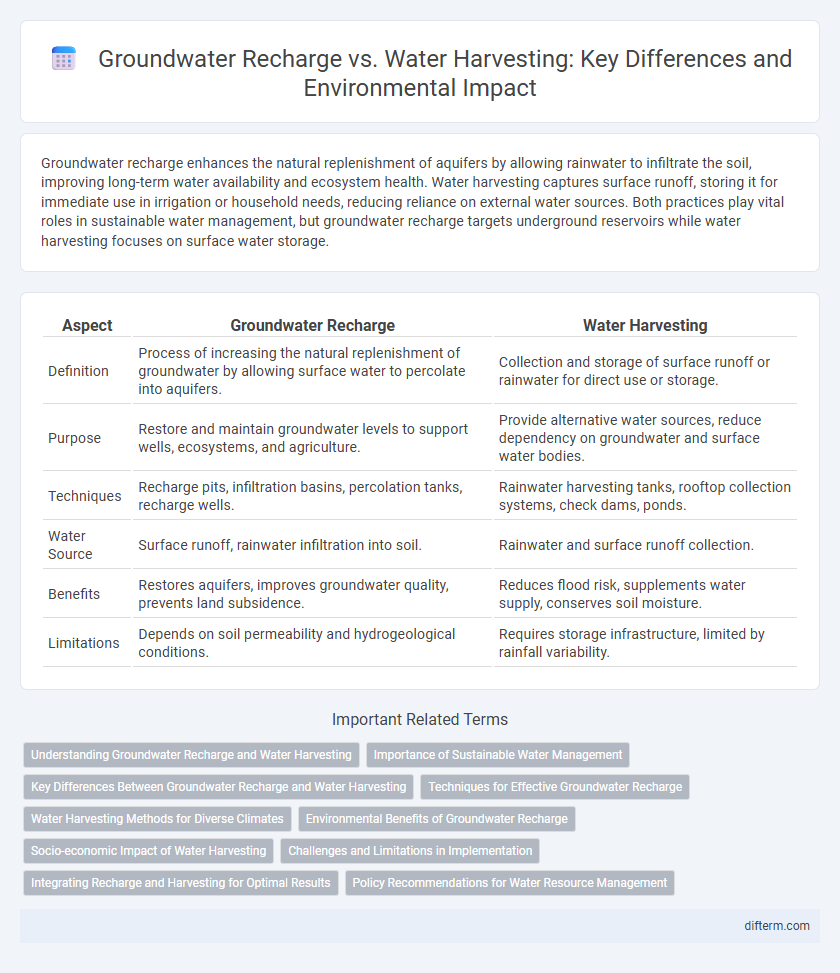
Groundwater recharge enhances the natural replenishment of aquifers by allowing rainwater to infiltrate the soil, improving long-term water availability and ecosystem health. Water harvesting captures surface runoff, storing it for immediate use in irrigation or household needs, reducing reliance on external water sources. Both practices play vital roles in sustainable water management, but groundwater recharge targets underground reservoirs while water harvesting focuses on surface water storage.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Groundwater Recharge | Water Harvesting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of increasing the natural replenishment of groundwater by allowing surface water to percolate into aquifers. | Collection and storage of surface runoff or rainwater for direct use or storage. |
| Purpose | Restore and maintain groundwater levels to support wells, ecosystems, and agriculture. | Provide alternative water sources, reduce dependency on groundwater and surface water bodies. |
| Techniques | Recharge pits, infiltration basins, percolation tanks, recharge wells. | Rainwater harvesting tanks, rooftop collection systems, check dams, ponds. |
| Water Source | Surface runoff, rainwater infiltration into soil. | Rainwater and surface runoff collection. |
| Benefits | Restores aquifers, improves groundwater quality, prevents land subsidence. | Reduces flood risk, supplements water supply, conserves soil moisture. |
| Limitations | Depends on soil permeability and hydrogeological conditions. | Requires storage infrastructure, limited by rainfall variability. |
Understanding Groundwater Recharge and Water Harvesting
Groundwater recharge involves the natural or artificial process of water permeating the soil to replenish aquifers, essential for sustaining the subsurface water supply. Water harvesting captures and stores surface runoff using structures like ponds, tanks, or check dams to manage water availability during dry periods. Effective integration of groundwater recharge techniques with water harvesting strategies enhances groundwater levels, supports agricultural productivity, and mitigates water scarcity.
