Government strategies leverage hard power through military force and economic sanctions to enforce policies and influence other nations decisively. Soft power relies on cultural diplomacy, international aid, and the promotion of values to shape global perceptions and foster cooperation. Balancing these approaches enhances a government's ability to achieve strategic objectives while maintaining international legitimacy.
Table of Comparison
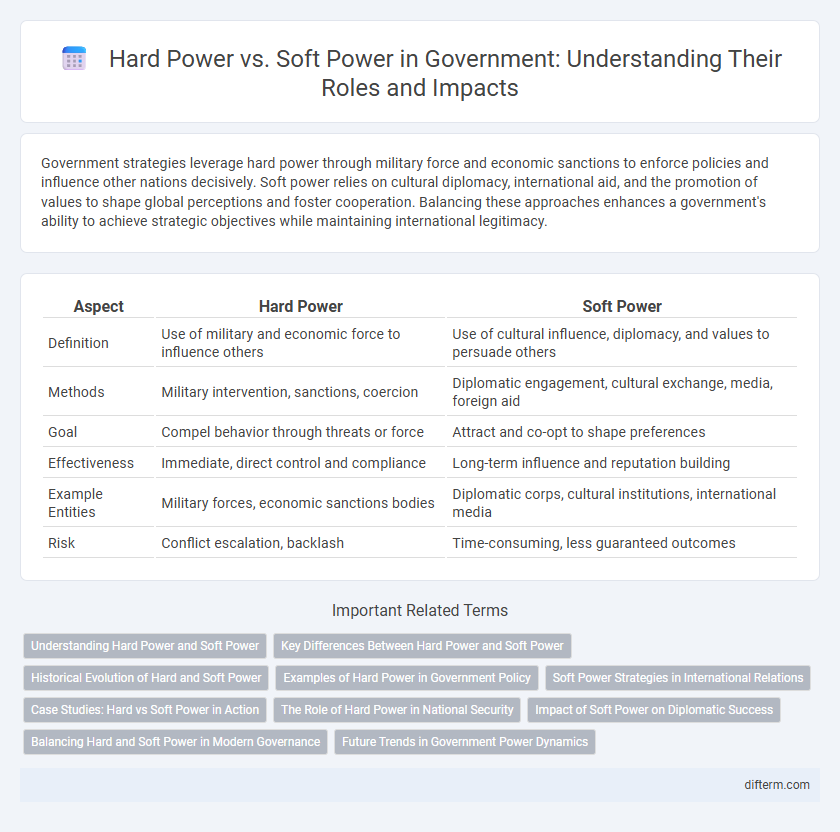
| Aspect | Hard Power | Soft Power |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of military and economic force to influence others | Use of cultural influence, diplomacy, and values to persuade others |
| Methods | Military intervention, sanctions, coercion | Diplomatic engagement, cultural exchange, media, foreign aid |
| Goal | Compel behavior through threats or force | Attract and co-opt to shape preferences |
| Effectiveness | Immediate, direct control and compliance | Long-term influence and reputation building |
| Example Entities | Military forces, economic sanctions bodies | Diplomatic corps, cultural institutions, international media |
| Risk | Conflict escalation, backlash | Time-consuming, less guaranteed outcomes |
Understanding Hard Power and Soft Power
Hard power involves a government's use of military force, economic sanctions, and coercion to influence other nations, emphasizing tangible actions and direct control. Soft power relies on cultural influence, diplomacy, and political values to shape preferences and build alliances without coercion. Understanding the balance between hard power and soft power is crucial for effective foreign policy, enabling governments to achieve strategic goals through a combination of persuasion and strength.
Key Differences Between Hard Power and Soft Power
Hard power relies on military force and economic sanctions to influence other states, emphasizing coercion and tangible leverage. Soft power leverages cultural influence, diplomacy, and values to shape preferences and gain voluntary cooperation. Key differences include the use of force versus attraction, direct versus indirect influence, and short-term versus long-term effectiveness in foreign policy.
Historical Evolution of Hard and Soft Power
The historical evolution of hard power and soft power reveals a transition from reliance on military force and economic sanctions toward the strategic use of cultural influence and diplomacy. In the 20th century, the Cold War exemplified hard power through military alliances and nuclear deterrence, while the rise of the United States and Western Europe highlighted soft power via media, education, and political values. Contemporary governments integrate both hard and soft power tools to shape global order, reflecting the complex dynamics of international relations.
Examples of Hard Power in Government Policy
Hard power in government policy includes military interventions, economic sanctions, and coercive diplomacy aimed at influencing other states' behavior. Examples encompass the U.S. military presence in conflict zones, trade embargoes like those imposed on North Korea, and the use of intelligence operations to undermine hostile regimes. These strategies rely on force or the threat of force to achieve political objectives.
Soft Power Strategies in International Relations
Soft power strategies in international relations emphasize cultural diplomacy, economic aid, and the promotion of political values to build influence without coercion. Governments leverage institutions like international organizations, media, and educational exchanges to foster cooperation and goodwill among nations. Investment in cultural exports, such as films and language programs, enhances a country's attractiveness and long-term diplomatic standing globally.
Case Studies: Hard vs Soft Power in Action
The U.S. invasion of Iraq in 2003 exemplifies hard power, utilizing military force to achieve geopolitical objectives, while Japan's post-war economic aid and cultural diplomacy showcase soft power's effectiveness in building international influence. China's Belt and Road Initiative blends soft power through infrastructure investment with hard power elements like military presence in the South China Sea. These case studies illustrate how governments strategically deploy hard and soft power to shape global alliances and regional dominance.
The Role of Hard Power in National Security
Hard power remains a critical component of national security by enabling governments to enforce laws, protect borders, and project military strength against external threats. Strategic deployment of military capabilities and economic sanctions serves as a deterrent, ensuring state sovereignty and stability. Effective integration of hard power tools supports a government's ability to respond decisively to emerging security challenges.
Impact of Soft Power on Diplomatic Success
Soft power enhances diplomatic success by fostering trust, cultural exchange, and mutual understanding, which leads to more sustainable international relationships. Nations leveraging soft power can influence other countries' policies and behaviors without coercion, often achieving concessions unattainable through hard power tactics like military or economic pressure. Empirical studies confirm that soft power investments such as public diplomacy, educational exchanges, and media influence correlate strongly with increased diplomatic influence and cooperation.
Balancing Hard and Soft Power in Modern Governance
Modern governance requires a strategic balance between hard power, exemplified by military strength and economic sanctions, and soft power, which leverages cultural influence and diplomatic relationships. Effective governments integrate coercive capabilities with persuasive tactics to achieve sustainable international stability and domestic compliance. Emphasizing this equilibrium enhances national security while promoting global cooperation and positive public perception.
Future Trends in Government Power Dynamics
Future trends in government power dynamics reveal a shift toward blending hard power, such as military strength and economic sanctions, with soft power elements like cultural influence and digital diplomacy. Emerging technologies, including cybersecurity measures and AI-driven information campaigns, are reshaping how governments project authority both domestically and internationally. Data-driven strategies and multilateral cooperation platforms are increasingly crucial for states seeking sustainable influence in a complex geopolitical environment.
hard power vs soft power Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com