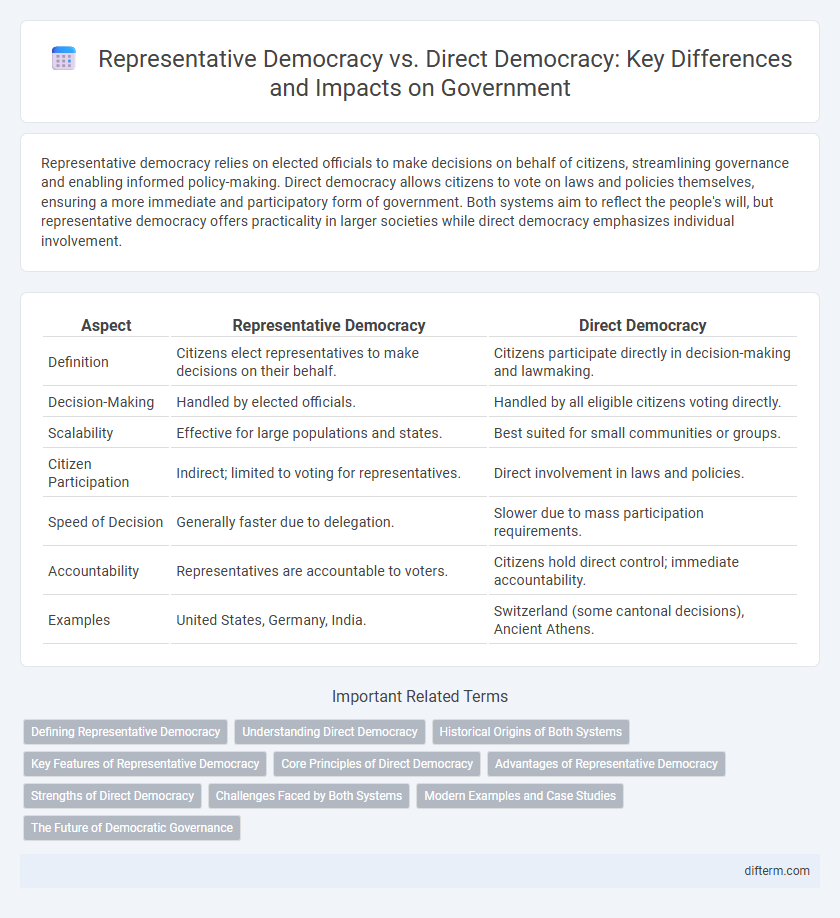
Representative democracy relies on elected officials to make decisions on behalf of citizens, streamlining governance and enabling informed policy-making. Direct democracy allows citizens to vote on laws and policies themselves, ensuring a more immediate and participatory form of government. Both systems aim to reflect the people's will, but representative democracy offers practicality in larger societies while direct democracy emphasizes individual involvement.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Representative Democracy | Direct Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Citizens elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf. | Citizens participate directly in decision-making and lawmaking. |
| Decision-Making | Handled by elected officials. | Handled by all eligible citizens voting directly. |
| Scalability | Effective for large populations and states. | Best suited for small communities or groups. |
| Citizen Participation | Indirect; limited to voting for representatives. | Direct involvement in laws and policies. |
| Speed of Decision | Generally faster due to delegation. | Slower due to mass participation requirements. |
| Accountability | Representatives are accountable to voters. | Citizens hold direct control; immediate accountability. |
| Examples | United States, Germany, India. | Switzerland (some cantonal decisions), Ancient Athens. |
Defining Representative Democracy
Representative democracy is a system of government where citizens elect officials to make decisions and create laws on their behalf, ensuring political accountability through periodic elections. This model contrasts with direct democracy, where citizens participate directly in decision-making processes without intermediaries. Key features of representative democracy include elected legislatures, separation of powers, and the protection of minority rights within a majority rule framework.
Understanding Direct Democracy
Direct democracy empowers citizens to make decisions on policy initiatives without intermediaries, enabling greater public involvement in legislative processes. This system relies on mechanisms such as referendums, initiatives, and recalls, allowing voters to directly influence laws and governance. Contrasting with representative democracy, direct democracy enhances political accountability by minimizing delegation and increasing citizen control over government actions.
Historical Origins of Both Systems
Representative democracy originated in ancient Rome, where elected officials governed on behalf of citizens, while direct democracy traces back to ancient Athens, where citizens participated directly in decision-making assemblies. The Roman Republic established a system of elected senators and magistrates, emphasizing delegation and representation. In contrast, Athenian democracy relied on widespread citizen involvement in legislative and judicial functions, highlighting direct participation.
Key Features of Representative Democracy
Representative democracy features elected officials who act on behalf of citizens, enabling efficient governance in larger populations. It includes regular elections, accountability mechanisms, and the protection of minority rights through constitutional frameworks. This system balances public participation with practical decision-making processes to maintain political stability and responsiveness.
Core Principles of Direct Democracy
Direct democracy is grounded in the principle of majority rule, allowing citizens to vote directly on laws and policies without intermediary representatives. Key elements include initiatives, referendums, and recall elections that empower individuals to influence governance actively. This system emphasizes transparency, accountability, and the decentralization of political power to enhance civic participation.
Advantages of Representative Democracy
Representative democracy enables efficient decision-making by delegating authority to elected officials who possess expertise in policy matters, ensuring informed governance. This system allows for scalability in large populations, reducing the logistical challenges and costs associated with direct citizen participation in every decision. Furthermore, representative democracy offers stability by providing structured mechanisms for accountability and conflict resolution through periodic elections.
Strengths of Direct Democracy
Direct democracy empowers citizens by allowing them to participate directly in decision-making processes, enhancing political engagement and accountability. It minimizes the risk of misrepresentation often seen in representative systems, ensuring that policies reflect the immediate will of the people. This form of governance is highly effective in promoting transparency, as every vote directly influences legislative outcomes.
Challenges Faced by Both Systems
Representative democracy struggles with ensuring elected officials truly reflect their constituents' interests, often facing issues like voter disengagement and political polarization. Direct democracy encounters obstacles in implementing large-scale citizen participation and managing complex policy decisions without expert guidance. Both systems grapple with balancing effective governance and meaningful public involvement to maintain legitimacy and responsiveness.
Modern Examples and Case Studies
Representative democracy, exemplified by the United States and Germany, relies on elected officials to make decisions on behalf of citizens, ensuring efficient governance in large populations. Direct democracy, as practiced in Switzerland through frequent referenda, allows citizens to vote on specific policies, fostering higher political engagement and accountability. Modern case studies reveal hybrid systems, such as Ireland's use of referenda alongside parliamentary decisions, balancing citizen input with representative structures.
The Future of Democratic Governance
Representative democracy leverages elected officials to make policy decisions, ensuring scalability and manageability in complex, populous societies. Direct democracy promotes citizen participation through referendums and initiatives, enhancing transparency and accountability but often facing logistical challenges. Emerging digital technologies and e-governance platforms are reshaping democratic governance by enabling hybrid models that combine representative structures with increased direct public engagement.
representative democracy vs direct democracy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com