Quorum busting involves deliberately reducing the number of lawmakers present to prevent a legislative body from meeting the minimum attendance needed to conduct official business, effectively stalling decision-making. Abstention, on the other hand, is the act of legislators choosing not to vote on a motion or bill, without necessarily impacting the quorum or the ability of the body to proceed. While both tactics can influence legislative outcomes, quorum busting targets attendance to halt proceedings, whereas abstention impacts the vote count without stopping the session itself.
Table of Comparison
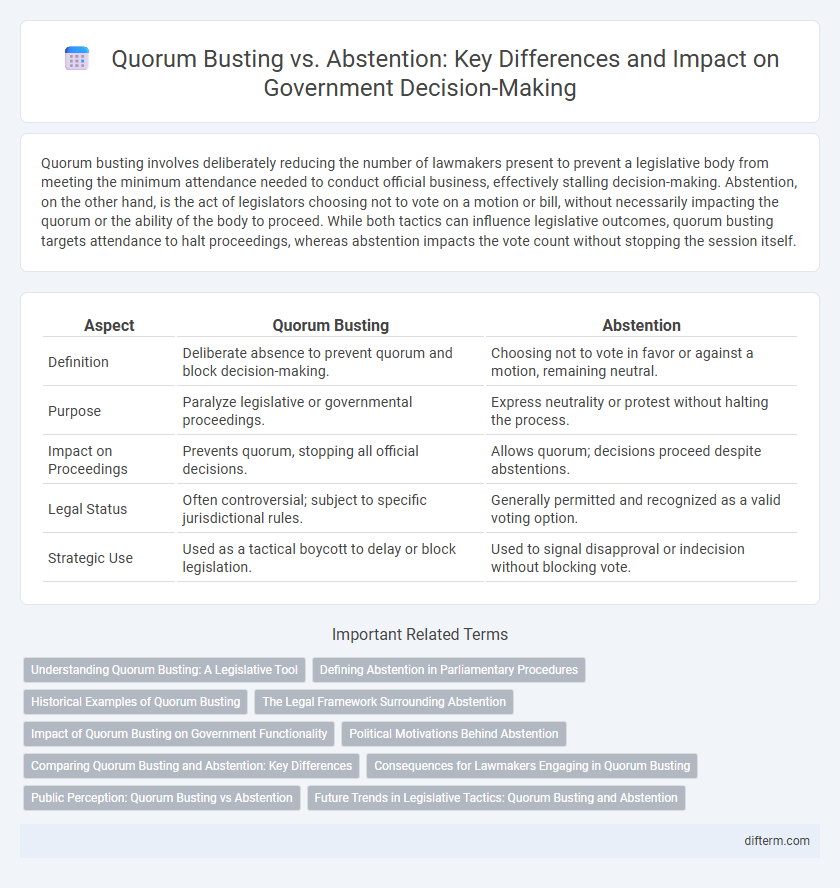
| Aspect | Quorum Busting | Abstention |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate absence to prevent quorum and block decision-making. | Choosing not to vote in favor or against a motion, remaining neutral. |
| Purpose | Paralyze legislative or governmental proceedings. | Express neutrality or protest without halting the process. |
| Impact on Proceedings | Prevents quorum, stopping all official decisions. | Allows quorum; decisions proceed despite abstentions. |
| Legal Status | Often controversial; subject to specific jurisdictional rules. | Generally permitted and recognized as a valid voting option. |
| Strategic Use | Used as a tactical boycott to delay or block legislation. | Used to signal disapproval or indecision without blocking vote. |
Understanding Quorum Busting: A Legislative Tool
Quorum busting is a legislative strategy used by minority parties to prevent a voting session from reaching the minimum number of members required to conduct official business, effectively halting the legislative process. Unlike abstention, where members are present but choose not to vote, quorum busting involves the physical absence of legislators to manipulate procedural rules and delay or block legislation. This tactic highlights the importance of quorum rules in government operations and serves as a critical tool for political leverage in legislative bodies.
