributing decision-making power closer to the population impacted, reducing bureaucratic inefficiencies. Furthermore, decentralization fosters innovation and competition among regions, leading to improved public service delivery and more effective resource allocation.
Challenges of Centralized Government
Centralized governments often face challenges such as bureaucratic inefficiency, slow decision-making processes, and limited responsiveness to local needs. Concentrated power can lead to reduced transparency and increased risk of corruption due to lack of oversight at lower administrative levels. This central concentration may also hinder innovation and adaptability in addressing diverse regional issues within a nation.
Impacts on Policy Implementation
Centralization in government streamlines decision-making, enabling uniform policy implementation and consistency across regions, which enhances efficiency and control. Decentralization disperses authority to local governments, allowing tailored policies that address regional needs and improve responsiveness, but may cause inconsistencies and coordination challenges. The choice between centralization and decentralization directly impacts the effectiveness, adaptability, and equity of policy outcomes.
Decentralization and Local Empowerment
Decentralization enhances government effectiveness by transferring decision-making authority to local governments, promoting responsiveness to community needs and fostering innovation. Local empowerment strengthens democratic participation, enabling citizens to influence policies directly and hold officials accountable. This approach improves public service delivery and supports sustainable development by aligning governance with regional priorities and resources.
Centralization vs Decentralization: Global Perspectives
Centralization in government consolidates decision-making authority within a single central entity, enabling uniform policy enforcement and streamlined governance, as observed in countries like China and France. Decentralization disperses power to regional or local authorities, fostering responsiveness and local autonomy, exemplified by the federal systems of the United States and Germany. Comparative analysis highlights that centralized systems often achieve cohesive national strategies, while decentralized structures enhance flexibility and accommodate diverse regional needs.
Case Studies: Successful Models
The Nordic countries exemplify successful decentralization models, where local governments have significant autonomy in welfare and education services, resulting in high public satisfaction and efficient resource allocation. In contrast, Singapore's highly centralized government structure enables swift policy implementation and coordinated urban development that drives economic growth and social stability. These case studies highlight the balance between centralized control for uniformity and decentralized governance for local adaptability, emphasizing context-dependent governance effectiveness.
Future Trends in Government Organization
Emerging trends in government organization emphasize a nuanced balance between centralization and decentralization to enhance efficiency and citizen engagement. Advances in digital governance and data analytics enable decentralized decision-making while ensuring centralized oversight and policy coherence. Future government structures will likely integrate hybrid models that leverage technology to optimize resource allocation and responsiveness at multiple administrative levels.
Centralization vs Decentralization Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com