Green buildings aim to minimize environmental impact through sustainable materials and energy-efficient designs, while net-zero buildings go further by producing as much energy as they consume, achieving a balance of zero net energy use. Both concepts prioritize reducing carbon footprints, but net-zero buildings require renewable energy integration and advanced technologies. Choosing between them depends on project goals, budget, and long-term sustainability commitments.
Table of Comparison
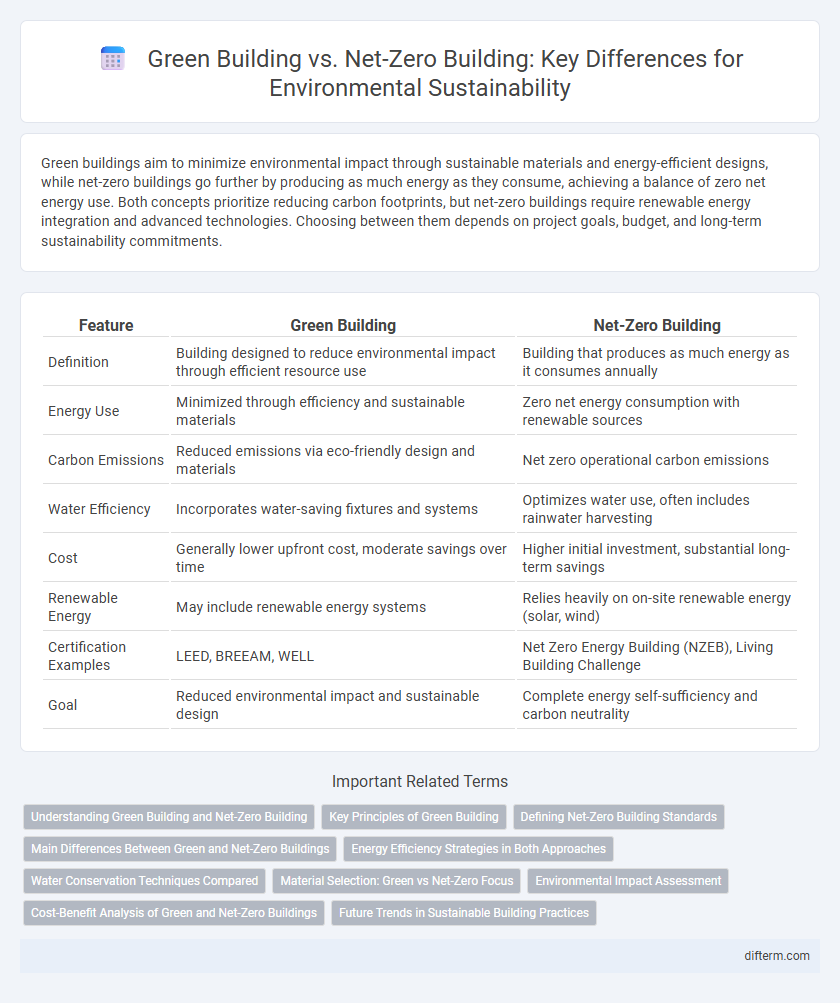
| Feature | Green Building | Net-Zero Building |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building designed to reduce environmental impact through efficient resource use | Building that produces as much energy as it consumes annually |
| Energy Use | Minimized through efficiency and sustainable materials | Zero net energy consumption with renewable sources |
| Carbon Emissions | Reduced emissions via eco-friendly design and materials | Net zero operational carbon emissions |
| Water Efficiency | Incorporates water-saving fixtures and systems | Optimizes water use, often includes rainwater harvesting |
| Cost | Generally lower upfront cost, moderate savings over time | Higher initial investment, substantial long-term savings |
| Renewable Energy | May include renewable energy systems | Relies heavily on on-site renewable energy (solar, wind) |
| Certification Examples | LEED, BREEAM, WELL | Net Zero Energy Building (NZEB), Living Building Challenge |
| Goal | Reduced environmental impact and sustainable design | Complete energy self-sufficiency and carbon neutrality |
Understanding Green Building and Net-Zero Building
Green buildings prioritize sustainable design, energy efficiency, and reduced environmental impact through materials, water use, and indoor air quality improvements. Net-zero buildings go a step further by producing as much energy as they consume, often through on-site renewable energy sources like solar panels. While all net-zero buildings are green, not all green buildings achieve net-zero energy status, highlighting the distinction in energy performance goals.