Importance of Sustainable Water Management
Sustainable water management relies heavily on effective groundwater recharge and water harvesting techniques to maintain water availability and ecosystem balance. Groundwater recharge replenishes aquifers, ensuring long-term water security, while water harvesting captures surface runoff, reducing dependence on external sources. Integrating both methods supports resilience against climate variability and enhances environmental sustainability.
Key Differences Between Groundwater Recharge and Water Harvesting
Groundwater recharge involves the natural or artificial process of increasing the volume of water that infiltrates into underground aquifers, ensuring sustainable water supply and ecosystem balance. Water harvesting refers to the collection and storage of surface runoff or rainwater for direct use, reducing dependence on groundwater sources. Key differences include groundwater recharge enhancing subsurface water reserves permanently, while water harvesting primarily focuses on capturing water for immediate consumption or irrigation needs.
Techniques for Effective Groundwater Recharge
Techniques for effective groundwater recharge include constructing recharge wells, percolation tanks, and check dams to facilitate water infiltration into aquifers. Rainwater harvesting systems combined with suitable soil and geological assessments optimize water retention and recharge rates. Implementing contour bunding and managed aquifer recharge (MAR) enhances sustainable groundwater levels and mitigates water scarcity.
Water Harvesting Methods for Diverse Climates
Water harvesting methods adapt to diverse climates by capturing and storing surface runoff to enhance groundwater recharge and meet water demands sustainably. Techniques such as rooftop rainwater harvesting, contour bunding, and check dams are tailored to arid, semi-arid, and humid regions to optimize water availability. Integrating these methods with local hydrological conditions improves soil moisture levels, reduces erosion, and supports ecosystem resilience.
Environmental Benefits of Groundwater Recharge
Groundwater recharge replenishes aquifers, maintaining water availability during dry periods and supporting ecosystem sustainability. It reduces soil erosion and surface runoff, enhancing water quality by filtering contaminants through natural soil processes. This method promotes long-term water security and helps mitigate the impacts of climate change on freshwater resources.
Socio-economic Impact of Water Harvesting
Water harvesting significantly enhances socio-economic conditions by increasing water availability for agriculture, leading to improved crop yields and food security in arid and semi-arid regions. It supports livelihood diversification by providing water for livestock and small-scale enterprises, which boosts local economies and reduces poverty. Moreover, water harvesting reduces dependency on groundwater sources, promoting sustainable water management and mitigating the risks of groundwater depletion.
Challenges and Limitations in Implementation
Groundwater recharge faces challenges such as soil permeability issues and contamination risks, limiting effective infiltration rates and long-term sustainability. Water harvesting systems often encounter constraints like high initial costs, land availability, and maintenance difficulties in arid regions. Both methods require careful site assessment and community engagement to address socio-economic barriers and ensure successful implementation.
Integrating Recharge and Harvesting for Optimal Results
Integrating groundwater recharge with water harvesting techniques enhances sustainable water management by maximizing infiltration and storage capacity. Utilizing methods such as rainwater harvesting, infiltration trenches, and recharge wells improves aquifer replenishment while reducing surface runoff and erosion. Combining these practices supports ecosystem resilience, agricultural productivity, and climate adaptation in water-scarce regions.
Policy Recommendations for Water Resource Management
Policy recommendations for water resource management emphasize integrating groundwater recharge techniques with water harvesting systems to enhance sustainable water availability. Implementing regulatory frameworks that promote aquifer recharge through rainwater infiltration alongside incentives for decentralized water harvesting can strengthen water security in drought-prone areas. Prioritizing investments in infrastructure that capture and store surface runoff while facilitating natural groundwater replenishment supports resilience against climate variability and ensures long-term ecosystem health.
groundwater recharge vs water harvesting Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com