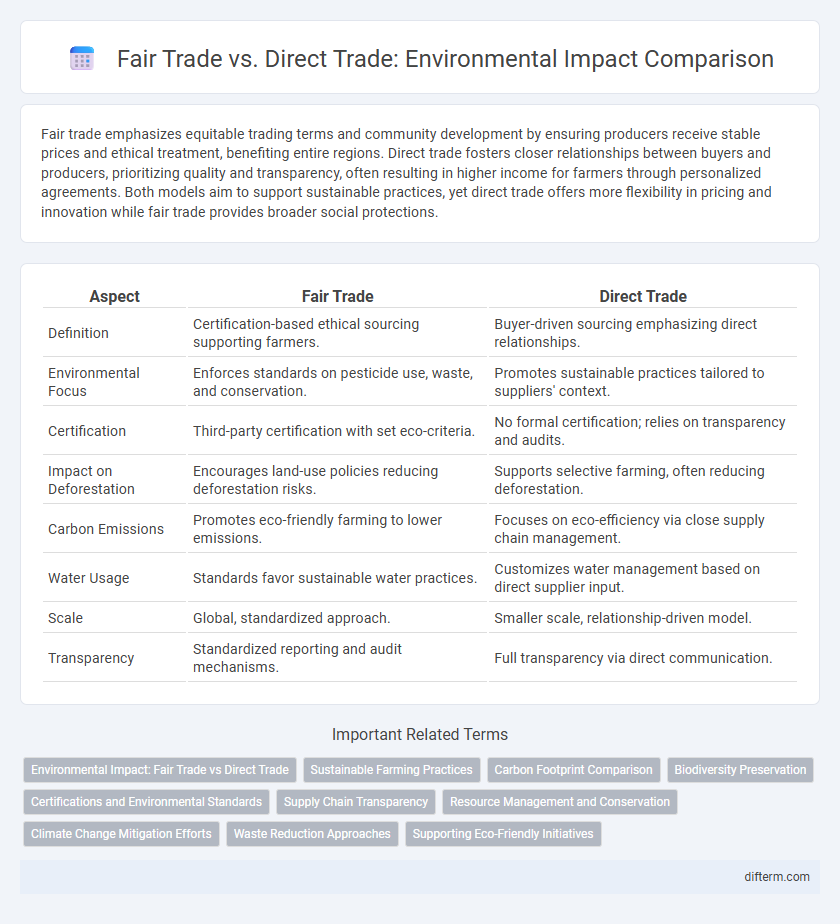
Fair trade emphasizes equitable trading terms and community development by ensuring producers receive stable prices and ethical treatment, benefiting entire regions. Direct trade fosters closer relationships between buyers and producers, prioritizing quality and transparency, often resulting in higher income for farmers through personalized agreements. Both models aim to support sustainable practices, yet direct trade offers more flexibility in pricing and innovation while fair trade provides broader social protections.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fair Trade | Direct Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Certification-based ethical sourcing supporting farmers. | Buyer-driven sourcing emphasizing direct relationships. |
| Environmental Focus | Enforces standards on pesticide use, waste, and conservation. | Promotes sustainable practices tailored to suppliers' context. |
| Certification | Third-party certification with set eco-criteria. | No formal certification; relies on transparency and audits. |
| Impact on Deforestation | Encourages land-use policies reducing deforestation risks. | Supports selective farming, often reducing deforestation. |
| Carbon Emissions | Promotes eco-friendly farming to lower emissions. | Focuses on eco-efficiency via close supply chain management. |
| Water Usage | Standards favor sustainable water practices. | Customizes water management based on direct supplier input. |
| Scale | Global, standardized approach. | Smaller scale, relationship-driven model. |
| Transparency | Standardized reporting and audit mechanisms. | Full transparency via direct communication. |
Environmental Impact: Fair Trade vs Direct Trade
Fair Trade certification enforces strict environmental standards, promoting sustainable farming practices that reduce pesticide use and encourage organic methods, leading to enhanced biodiversity and soil health. Direct Trade often emphasizes close relationships between buyers and producers, allowing for customized, eco-friendly agricultural techniques that can minimize carbon footprints and waste. Both models contribute to environmental sustainability, but Fair Trade offers more standardized protections, while Direct Trade provides flexibility for innovative, localized environmental solutions.