Defining Abstention in Parliamentary Procedures
Abstention in parliamentary procedures refers to the intentional decision by a member to refrain from voting either in favor or against a motion, effectively remaining neutral. This act does not count towards the quorum, distinguishing it from quorum busting, where members deliberately absent themselves to disrupt proceedings. Abstention allows legislators to express neutrality or avoid conflict without impeding the legislative process.
Historical Examples of Quorum Busting
Quorum busting, a legislative tactic used to halt proceedings by preventing a quorum, has historical significance in government, notably during the 19th-century Texas legislature where members fled to avoid voting on controversial bills. This method differs from abstention, where lawmakers remain present but choose not to vote. The 1979 Wisconsin Senate quorum break provides a modern example, highlighting quorum busting's impact on legislative processes and political strategy.
The Legal Framework Surrounding Abstention
The legal framework surrounding abstention in government is defined by specific legislative and procedural rules that distinguish it from quorum busting, which involves intentionally breaking quorum to halt proceedings. Abstention is legally recognized as a passive form of non-voting where members choose not to cast a vote while maintaining presence, ensuring quorum remains intact and the legislative process continues. Regulations typically outline the conditions under which abstention is permitted, the impact on vote outcomes, and the accountability mechanisms to prevent misuse within parliamentary procedures.
Impact of Quorum Busting on Government Functionality
Quorum busting significantly disrupts government functionality by preventing the required minimum number of members from being present to conduct official business, effectively stalling legislative processes. This tactic can delay or block the passage of critical laws and budget approvals, impacting governance and public policy implementation. The inability to meet quorum undermines the legislative body's efficiency and accountability, often leading to political gridlock and diminished public trust.
Political Motivations Behind Abstention
Political motivations behind abstention often stem from strategic calculations to avoid endorsing a policy without directly opposing it, preserving party unity or public image. Abstention allows legislators to express dissent or ambivalence without triggering a quorum bust, which can stall legislative processes and draw institutional criticism. This tactic serves as a political tool to influence outcomes subtly while managing intra-party dynamics and voter perceptions.
Comparing Quorum Busting and Abstention: Key Differences
Quorum busting involves members deliberately absenting themselves to prevent a legislative body from achieving the minimum number of members required to conduct official business, effectively halting decision-making processes. Abstention, on the other hand, occurs when members are present but choose not to vote, signaling neutrality or indecision while still allowing the assembly to meet quorum requirements. The strategic use of quorum busting directly impedes legislative function, whereas abstention influences outcomes by withholding support without obstructing proceedings.
Consequences for Lawmakers Engaging in Quorum Busting
Lawmakers engaging in quorum busting face legal repercussions including fines, censure, or loss of committee assignments, impacting their legislative influence and political careers. This tactic can halt legislative processes, causing political gridlock and undermining governance efficiency. Persistent quorum busting may prompt rule changes or enforcement of attendance policies to ensure legislative operations proceed smoothly.
Public Perception: Quorum Busting vs Abstention
Quorum busting, often perceived as a strategic blockage tactic, can lead to public frustration due to its disruption of governmental processes. Abstention is generally viewed as a neutral stance, reflecting indecision or protest without halting legislative progress. Public perception tends to favor abstention over quorum busting because it maintains procedural integrity while allowing legislators to express dissent.
Future Trends in Legislative Tactics: Quorum Busting and Abstention
Future trends in legislative tactics indicate increased use of quorum busting as a strategic tool to delay or block legislation by denying the minimum number of members required for a vote. Abstention, while traditionally a passive form of dissent, is evolving into a calculated maneuver to influence legislative outcomes without casting explicit votes. As legislative bodies adapt to political polarization, these tactics may become more prevalent, affecting the pace and efficiency of government decision-making processes.
Quorum Busting vs Abstention Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com