A revenue model defines the specific way a business generates income from its products or services, while a business model outlines the overall plan for creating, delivering, and capturing value in the market. Understanding the difference between revenue model and business model is crucial for entrepreneurs seeking to optimize profitability and long-term sustainability. Streamlining the revenue model within the broader business model can significantly impact cash flow and growth potential.
Table of Comparison
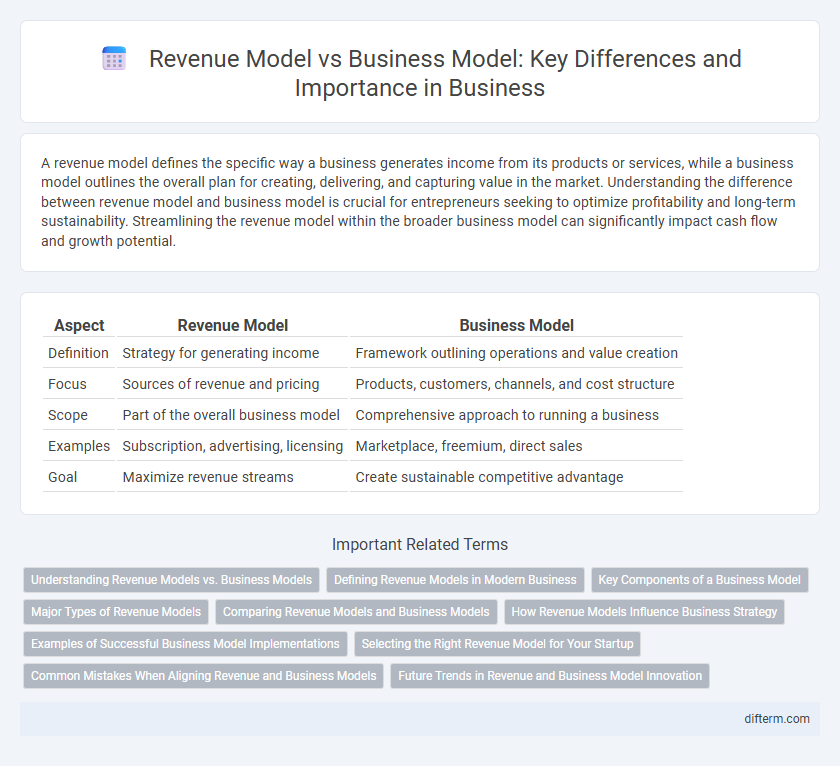
| Aspect | Revenue Model | Business Model |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy for generating income | Framework outlining operations and value creation |
| Focus | Sources of revenue and pricing | Products, customers, channels, and cost structure |
| Scope | Part of the overall business model | Comprehensive approach to running a business |
| Examples | Subscription, advertising, licensing | Marketplace, freemium, direct sales |
| Goal | Maximize revenue streams | Create sustainable competitive advantage |
Understanding Revenue Models vs. Business Models
Revenue models define how a company generates income through specific streams such as subscriptions, sales, or advertising, while business models encompass the overall strategy, including value proposition, target market, and operational structure. Understanding the distinction helps businesses optimize profitability by aligning revenue streams with customer needs and market dynamics. Effective revenue model selection directly impacts cash flow, scalability, and long-term sustainability within the broader business model framework.
Defining Revenue Models in Modern Business
Revenue models define how a business generates income through specific streams such as subscription fees, direct sales, or advertising. Unlike the broader business model, which outlines the overall strategy including value proposition, target market, and operational structure, revenue models concentrate on the mechanisms of monetization. Understanding revenue models is essential for modern businesses to diversify income sources and optimize profitability in competitive markets.
Key Components of a Business Model
A business model outlines the strategic framework for creating, delivering, and capturing value, encompassing key components such as customer segments, value propositions, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure. The revenue model specifically focuses on the methods through which a company generates income, highlighting sales strategies, pricing structures, and revenue sources within the broader business model. Understanding these components enables businesses to design effective strategies that align operational activities with financial objectives for sustainable growth.
Major Types of Revenue Models
Major types of revenue models include subscription, freemium, licensing, advertising, and transaction-based approaches, each defining how a business generates income from its products or services. The subscription model generates recurring revenue by charging customers regularly, while freemium offers basic services free with paid upgrades. Advertising relies on selling ad space, licensing permits usage rights for a fee, and transaction-based models earn through sales or commissions per transaction.
Comparing Revenue Models and Business Models
Revenue models define specific methods by which a company generates income, such as subscription fees, licensing, or advertising, while business models encompass the broader strategy for delivering value to customers and achieving sustainable profitability. Key differences include revenue models focusing solely on monetization streams, whereas business models incorporate aspects like target market, value proposition, cost structure, and operational processes. Understanding the interplay between revenue and business models enables businesses to align income generation with overall strategic goals and market positioning.
How Revenue Models Influence Business Strategy
Revenue models directly shape business strategy by defining how a company generates income through specific channels such as subscriptions, advertising, or product sales, guiding resource allocation and market positioning. Clear revenue streams enable businesses to forecast financial performance, optimize pricing strategies, and target customer segments effectively. Strategic alignment of the revenue model ensures sustainable growth and competitive advantage within the industry's economic framework.
Examples of Successful Business Model Implementations
Uber's business model leverages a platform-based ecosystem that connects drivers and riders, generating revenue through commission fees on each ride, demonstrating a scalable marketplace approach. Amazon employs a hybrid business model combining e-commerce retail, subscription services like Amazon Prime, and third-party seller fees, creating multiple revenue streams that stabilize income. Netflix revolutionized content consumption with a subscription-based revenue model within its direct-to-consumer streaming business model, securing consistent recurring revenue through unlimited access for a monthly fee.
Selecting the Right Revenue Model for Your Startup
Choosing the right revenue model is crucial for aligning your startup's financial strategy with its business goals, influencing cash flow and scalability. Key revenue models include subscription, freemium, direct sales, and advertising, each offering distinct advantages depending on the target market and product type. Evaluating customer behavior, market demand, and competitive landscape helps determine the optimal revenue model to maximize profitability and sustain long-term growth.
Common Mistakes When Aligning Revenue and Business Models
Common mistakes when aligning revenue models with business models include over-reliance on a single revenue stream, which limits scalability and increases financial risk. Businesses often misinterpret customer value propositions, resulting in revenue strategies that fail to capture the full market potential. Ignoring the cost structure and operational capabilities during revenue model design can lead to unsustainable profit margins and hinder long-term growth.
Future Trends in Revenue and Business Model Innovation
Future trends in revenue and business model innovation emphasize subscription-based models, platform ecosystems, and data monetization as key drivers of sustained growth. Businesses increasingly leverage artificial intelligence and blockchain technologies to create transparent, scalable, and customer-centric revenue streams. Embracing these innovations enables companies to adapt to evolving market demands and capture new value opportunities.
revenue model vs business model Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com