Sustainable Farming Practices
Fair trade emphasizes certified standards that ensure environmental sustainability by promoting organic farming, reducing chemical use, and supporting biodiversity conservation. Direct trade fosters close relationships between buyers and farmers, enabling tailored sustainable practices and incentives for long-term soil health and water conservation. Both models contribute to eco-friendly agriculture but direct trade often allows more flexibility in implementing innovative sustainable farming techniques.
Carbon Footprint Comparison
Fair trade products often have a higher carbon footprint due to complex supply chains involving multiple intermediaries, leading to increased transportation emissions. Direct trade minimizes carbon emissions by shortening the supply chain, enabling more localized and efficient shipping practices. Lower carbon footprints in direct trade support sustainable environmental practices by reducing the overall greenhouse gas emissions associated with product distribution.
Biodiversity Preservation
Fair trade practices promote biodiversity preservation by supporting small-scale farmers who use traditional, eco-friendly farming techniques that maintain local ecosystems. Direct trade emphasizes transparency and stronger relationships between buyers and producers, encouraging sustainable agricultural methods that reduce habitat destruction. Both trading models contribute to environmental sustainability by fostering responsible land use and protecting native species diversity.
Certifications and Environmental Standards
Fair trade certifications ensure compliance with strict environmental standards, promoting sustainable farming practices, reduced pesticide use, and ecosystem preservation. Direct trade often bypasses third-party certifications, allowing for more flexible and transparent relationships but relying on the buyer's commitment to environmental responsibility. Both approaches emphasize reducing environmental impact, though fair trade provides standardized certification while direct trade depends on individual accountability.
Supply Chain Transparency
Supply chain transparency in fair trade emphasizes third-party certification to ensure ethical sourcing and environmental standards are met throughout the supply chain. Direct trade fosters closer relationships between producers and buyers, enabling real-time oversight and accountability for sustainable practices. Both models enhance traceability but differ in approach: fair trade relies on standardized audits, while direct trade leverages direct communication and customized agreements.
Resource Management and Conservation
Fair trade emphasizes sustainable resource management by enforcing strict environmental standards and supporting community-based conservation efforts, ensuring long-term ecosystem health. Direct trade fosters closer relationships between producers and buyers, often promoting innovative, localized resource conservation practices that reduce waste and enhance biodiversity. Both models contribute to environmental stewardship, but direct trade tends to allow greater flexibility for adaptive resource management tailored to specific ecological contexts.
Climate Change Mitigation Efforts
Fair trade emphasizes climate change mitigation by supporting sustainable agriculture practices that reduce carbon emissions and enhance soil health, benefiting smallholder farmers globally. Direct trade often prioritizes transparency and quality but also fosters environmental responsibility through close partnerships that implement localized eco-friendly farming techniques. Both models contribute to climate resilience by promoting adaptive strategies, yet fair trade's certification systems systematically integrate climate-focused standards guiding broader impact.
Waste Reduction Approaches
Fair trade emphasizes community-based waste reduction through collaborative recycling programs and sustainable packaging initiatives that reduce environmental impact at the production level. Direct trade promotes waste minimization by fostering transparent relationships between buyers and producers, enabling efficient resource management and reducing overproduction. Both approaches contribute to lowering carbon footprints by encouraging sustainable practices and waste-conscious supply chains in the agricultural sector.
Supporting Eco-Friendly Initiatives
Fair trade emphasizes fair wages and community development while promoting environmentally friendly farming practices such as organic cultivation and reforestation efforts. Direct trade fosters strong relationships between buyers and producers, ensuring transparency and often prioritizing sustainable methods tailored to local ecosystems. Both models contribute to supporting eco-friendly initiatives by encouraging responsible resource management and reducing harmful chemical use in agricultural processes.
fair trade vs direct trade Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com