Key Principles of Green Building
Green building emphasizes sustainable site development, efficient water use, energy efficiency, and the use of environmentally friendly materials to minimize ecological impact. It incorporates principles such as indoor environmental quality, waste reduction, and resource conservation to promote health and sustainability. These key principles collectively aim to create buildings that are both resource-efficient and environmentally responsible throughout their lifecycle.
Defining Net-Zero Building Standards
Net-zero building standards require structures to produce as much energy as they consume, often through renewable energy integration and highly efficient design. Green buildings emphasize sustainability by minimizing environmental impact via resource conservation and healthier materials but do not necessarily achieve net-zero energy balance. Defining net-zero standards involves rigorous energy modeling, on-site renewable generation, and strict performance verification to ensure compliance and measurable impact.
Main Differences Between Green and Net-Zero Buildings
Green buildings prioritize sustainable materials, energy efficiency, and reduced environmental impact throughout the construction and operation phases. Net-zero buildings specifically focus on balancing energy consumption with on-site renewable energy production to achieve a net-zero energy footprint annually. While green buildings encompass broader sustainability practices, net-zero buildings have a precise energy performance goal to eliminate carbon emissions related to energy use.
Energy Efficiency Strategies in Both Approaches
Green buildings incorporate energy efficiency strategies like improved insulation, energy-efficient windows, and HVAC systems to reduce overall energy consumption. Net-zero buildings go further by integrating renewable energy sources such as solar panels and advanced energy management systems to produce as much energy as they consume annually. Both approaches emphasize passive design techniques, daylighting, and smart controls to optimize energy performance and minimize environmental impact.
Water Conservation Techniques Compared
Green buildings incorporate water-efficient fixtures, rainwater harvesting, and greywater recycling to reduce overall water consumption and minimize environmental impact. Net-zero buildings enhance these techniques by integrating advanced systems like smart irrigation, onsite water treatment, and closed-loop water cycles to achieve total water self-sufficiency. Both strategies prioritize sustainable water management but net-zero buildings aim for complete water independence and zero wastewater discharge.
Material Selection: Green vs Net-Zero Focus
Green buildings prioritize sustainable, low-impact materials such as recycled steel, bamboo, and low-VOC paints to minimize environmental harm during construction. Net-zero buildings emphasize materials with superior thermal resistance and energy efficiency, including advanced insulation, triple-glazed windows, and phase-change materials to achieve zero energy consumption. Both approaches integrate eco-friendly materials, but net-zero construction targets enhanced energy performance alongside sustainability.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Green buildings reduce environmental impact through energy efficiency, sustainable materials, and waste reduction, minimizing resource consumption and pollution. Net-zero buildings surpass these standards by producing as much energy as they consume, achieving a balance that significantly lowers carbon footprints in Environmental Impact Assessments. Both frameworks emphasize lifecycle analysis, but net-zero buildings offer enhanced long-term benefits for climate change mitigation and resource sustainability.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Green and Net-Zero Buildings
Green buildings offer reduced operational costs through energy efficiency and sustainable materials, yielding significant long-term savings despite higher initial investments. Net-zero buildings demand greater upfront expenses due to advanced technologies like solar panels and energy storage but achieve complete energy self-sufficiency, resulting in minimal utility costs over time. Cost-benefit analysis reveals that while green buildings balance moderate costs with environmental benefits, net-zero buildings provide superior financial returns in the long run through substantial energy savings and potential government incentives.
Future Trends in Sustainable Building Practices
Green building practices emphasize energy efficiency, resource conservation, and indoor environmental quality, while net-zero buildings push further by generating as much energy as they consume, often through on-site renewable sources like solar and wind. Future trends showcase a growing integration of smart technologies, advanced materials with low embodied carbon, and circular economy principles to maximize sustainability and resilience in both building types. Increasing regulatory support and market demand drive innovations toward carbon-negative buildings and enhanced occupant well-being in sustainable construction.
green building vs net-zero building Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com