Sustainable pet care emphasizes long-term environmental balance by promoting products and practices that minimize resource depletion and waste generation. Eco-friendly pet products specifically reduce immediate environmental impact through biodegradable materials and non-toxic ingredients that ensure safety for pets and the planet. Choosing sustainable options often supports broader ecological health, while eco-friendly choices highlight reduced harm during production and use.
Table of Comparison
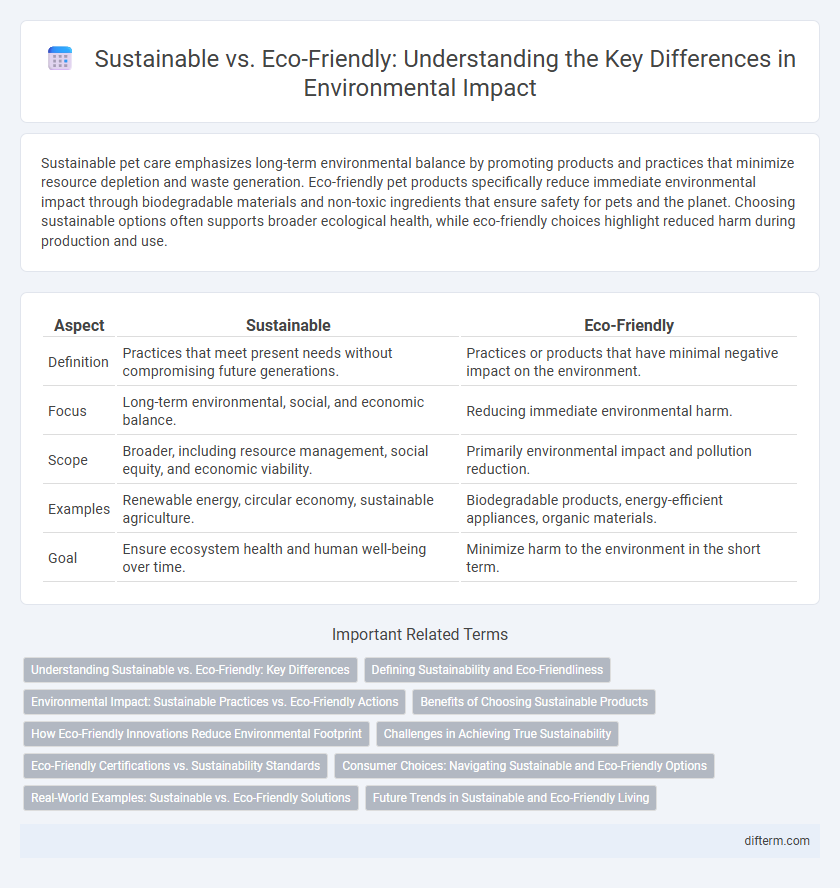
| Aspect | Sustainable | Eco-Friendly |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Practices that meet present needs without compromising future generations. | Practices or products that have minimal negative impact on the environment. |
| Focus | Long-term environmental, social, and economic balance. | Reducing immediate environmental harm. |
| Scope | Broader, including resource management, social equity, and economic viability. | Primarily environmental impact and pollution reduction. |
| Examples | Renewable energy, circular economy, sustainable agriculture. | Biodegradable products, energy-efficient appliances, organic materials. |
| Goal | Ensure ecosystem health and human well-being over time. | Minimize harm to the environment in the short term. |
Understanding Sustainable vs. Eco-Friendly: Key Differences
Sustainable practices focus on meeting present needs without compromising future generations by balancing environmental, economic, and social factors. Eco-friendly products or actions specifically minimize harm to the environment through reduced energy consumption, waste, and pollutant emissions. Understanding these distinctions helps consumers and businesses make informed choices that support long-term ecological health and responsible resource management.
Defining Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Sustainability refers to meeting present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs, emphasizing long-term environmental, social, and economic balance. Eco-friendliness focuses specifically on minimizing harm to the environment through practices that reduce pollution, waste, and resource depletion. Both concepts prioritize conservation, but sustainability encompasses a broader framework integrating environmental stewardship with social responsibility and economic viability.
Environmental Impact: Sustainable Practices vs. Eco-Friendly Actions
Sustainable practices prioritize long-term environmental health by balancing resource consumption with natural regeneration, reducing carbon footprint through renewable energy and circular economy models. Eco-friendly actions focus on immediate, low-impact behavior changes such as using biodegradable products and minimizing waste to protect local ecosystems. Both approaches contribute to reducing pollution and conserving biodiversity but differ in scope and duration of environmental impact.
Benefits of Choosing Sustainable Products
Choosing sustainable products helps conserve natural resources by using materials that are renewable and have a lower environmental footprint compared to conventional options. Sustainable products often support fair labor practices and promote biodiversity by encouraging responsible sourcing and manufacturing processes. Consumers benefit from improved health outcomes by avoiding harmful chemicals commonly found in non-sustainable goods.
How Eco-Friendly Innovations Reduce Environmental Footprint
Eco-friendly innovations significantly reduce environmental footprints by minimizing resource consumption and waste production through renewable materials and energy-efficient technologies. Sustainable practices integrate circular economy principles, promoting reuse, recycling, and reducing emissions throughout product life cycles. These advancements drive measurable decreases in carbon footprints, water usage, and pollution, fostering long-term ecological balance.
Challenges in Achieving True Sustainability
Achieving true sustainability faces challenges such as resource depletion, economic constraints, and social inequality that eco-friendly practices alone cannot resolve. Sustainable solutions require systemic changes in energy consumption, waste management, and equitable resource distribution to balance environmental, economic, and social needs. The complexity of integrating these factors often limits the effectiveness of purely eco-friendly initiatives in fostering long-term planetary health.
Eco-Friendly Certifications vs. Sustainability Standards
Eco-friendly certifications such as ENERGY STAR, LEED, and Green Seal validate products and buildings based on specific environmental criteria, ensuring reduced pollution, energy efficiency, and less waste. Sustainability standards like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and ISO 14001 provide comprehensive frameworks for organizations to measure and improve their environmental, social, and economic impacts over time. While eco-friendly certifications focus on tangible product or service attributes, sustainability standards emphasize broader corporate responsibility and long-term ecosystem health.
Consumer Choices: Navigating Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Options
Consumers increasingly evaluate products based on sustainable and eco-friendly attributes to reduce environmental impact and support ethical manufacturing practices. Choosing items with certification labels such as Fair Trade, Organic, or Energy Star helps ensure responsible resource use and lower carbon footprints. Prioritizing reusable, biodegradable, or non-toxic materials fosters long-term ecological balance and aligns purchasing decisions with global sustainability goals.
Real-World Examples: Sustainable vs. Eco-Friendly Solutions
Urban green roofs represent sustainable solutions by improving air quality, reducing energy consumption, and managing stormwater effectively, as seen in cities like Chicago and Berlin. Eco-friendly products such as biodegradable packaging and reusable shopping bags minimize waste and pollution but may require ongoing consumer participation to maintain their environmental benefits. Implementing sustainable agriculture practices, like crop rotation and organic farming, builds long-term soil health while eco-friendly alternatives like plant-based diets reduce carbon footprints on an individual level.
Future Trends in Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Living
Future trends in sustainable and eco-friendly living emphasize the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power into everyday life. Innovations in biodegradable materials and circular economy practices are driving waste reduction and resource efficiency. Smart home technologies paired with green building certifications like LEED and WELL promote energy conservation and healthier living environments.
sustainable vs eco-friendly Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com