Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) measure specific metrics to track the success of ongoing business activities, providing quantifiable data on performance efficiency. Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) align broader strategic goals with measurable outcomes, driving focused progress and organizational priorities through time-bound milestones. Combining KPIs and OKRs enhances performance management by balancing detailed measurement with strategic ambition.
Table of Comparison
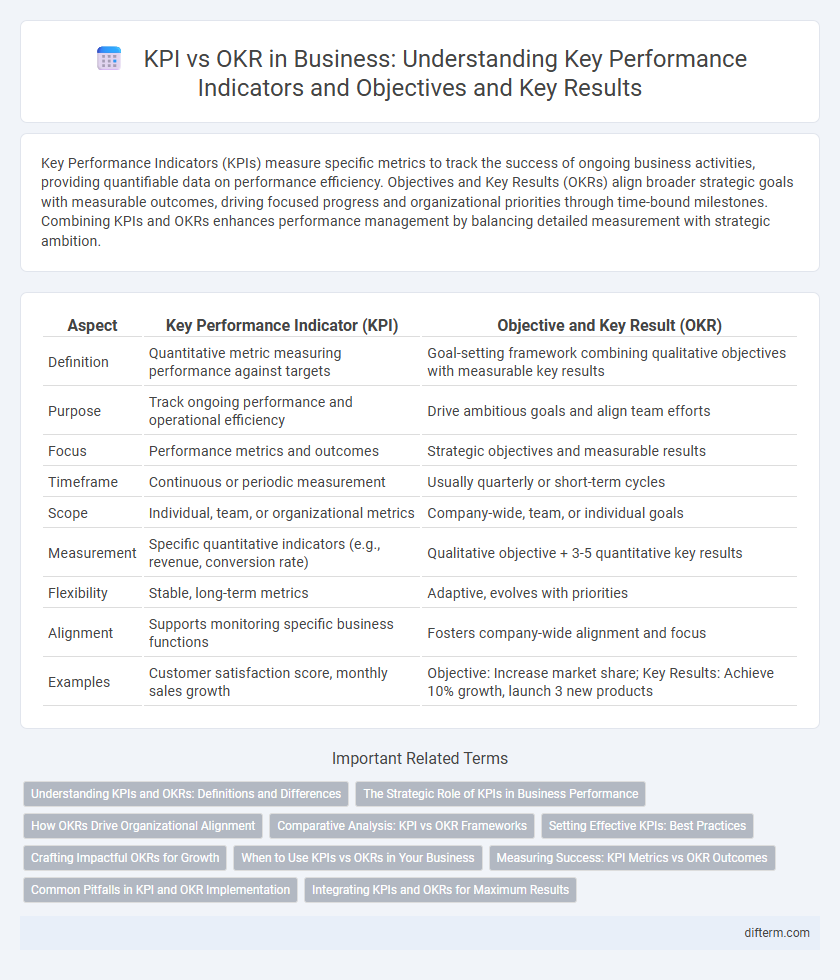
| Aspect | Key Performance Indicator (KPI) | Objective and Key Result (OKR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Quantitative metric measuring performance against targets | Goal-setting framework combining qualitative objectives with measurable key results |
| Purpose | Track ongoing performance and operational efficiency | Drive ambitious goals and align team efforts |
| Focus | Performance metrics and outcomes | Strategic objectives and measurable results |
| Timeframe | Continuous or periodic measurement | Usually quarterly or short-term cycles |
| Scope | Individual, team, or organizational metrics | Company-wide, team, or individual goals |
| Measurement | Specific quantitative indicators (e.g., revenue, conversion rate) | Qualitative objective + 3-5 quantitative key results |
| Flexibility | Stable, long-term metrics | Adaptive, evolves with priorities |
| Alignment | Supports monitoring specific business functions | Fosters company-wide alignment and focus |
| Examples | Customer satisfaction score, monthly sales growth | Objective: Increase market share; Key Results: Achieve 10% growth, launch 3 new products |
Understanding KPIs and OKRs: Definitions and Differences
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable metrics used to evaluate the success of specific business activities in achieving operational goals, while Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) combine qualitative objectives with measurable key results to drive strategic progress and alignment. KPIs focus on ongoing performance monitoring, providing clear benchmarks for efficiency and effectiveness, whereas OKRs emphasize ambitious goal-setting and measurable outcomes that encourage innovation and continuous improvement. Understanding the distinction allows businesses to effectively measure performance (KPIs) and set transformative goals that guide organizational growth (OKRs).
