Governance refers to the processes, systems, and practices through which authority is exercised and decisions are made within a government framework. Government, on the other hand, is the formal institution or organization that holds the authority to govern a specific geographic area or community. Effective governance ensures transparency, accountability, and responsiveness, which strengthens the legitimacy and functionality of government structures.
Table of Comparison
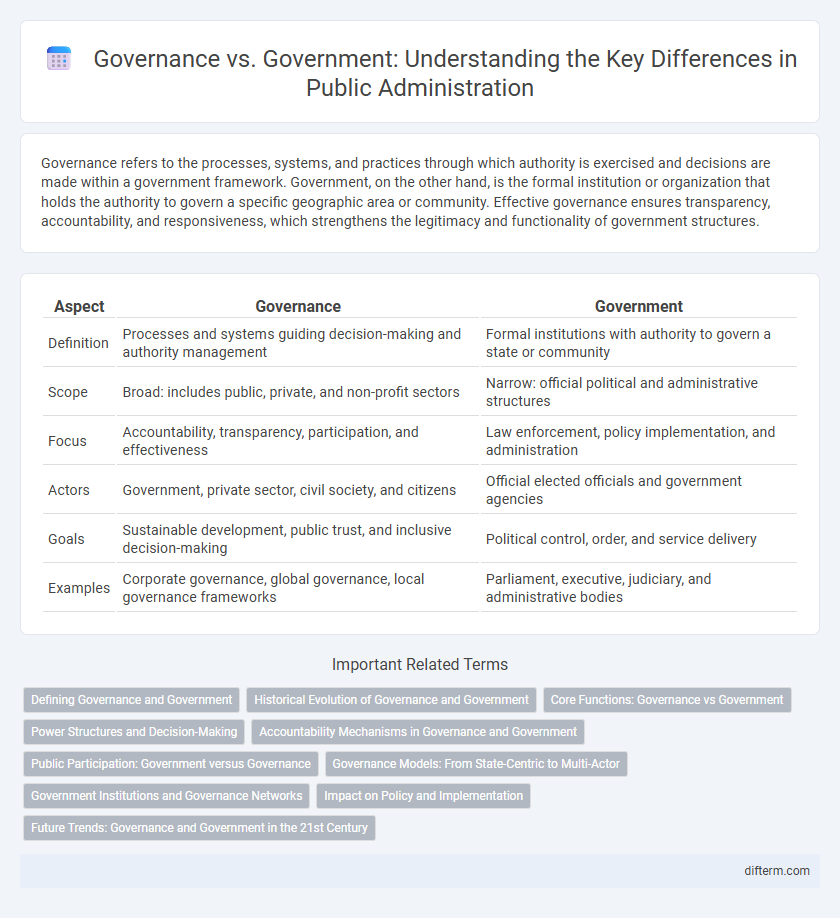
| Aspect | Governance | Government |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processes and systems guiding decision-making and authority management | Formal institutions with authority to govern a state or community |
| Scope | Broad: includes public, private, and non-profit sectors | Narrow: official political and administrative structures |
| Focus | Accountability, transparency, participation, and effectiveness | Law enforcement, policy implementation, and administration |
| Actors | Government, private sector, civil society, and citizens | Official elected officials and government agencies |
| Goals | Sustainable development, public trust, and inclusive decision-making | Political control, order, and service delivery |
| Examples | Corporate governance, global governance, local governance frameworks | Parliament, executive, judiciary, and administrative bodies |
Defining Governance and Government
Governance refers to the frameworks, processes, and systems by which organizations and societies are directed, regulated, and held accountable, encompassing policy-making, resource management, and stakeholder engagement. Government denotes the formal institutions and elected officials responsible for creating and enforcing laws, delivering public services, and maintaining order within a defined political territory. Effective governance requires transparent decision-making, inclusive participation, and accountability mechanisms, whereas government acts as the operational body executing those governance principles.
Historical Evolution of Governance and Government
Governance and government have evolved distinctly throughout history, with governance encompassing the broader mechanisms and processes by which societies manage collective affairs, while government refers specifically to the formal institutions and authorities established to enforce laws and policies. Early civilizations like Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt demonstrated rudimentary governance through code systems and centralized rulers, marking the genesis of structured government. Over time, governance expanded to include participatory and decentralized practices, reflecting shifts from monarchies to modern democratic states with complex administrative frameworks.
Core Functions: Governance vs Government
Governance refers to the frameworks, policies, and processes that guide decision-making and accountability, emphasizing transparency and stakeholder participation. Government, as the formal institution, enforces laws, implements policies, and delivers public services within a defined jurisdiction. Core functions of governance include regulation, oversight, and resource allocation, while government focuses on administration, law enforcement, and public service management.
Power Structures and Decision-Making
Governance encompasses the frameworks and processes through which power is exercised and decisions are made within a society, often involving multiple stakeholders beyond formal government institutions. Government refers specifically to the official institutions and bodies vested with authority to implement laws and policies, operating within defined power structures. Effective decision-making depends on the dynamic interaction between governance mechanisms, such as transparency and accountability, and the hierarchical structures of government authority.
Accountability Mechanisms in Governance and Government
Accountability mechanisms in governance encompass a broad spectrum of processes, including transparency, stakeholder engagement, and performance evaluation, which ensure that public authorities act in the best interest of the community. Government accountability specifically involves formal institutional frameworks such as legislative oversight, judicial review, and audit institutions that monitor and enforce compliance with laws and policies. Effective accountability mechanisms in both governance and government enhance trust, reduce corruption, and promote responsive decision-making in public administration.
Public Participation: Government versus Governance
Public participation in governance emphasizes collaborative decision-making processes where citizens actively engage in policy development and implementation, fostering transparency and accountability. In contrast, government typically refers to formal institutions and authorities responsible for enforcing laws and managing public resources with limited direct citizen input. Enhanced public participation in governance models strengthens democratic legitimacy and responsiveness beyond traditional government structures.
Governance Models: From State-Centric to Multi-Actor
Governance models have evolved from traditional state-centric approaches, where government institutions held centralized authority, to multi-actor frameworks that incorporate NGOs, private sectors, and civil society. This shift enhances policy-making through collaborative networks, increasing transparency, accountability, and citizen participation. Modern governance emphasizes decentralized decision-making, leveraging diverse stakeholders to address complex social, economic, and environmental challenges effectively.
Government Institutions and Governance Networks
Government institutions represent formal structures like legislatures, courts, and agencies responsible for implementing laws and policies, ensuring accountability and public service delivery. Governance networks encompass collaborative frameworks involving public, private, and civil society actors coordinating efforts beyond traditional hierarchical institutions to address complex societal challenges. Effective governance often relies on the interplay between established government institutions and dynamic governance networks to enhance transparency, inclusiveness, and policy innovation.
Impact on Policy and Implementation
Governance shapes the frameworks and processes that influence how policies are formulated, promoting transparency, accountability, and stakeholder engagement. Government executes these policies through institutional structures, ensuring compliance and public service delivery. Effective governance enhances policy impact by fostering inclusive decision-making and adaptive implementation strategies.
Future Trends: Governance and Government in the 21st Century
Future trends in governance emphasize adaptive, collaborative approaches that leverage digital technologies and data analytics to enhance transparency and citizen engagement. Governments are increasingly integrating artificial intelligence, blockchain, and smart city infrastructures to streamline public services and improve decision-making processes. The evolving landscape requires a shift from traditional hierarchical government models to more networked governance systems that prioritize inclusivity and responsiveness in the 21st century.
governance vs government Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com