The Strategic Role of KPIs in Business Performance
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) serve as quantifiable metrics that track business performance against strategic goals, enabling precise measurement and management of progress. Unlike Objectives and Key Results (OKRs), which emphasize aspirational goals and alignment, KPIs focus on ongoing performance monitoring to ensure operational efficiency and effectiveness. Effective use of KPIs drives data-informed decision-making and continuous improvement, directly impacting profitability and competitive advantage.
How OKRs Drive Organizational Alignment
OKRs drive organizational alignment by clearly defining measurable objectives and key results that connect individual and team efforts to the company's strategic goals. Unlike KPIs, which track performance metrics independently, OKRs promote transparency and accountability across all levels, fostering collaboration and focused execution. This alignment ensures that every employee's work contributes directly to overarching business priorities, accelerating growth and innovation.
Comparative Analysis: KPI vs OKR Frameworks
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable metrics that track ongoing performance and operational efficiency, enabling businesses to measure success against predefined standards. Objective and Key Results (OKRs) provide a goal-setting framework that aligns ambitious objectives with measurable key results, fostering transparency and strategic focus across teams. While KPIs monitor continuous performance, OKRs drive transformative change by setting stretch goals and encouraging cross-functional collaboration, making OKRs more dynamic for growth-oriented organizations.
Setting Effective KPIs: Best Practices
Setting effective KPIs requires alignment with specific business goals, measurable outcomes, and regular performance tracking to drive accountability. Best practices include defining clear, quantifiable metrics that reflect critical success factors and ensuring KPIs are realistic yet challenging to motivate progress. Integrating KPIs within the broader OKR framework enhances focus by linking measurable key results directly to overarching objectives, promoting strategic clarity and operational efficiency.
Crafting Impactful OKRs for Growth
Crafting impactful OKRs for growth requires aligning ambitious objectives with measurable key results that directly influence business outcomes. Unlike KPIs that track ongoing performance metrics, OKRs drive strategic initiatives by setting clear, time-bound targets fostering accountability and innovation. Prioritizing OKRs with specific growth indicators such as customer acquisition rate, feature adoption, or revenue expansion enhances focus and accelerates organizational progress.
When to Use KPIs vs OKRs in Your Business
KPIs are best used for measuring ongoing performance against established targets, providing clear metrics that track efficiency and productivity over time. OKRs are ideal for setting ambitious, time-bound goals that drive strategic change and innovation within a business. Choosing between KPIs and OKRs depends on whether the focus is on maintaining steady progress or pushing transformational growth initiatives.
Measuring Success: KPI Metrics vs OKR Outcomes
Key Performance Indicator (KPI) metrics focus on quantifiable measurements that track the efficiency and performance of specific business processes, providing a clear snapshot of operational success. Objective and Key Result (OKR) outcomes emphasize ambitious goal-setting paired with measurable results, fostering alignment and progress toward strategic priorities. While KPIs evaluate ongoing performance, OKRs drive transformational growth through targeted objectives and measurable key results.
Common Pitfalls in KPI and OKR Implementation
Common pitfalls in KPI and OKR implementation often include setting vague or overly ambitious goals that lack clear metrics, leading to misaligned team efforts and poor performance tracking. Inadequate communication about the purpose and expectations of KPIs and OKRs can result in low employee engagement and inconsistent measurement standards. Frequent failure to review and adjust these performance indicators hinders organizational agility and reduces the effectiveness of strategic initiatives.
Integrating KPIs and OKRs for Maximum Results
Integrating KPIs and OKRs maximizes business performance by aligning measurable metrics with strategic goals to drive execution and accountability. KPIs provide quantifiable benchmarks that track ongoing operational efficiency, while OKRs set ambitious, time-bound objectives with measurable key results to inspire growth and innovation. Combining both frameworks enables continuous performance monitoring and strategic agility, ensuring teams stay focused on critical outcomes and adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
Key Performance Indicator (KPI) vs Objective and Key Result (OKR) Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com